Abstract
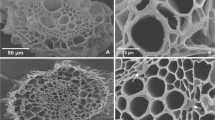
Copper is an essential plant micronutrient, vital in physiological processes. However, excessive copper concentrations can lead to toxicity, adversely impacting biomass accumulation. This study aimed to investigate the effects of toxic copper doses on establishing Rhizobium nodulation, biomass accumulation capacity, and anatomical changes in leaves and roots of Calopogonium mucunoides plants. The hypothesis was that C. mucunoides plants could sustain growth even under toxic copper doses and exhibit anatomical alterations after 45 days of cultivation. Soil contamination was conducted using copper sulfate at various doses: 0 (control), 30, 60, 120, 240, and 480 mg dm−3. Root, nodule, and shoot dry mass values were obtained by drying and weighing the plants after 72 h. For anatomical analysis, samples were fixed in 70% FAA, dehydrated using an ethyl series, and embedded in historesin. Slides were stained with toluidine blue, and histochemical tests were performed. No anatomical changes were observed in the leaves across all analyzed tissues. However, in the roots, a decrease in xylem and secondary phloem thickness was observed at the dose of 30 mg dm−3, while an increase in vessel element thickness was observed at the doses of 60 and 120 mg dm−3. Histochemical tests revealed the presence of compounds such as starch and pectins in both leaves and roots, as well as lipids at the base of the tector trichomes in the leaves. C. mucunoides demonstrated the ability to maintain growth and nodulation at concentrations of up to 120 mg dm−3 of copper in the soil, with impaired growth observed at higher doses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4496-5
Ahmad E, Zaidi A, Khan MS, Oves M (2012) Heavy metal toxicity to symbiotic nitrogen-fixing microorganism and host legumes. In: Zaidi A, Wani PA, Khan MS (eds) Toxicity of heavy metals to legumes and bioremediation. Springer, Vienna, pp 29–44
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang M-Q (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9030042
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Angulo-Bejarano PI, Puente-Rivera J, Cruz-Ortega R (2021) Metal and metalloid toxicity in plants: an overview on molecular aspects. Plants 10:635. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040635
Apori OS, Hanyabui E, Asiamah YJ (2018) Remediation technology for copper contaminated soil: a review. Asian Soil Res J. 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.9734/asrj/2018/v1i326338
Araujo MA, Leite MCM, Camargos LS, Martins AR (2020) Tolerance evaluation and morphophysiological responses of Astronium graveolens, a native brazilian Cerrado, to addition of lead in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 195:110524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110524
Berlyn GP, Miksche JP, Sass JE (1976) Botanical microtechnique and cytochemistry, 1st edn. Iowa State University Press, Iowa
Bhat SA, Bashir O, Ul Haq SA, Amin T, Rafiq A, Ali M, Américo-Pinheiro JHP, Sher F (2022) Phytoremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: an eco-friendly, sustainable and multidisciplinary approach. Chemosphere 303:134788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134788
Brewer GJ (2010) Risks of copper and iron toxicity during aging in humans. Chem Res Toxicol 23:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx900338d
Camargos LS de (2018) Calopogonium mucunoides, um modelo de estudo para estresses abióticos em climas tropicais. Tese de livre-docência. UNESP—Faculdade de Engenharia (FEIS)—Ilha Solteira.
