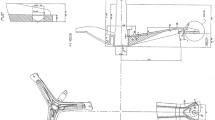
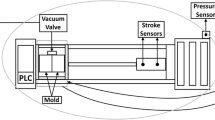
Abstract
The resulting porosity is responsible to 70% of failures on the high-pressure aluminum die casting process. The determination of the origin and setting the pore elimination is a complex mechanism. There are several factors that induce their occurrence. Thus, it is common to employ process and engineering alternatives to try to solve the issue. Faced with such complexity we tried to understand how to apply the finite element methods to minimize the occurrence of pores in high-pressure die casting products. The objective of this study was to develop a methodology to generate an equation that represents the porosity behavior aiming to determine the best engineering and process settings to reduce the pore volume in aluminum injected products. The aim of this study was to develop a methodology to generate an equation that represents the porosity behavior. To do that, the results obtained with the variation of some boundary conditions which were applied to computer simulations in commercial dedicated software were analyzed. It was observed that a flow and solidification analysis of the product in the mold can determine the probability of occurrence of pores in the product already during injection process.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASTM:
-
American society for testing material
- CAD:
-
Computer aided design
- CAE:
-
Computer aided engineering
- HPDC:
-
High-pressure die casting
- FEM:
-
Finite element method
- nadca:
-
North American die casting association
References
Aminul I, Zoheir NF (2011) The influence of porosity and hot isostatic pressing treatment on wear characteristics of cast and P/M aluminum alloys. Department of Process Engineering and Applied Science, Materials Engineering Program, Dalhousie University, Halifax
Ammar HR, Samuel AM, Samuel FH (2008) Porosity and the fatigue behavior of hypoeutectic and hypereutectic aluminum-silicon casting alloys. In: International Journal of Fatigue, Département des Sciences Appliquées, vol 30, Université, Chicoutimi, Québec, pp 1024–1035
Campatelli G, Scippa A (2011) A heuristic approach to meet geometric tolerance in high pressure die casting. Department of Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Technologies, University of Firenze, Firenze
CIMM (2016) http://www.cimm.com.br/portal/material_didatico/3686-microporosidade#.V4z GgMvrs08, Brasil
Hangai Y, Kitahara S (2008) Quantitative evaluation of porosity in aluminum die castings by fractal analysis of perimeter. Mater Trans 49(4):782–786 (Japan, 2008)
Irfan M, Schwam D, Karve A, Ryder R (2010) Improvements of Mechanical Properties in Die Cast Engine Blocks. In: 114th Metalcasting Congress, FL: North American Die Casting Assocation, Orlando, EUA
Jakumeit J, Jana S, Böttger B, Laqua R, Jouani M, Bührig-Polaczek D (2011) Simulation-based prediction of micro-shrinkage porosity in aluminum casting: Fully-coupled numerical calculation vs. criteria functions. In: The 3rd International Conference on Advances in Solidification Processes, Germany
Jin CK, Kang CG (2011) Fabrication by vacuum die casting and simulation of aluminum bipolar plates with micro-channels on both sides for proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, Precision Manufacturing System Division, Graduate School, Pusan National University, San 30 Chang Jun-dong, Geum Jung-Gu, Busan 609–735. In: Engineering Research Center for Net Shape and Die Manufacturing, School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, San 30 Jangjeon-dong, Geumjeon-gu, Busan, pp 609–735
Johnson A (2012) An Investigation of Internal Logistics of a Lean Bus Assembly System via Simulation: a Case Study. In: The international journal of industrial engineering is abstracted by thomson reuters science citation index, engineering index/compendex, eipage1, and current contents e engineering, computing and technology, New York, EUA
Jorstad J, Pan Q, Apelian D (2007) Interaction of key variables during rheocasting: effects of fraction solid and flow velocity on performance. In: 111th Metalcasting Congress. Houston, TX: North American Die Casting Association, EUA
Kirkman S (2006) Shrinkage porosity: a guide to correcting the problems. North American Die Casting Association, EUA, Wheeling
Klobcar D, Tusek J, Taljat B (2007) Thermal Fatigue of Materials for DieCasting Tooling, University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering. Materials Technology Department, Slovenia
Miller R (2010) An Extension to PQ analysis: selecting die and machine to quantitatively maximize operating flexibility. CastExpo’10, FL: North American Die Casting Association, Orlando, EUA
North American Die Casting Association, Die Materials & Technologies. (2011). Wheeling, IL: North American Die Casting Association, EUA
Nooruddin AH, Anifowose F, Abdulraheem A (2014) Using soft computing techniques to predict corrected air permeability using thomeer parameters, air porosity and grain density. In: Computers & Geosciences, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, vol 64, Dhahran, pp 9–80
Proske M, Gaddam D (2009) Autonomous Optimization: Determining the Process Window before Casting the First Part. In: Die Casting Engineer, North American Die Casting Assn, Die Casting Engineer; 53, 3; 22–25, EUA
Sakundarini N (2012) A framework of integrated recyclability tools for automobile design. In: The International Journal of Industrial Engineering, International Journal of Industrial Engineering, vol. 19 Issue 10, pp 401–411 (11p)
Sholapurwalla S, Mathier V (2010) Optimizing the High pressure die casting process using computer simulation; CastExpo’10. North American Die Casting Association, EUA
Steedman G, Bishop DP, Caleyw F, Kipouros GJ (2012) Surface porosity investigation of aluminum-silicon PM alloys. In: Materials Engineering Program, Department of Process Engineering and Applied Science, Dalhousie University, 1459 Oxford Street, Halifax
Tsoukalas VD (2008) Optimization of porosity formation in AlSi9Cu3 pressure die castings using genetic algorithm analysis. In: Materials and Design, Department of Marine Engineering, Athens Merchant Marine Academy, Paralia Aspropyrgou 19300, Aspropyrgos, Athens
Vanderesse N, Maire E, Chabod A, Buffière J (2011) Microtomographic study and finite element analysis of the porosity harmfulness in a cast aluminium alloy. In: International Journal of Fatigue, Université de Lyon, INSA-Lyon, MATEIS CNRS UMR 5510, 69621 Villeurbanne, Centre Technique des Industries de la Fonderie (CTIF), vol 33, France, pp 1514–1525
Vinarcik EJ (2002) High integrity die casting processes, Wiley, Hoboken, Includes index, ISBN 0-471-20131-6, die-casting. I. Title. TS239.V56 671.2 53 dc21, Canada
Wannarumon S, Actis M (2009) Comparisons of computer fluid dynamic software programs applied to jewelry investment casting process. In: World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 55, EUA
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Federal University of Paraná (UFPR). The authors gratefully extend their gratitude to Metalkraft injection Ltda for the numerical simulations in Magma software, Metallurgical Starcast Ltda by providing the mold and the injection of the test samples and Alumec Industry Ltda by the of X-ray analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Márcio Bacci da Silva.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Concer, D., Marcondes, P.V.P. Experimental and numerical simulation study of porosity on high-pressure aluminum die casting process. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 3079–3088 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0672-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0672-x