Abstract
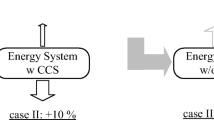
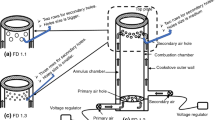
This paper presents the analysis of ecological and economical availability for using syngas from gasification of biomass waste or other solid fuels into diesel with ICE-based combined cycle (CC). The new approach is proposed to improve the ecological efficiency of the CC system and decrease the cost of electricity which can be produced with electric generator. For optimization of design of the combined system the new diagrams were obtained to determine characteristics of mixed fuel (diesel + syngas) for the engine at varied syngas fuel parameters after the gasifier with steam agent (plasma or other type). Based on these diagrams it is possible to obtain total reducing CO2 emission in atmosphere of ~1.5 times in the CC system with biomass gasifier.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boloy RAM (2011) Ecological impacts from syngas burning in internal combustion engine: technical and economical aspects. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:5194–5201
Sahoo BB, Saha UK, Sahoo N (2011) Theoretical performance of limits of a syngas–diesel fueled compression ignition engine from second law analysis. Energy 36:760–769
Shah A (2010) Performance and emissions of a spark-ignited engine driven generator on biomass based syngas. Bioresour Technol 101:4656–4661
Sobynin V (2010) Syngasas a fuel for IC and diesel engines: efficiency and harmful emissions cut-off. International Hydrogen Energy Congress and Exhibition, Istanbul
Mourão R, Marquesi AR, Gorbunov AV et al (2014) Thermochemical assessment of gasification process efficiency of biofuels industry waste with different plasma oxidants. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci No 2 (in press)
Kravchenko OP, Lepeshko II, Pilatau AY, Nozhenko OS (2011) Mathematical model of diffusive-kinetic renewal of foods of combustion of hydrocarbon fuels, coll, vol 2. Donetsk Academy of Motor Transport, Donetsk, pp 58–69
Coronado CR, Carvalho JA Jr, Silveira JL (2009) Biodiesel CO2 emissions: a comparison with the main fuels in the Brazilian market. Fuel Process Technol 90:204–211
Coronado CR, Carvalho JA Jr, Yoshioka JT (2009) Determination of ecological efficiency in internal combustion engines: the use of biodiesel. Appl Therm Eng 29:1887–1892
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of CAPES and FAPESP foundations of Brazil and Technological Institute of Aeronautics (ITA), SP, Brazil, for technical and information support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Luis Fernando Figueira da Silva.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilatau, A.Y., Viarshyna, H.A., Gorbunov, A.V. et al. Analysis of syngas formation and ecological efficiency for the system of treating biomass waste and other solid fuels with CO2 recuperation based on integrated gasification combined cycle with diesel engine. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 36, 673–679 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-014-0166-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-014-0166-7