CETESB (2021) Valores Orientadores Para Solo e Água Subterrânea no Estado de São Paulo. https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/solo/valores-orientadores-para-solo-e-agua-subterranea/
Chaffai R, Elhammadi MA, Seybou TN, Tekitek A, Marzouk B, El Ferjani E (2007) Altered fatty acid profile of polar lipids in maize seedlings in response to excess copper. J Agron Crop Sci 193:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2007.00252.x
Cornu J-Y, Huguenot D, Jézéquel K, Lollier M, Lebeau T (2017) Bioremediation of copper-contaminated soils by bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2191-4
da Silva VN, Frachia CDL, Barbosa ICF, da Silva MB, de Paiva WDS, Souza LA, de Camargos LS (2021) Tolerance and phytoremediation potential of Calopogonium mucunoides to boron. Environ Qual Manag 30:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem.21727
da Silva MB, Bomfim NCP, da Silva VN, de Lima FC, de Souza LA, Justino GC, de Camargos LS (2022) Response of Cajanus cajan to excess copper in the soil: tolerance and biomass production. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 28:1335–1345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01203-6
da Silva VN, Rosalem PF, de Araujo MA, Ferreira TC, Martins AR, de Camargos LS (2023) Anatomical changes caused by boron in Calopogonium mucunoides Desv. Braz J Bot 46:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-022-00868-3
Duan D, Tong J, Xu Q, Dai L, Ye J, Wu H, Xu C, Shi J (2020) Regulation mechanisms of humic acid on Pb stress in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). Environ Pollut 267:115546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115546
Ferreira TC, Aguilar JV, Souza LA, Justino GC, Aguiar LF, Camargos LS (2016) pH effects on nodulation and biological nitrogen fixation in Calopogonium mucunoides. Braz J Bot 39:1015–1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0300-0
Furlani (2004) Nutrição Mineral. In: Fisiologia Vegetal. Rio de Janeiro
González-Guerrero M, Matthiadis A, Saez Á, Long T (2014) Fixating on metals: new insights into the role of metals in nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Front Plant Sci 5:45
Gratão PL, Monteiro CC, Rossi ML, Martinelli AP, Peres LEP, Medici LO, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2009) Differential ultrastructural changes in tomato hormonal mutants exposed to cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 67:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.06.017
Hartmann H, Trumbore S (2016) Understanding the roles of nonstructural carbohydrates in forest trees—from what we can measure to what we want to know. New Phytol 211:386–403. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13955
Herling VR, Techio LE (2016) Leguminosas forrageiras de clima tropical e temperado, 1st ed.Pirassununga—SP
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circ Calif Agric Exp Stn. 347:32
Iqbal T, Shah SK, Ullah F, Mehmood S, Zeb MA (2020) Analysis of deformable distortion in the architecture of leaf xylary vessel elements of Carthamus oxycantha caused by heavy metals stress using image registration. Microsc Res Tech 83:843–849. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23476
Jach ME, Sajnaga E, Ziaja M (2022) Utilization of legume-nodule bacterial symbiosis in phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils. Biology 11:676. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050676
Jensen WA (1962) Botanical histochemistry: principles and practice. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco
Jian L, Bai X, Zhang H, Song X, Li Z (2019) Promotion of growth and metal accumulation of alfalfa by coinoculation with Sinorhizobium and Agrobacterium under copper and zinc stress. PeerJ 7:e6875. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6875
Johansen DA (1940) Plant microtechnique, 1st edn. McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc, New York
Kabata-Pendias A (2010) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kopittke PM, Dart PJ, Menzies NW (2007) Toxic effects of low concentrations of Cu on nodulation of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Environ Pollut 145:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.03.007
Krzesłowska M, Rabęda I, Basińska A, Lewandowski M, Mellerowicz EJ, Napieralska A, Samardakiewicz S, Woźny A (2016) Pectinous cell wall thickenings formation—A common defense strategy of plants to cope with Pb. Environ Pollut 214:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.019
Kumar V, Pandita S, Singh Sidhu GP, Sharma A, Khanna K, Kaur P, Bali AS, Setia R (2021) Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 262:127810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127810
Leite MCM, de Araujo MA, de Silva PW, Camargos LS, Martins AR (2022) Morphological responses and tolerance of a tree native to the Brazilian Cerrado Astronium fraxinifolium Schott to boron toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:6900–6910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15710-8
Liu X, Ma D, Zhang Z, Wang S, Du S, Deng X, Yin L (2019) Plant lipid remodeling in response to abiotic stresses. Environ Exp Bot 165:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.06.005
Loix C, Huybrechts M, Vangronsveld J, Gielen M, Keunen E, Cuypers A (2017) Reciprocal Interactions between cadmium-induced cell wall responses and oxidative stress in plants. Front Plant Sci 9:391
Mendonça GW de (2020) Tolerância e potencial fitorremediador de Crotalaria juncea em solos contaminados por boro, cobre e manganês. Tese de Doutorado. UNESP—Faculdade de Engenharia (FEIS)—Ilha Solteira
