Abstract
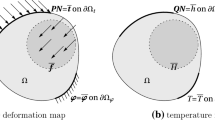
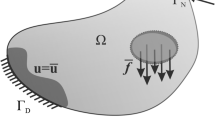
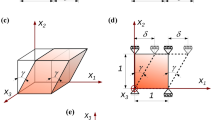
The element-based finite volume method (EbFVM) is well established in computational fluid dynamics; in the last decade, it has been extended to several areas of engineering and physics interest, such as electromagnetism, acoustics, and structural mechanics analysis with complex geometrical shapes. This paper describes the treatment of the conservative EbFVM approach for two-dimensional isotropic elastic–plastic rate-independent problems. In particular, we use plane strain and plane stress approaches upon incremental thermal and mechanical loads. In order to verify the performance of the EbFVM, numerical results are compared with a commercial simulator. Finally, from the present implementation and the comparisons performed, we can ensure that EbFVM makes accurate prediction as the traditional numerical approach commonly employed for the solution of mechanics problems.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Voller VR (2000) Basic control volume finite element methods for fluids and solids, vol 1. World Scientific, Singapore
Zienkiewicz O, Taylor R (2000) The finite element method: solid mechanics, vol 2, 5th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford
Demirdžić I, Martinović D (1993) Finite volume method for thermo-elastoplastic stress analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 109(3–4):331–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7825(93)90085-C
Maliska C (2004) Heat transfer and computational fluid mechanics. LTC, Florianópolis (in Portuguese)
Taylor G, Bailey C, Cross M (2003) A vertex-based finite volume method applied to non-linear material problems in computational solid mechanics. Int J Numer Methods Eng 56(4):507–529. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.574
Taylor G, Bailey C, Cross M (1995) Solution of the elastic/visco-plastic constitutive equations: a finite volume approach. Appl Math Model 19(12):746–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/0307-904X(95).455.00093-Y
Zienkiewick O, Taylor R (1989) The finite element method: basic formulation and linear problems, vol 1. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Maidenhead
Bilbao S, Hamilton B (2017) Wave-based room acoustics simulation: explicit/implicit finite volume modeling of viscothermal losses and frequency-dependent boundaries. J Audio Eng Soc 65(1/2):78–89. https://doi.org/10.17743/jaes.2016.0057
Slone A, Bailey C, Cross M (2003) Dynamic solid mechanics using finite volume methods. Appl Math Model 27(2):69–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-904X(02)00060-4
Zhang B, Xu C-L, Wang S-M (2017) Generalized source finite volume method for radiative transfer equation in participating media. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 189:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2016.11.025
Fernandes BRB, Marcondes F, Sepehrnoori K (2013) Investigation of several interpolation functions for unstructured meshes in conjunction with compositional reservoir simulation. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl 64(12):974–993. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407782.2013.812006
Patankar SV (1980) Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow: computational methods in mechanics and thermal science, vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Baliga B, Patankar S (1980) A new finite-element formulation for convection diffusion problems. Numer Heat Transf 3(4):393–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/01495728008961767
Filippini G, Maliska C, Vaz M (2014) A physical perspective of the element-based finite volume method and FEM-Galerkin methods within the framework of the space of finite elements. Int J Numer Meth Eng 98(1):24–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.4618
Wheel M (1996) A geometrically versatile finite volume formulation for plane elastostatic stress analysis. J Strain Anal Eng Design 31(2):111–116
Woodward CS, Dawson CN (2000) Analysis of expanded mixed finite element methods for a nonlinear parabolic equation modeling flow into variably saturated porous media. SIAM J Numer Anal 37(3):701–724
Forsyth PA, Kropinski M (1997) Monotonicity considerations for saturated unsaturated subsurface flow. SIAM J Sci Comput 18(5):1328–1354
Bause M, Knabner P (2004) Computation of variably saturated subsurface flow by adaptive mixed hybrid finite element methods. Adv Water Resour 27(6):565–581
Srivastava R, Yeh T-CJ (1992) A three-dimensional numerical model for water flow and transport of chemically reactive solute through porous media under variably saturated conditions. Adv Water Resour 15(5):275–287
Jasak H, Weller H (2000) Application of the finite volume method and unstructured meshes to linear elasticity. Int J Numer Meth Eng 48(2):267–287. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(20000520)48:2%3c267:AID-NME884%3e3.0.CO2-Q
Fallah N, Bailey C, Cross M, Taylor G (2000) Comparison of finite element and finite volume methods application in geometrically nonlinear stress analysis. Appl Math Model 24(7):439–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-904X(99)00047-5
Moczo P, Robertsson JO, Eisner L (2007) The finite-difference time-domain method for modeling of seismic wave propagation. Adv Geophys 48:421–516
Verzicco R, Orlandi P (1996) A finite-difference scheme for three-dimensional incompressible flows in cylindrical coordinates. J Comput Phys 123(2):402–414
Ryskin G, Leal L (1984) Numerical solution of free-boundary problems in fluid mechanics. Part 1. The finite-difference technique. J Fluid Mech 148:1–17
Suliman R, Oxtoby OF, Malan A, Kok S (2014) An enhanced finite volume method to model 2d linear elastic structures. Appl Math Model 38(7):2265–2279
Marcondes F, Sepehrnoori K (2010) An element-based finite-volume method approach for heterogeneous and anisotropic compositional reservoir simulation. J Petrol Sci Eng 73(1):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2010.05.011
Winslow AM (1966) Numerical solution of the quasilinear poisson equation in a nonuniform triangle mesh. J Comput Phys 1(2):149–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(66)90001-5
Schneider G, Zedan M (1983) Control-volume-based finite element formulation of the heat conduction equation. Spacecr Therm Control Design Oper Prog Astronaut Aeronaut 86:305–327
Fryer YD, Bailey C, Cross M, Lai C-H (1991) A control volume procedure for solving the elastic stress-strain equations on an unstructured mesh. Appl Math Model 15(11–12):639–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-904X(09)81010-X
Bailey C, Cross M (1995) A finite volume procedure to solve elastic solid mechanics problems in three dimensions on an unstructured mesh. Int J Numer Methods Eng 38(10):1757–1776. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620381010
Idelsohn SR, Oñate E (1994) Finite volumes and finite elements: two good friends. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37(19):3323–3341. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620371908
Vaz M, Muñoz-Rojas PA, Filippini G (2009) On the accuracy of nodal stress computation in plane elasticity using finite volumes and finite elements. Comput Struct 87(17):1044–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2009.05.007
Demirdžić I, Muzaferija S (1994) Finite volume method for stress analysis in complex domains. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37(21):3751–3766. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620372110
de Souza Neto EA, Peric D, Owen DR (2011) Computational methods for plasticity: theory and applications. Wiley, New York
Simo JC, Hughes TJ (2006) Computational inelasticity, vol 7. Springer, Berlin
Crisfield MA, Remmers JJ, Verhoosel CV et al (2012) Nonlinear finite element analysis of solids and structures. Wiley, New York
Kim N-H (2014) Introduction to nonlinear finite element analysis. Springer, Berlin
Logan D (2002) First course in finite element analysis. Brooks/Cole, Boston
Acknowledgements
The first and second authors would like to thank CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) and CNPq (the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development of Brazil), respectively, for the financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Paulo de Tarso Rocha de Mendonça, Ph.D.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Cassia Lima Pimenta, P.V., Marcondes, F. Two-dimensional rate-independent plasticity using the element-based finite volume method. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41, 142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1641-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1641-y