Minkina T, Rajput V, Fedorenko G, Fedorenko A, Mandzhieva S, Sushkova S, Morin T, Yao J (2020) Anatomical and ultrastructural responses of Hordeum sativum to the soil spiked by copper. Environ Geochem Health 42:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00269-8
Mir AR, Pichtel J, Hayat S (2021) Copper: uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants and management of Cu-contaminated soil. Biometals 34:737–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00306-z
Myburg AA, Lev-Yadun S, Sederoff RR (2013) Xylem Structure and function. In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. Wiley
Nazir A, Rafique F, Ahmed K, Khan SA, Khan N, Akbar M, Zafar M (2021) Evaluation of heavy metals effects on morpho-anatomical alterations of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Microsc Res Tech 84:2517–2529. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23801
O’Brien TP, McCully ME (1981) The study of plant structure: principles and selected methods. Termarcarphi, Melbourne, Australia
Okazaki Y, Saito K (2014) Roles of lipids as signaling molecules and mitigators during stress response in plants. Plant J 79:584–596. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12556
Pelloux J, Rustérucci C, Mellerowicz EJ (2007) New insights into pectin methylesterase structure and function. Trends Plant Sci 12:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.04.001
Pires-Lira MF, de Castro EM, Lira JMS, de Oliveira C, Pereira FJ, Pereira MP (2020) Potential of panicum aquanticum poir. (Poaceae) for the phytoremediation of aquatic environments contaminated by lead. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 193:110336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110336
R Core Team (2022) R: the R project for statistical computing. https://www.r-project.org/. Accessed 28 Nov 2022
Raij B, Andrade JC, Cantarella H, Quaggio JA (2001) Análise química para avaliação de fertilidade de solos tropicais. Instituto Agronômico, Campinas
Rajput V, Minkina T, Fedorenko A, Sushkova S, Mandzhieva S, Lysenko V, Duplii N, Fedorenko G, Dvadnenko K, Ghazaryan K (2018) Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles on spring barley (Hordeum sativum distichum). Sci Total Environ 645:1103–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.211
Rehman M, Liu L, Wang Q, Saleem MH, Bashir S, Ullah S, Peng D (2019) Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18003–18016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05073-6
Sakai WS (1973) Simple method for differential staining of paraffin embedded plant material using toluidine blue O. Stain Technol 48:247–249. https://doi.org/10.3109/10520297309116632
Santos H, Jacomine P, Anjos L, Oliveira V, Lumbrearas J, Coelho M, Almeida J, Filho J, Oliveira J, Cunha T (2018) Sistema brasileiro de classificação de solos, 5th edn. Embrapa Solos, Brasília
Seliga H (1993) The role of copper in nitrogen fixation in Lupinus luteus L. Plant Soil 155:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025054
Stambulska UY, Bayliak MM (2020) Legume-rhizobium symbiosis: secondary metabolites, free radical processes, and effects of heavy metals. In: Mérillon J-M, Ramawat KG (eds) Co-evolution of secondary metabolites. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 291–322
Vaculík M, Konlechner C, Langer I, Adlassnig W, Puschenreiter M, Lux A, Hauser M-T (2012) Root anatomy and element distribution vary between two Salix caprea isolates with different Cd accumulation capacities. Environ Pollut Barking Essex 163:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.031
Vorwerk S, Somerville S, Somerville C (2004) The role of plant cell wall polysaccharide composition in disease resistance. Trends Plant Sci 9:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.02.005
Wairich A, De Conti L, Lamb TI, Keil R, Neves LO, Brunetto G, Sperotto RA, Ricachenevsky FK (2022) Throwing copper around: how plants control uptake, distribution, and accumulation of copper. Agronomy 12:994. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12050994
Yaashikaa PR, Kumar PS, Jeevanantham S, Saravanan R (2022) A review on bioremediation approach for heavy metal detoxification and accumulation in plants. Environ Pollut 301:119035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119035
Yadav V, Arif N, Kováč J, Singh VP, Tripathi DK, Chauhan DK, Vaculík M (2021) Structural modifications of plant organs and tissues by metals and metalloids in the environment: a review. Plant Physiol Biochem 159:100–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.11.047
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support given to this work by the ‘Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo’ (FAPESP–Brazil, Grant No. 2011/00927-1 to TCF; Grant Nos. 2010/05299-6, 2015/09567-9 and 2018/01498-6 to LSC) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—CNPq (grant No. 302499/2021-0 to LSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LSC and ARM contributed to the conceptualization and study design. TCF, JVA, and VNS performed greenhouse research. TCF, JVA, VNS, and PFR performed laboratory research. TCF and PFR performed the statistical analysis. TCF and PFR wrote the first draft of the manuscript. LSC, ARM, JVA, and MAA performed editing and revision of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, T.C., Rosalem, P.F., Aguilar, J.V. et al. Growth, nodulation, and anatomical characterization of Calopogonium mucunoides Desv., a tropical legume, in copper-contaminated soil. Braz. J. Bot 46, 633–644 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-023-00900-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-023-00900-0