Abstract
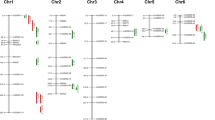
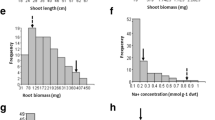
Salinity affects rice production worldwide. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) for different sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca++) accumulation traits were detected using 113 F2 individuals derived from a cross between IR36 (salt-susceptible) and Pokkali (salt-tolerant) rice cultivars. 17 QTLs were detected; three under control conditions, three under saline and 11 under relative value datasets. These QTLs were located on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 11, respectively. The R 2 (phenotypic variance explained) value for these QTLs ranged from 7.69 to 72.57 %. The QTLs identified on chromosomes 7 and 8 were novel as there were no previous reports of QTLs for Na+ uptake (SU) and K+ uptake (PU) for these genomic regions. PU and K+ uptake ratio (PUR) had significant positive correlation with grain yield under saline conditions. The QTLs identified for PU and PUR (QTLpur-3, QTLpurr-5-1, QTLpurr-5-2) will be helpful for increasing rice grain yield under salt stress conditions. A major locus controlling Na+ uptake (SU) (QTLsur-7) was identified on chromosome 7, with R 2 value of 72.57 %. This may be a major gene involved in SU. Additive effect of the salt-tolerant rice cultivar, Pokkali alleles increased this trait by 0.16 %. This QTL is important with respect to Na+ exclusion and may be a good candidate for marker-assisted selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asch F, Dingkuhn M, Dorffling K, Miezan K (2000) Leaf K/Na ratio predicts salinity induced yield loss in irrigated rice. Euphytica 113:109–118
Bimpong IK, Manneh B, El-Namaky R, Diaw F, Amoah NKA, Sanneh B, Ghislain K, Sow A, Singh RK, Gregorio G, Bizimana JB, Wopereis M (2014) Mapping QTLs related to salt tolerance in rice at the young seedling stage using 384-plex single nucleotide polymorphism SNP marker sets. Mol Plant Breed 5:47–63
Bonilla P, Dvorak J, Mackill D, Deal K, Gregorio G (2002) RFLP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philippine J Agric Sci 85:68–76
Chaubey CN, Senadhira D (1994) Conventional plant breeding for tolerance to problem soils. In: Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (eds) Soil mineral stresses: approaches to crop improvement. Monographs on theoretical and applied genetics no. 21. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 11–36
Cha-um S, Trakulyingcharoen T, Smitamana P, Kirdmanee C (2009) Salt tolerance in two rice cultivars differing salt tolerant abilities in responses to iso-osmotic stress. Aust J Crop Sci 3:221–230
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
FAO (2009) FAO statistical yearbook 2005–2006. FAO, Rome
Fuchs I, Stolzle S, Ivashikina N, Hedrich R (2005) Rice K+ uptake channel OsAKT1 is sensitive to salt stress. Planta 221:212–221
Ghomi K, Rabiei B, Sabouri H, Sabouri A (2013) Mapping QTLs for traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage of rice (Oryza sativa L.): An agrigenomics study of an Iranian rice population. OMICS 17:242–251
Gillingham AG, Sheath GW, Sutton MM (1987) Soil contamination and sample washing effects on major nutrient and soluble sugar concentration of pasture. N Z J Agric Res 30:281–285
Haro R, Banuelos MA, Rodríguez-Navarro A (2010) High-affinity sodium uptake in land plants. Plant Cell Physiol 51:68–79
Islam MR, Salam MA, Hassan L, Collard BCY (2011) QTL mapping for salinity tolerance at seedling stage in rice. Emirates J Food Agric 23:137–146
Kader MA, Lindberg S (2010) Cytosolic calcium and pH signaling in plants under salinity stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:233–238
Koyama ML, Levesley A, Koebner RMD, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 125:406–422
Kronzucker HJ, Britto DT (2011) Sodium transport in plants: a critical review. New Phytol 189:54–81
Kumar V, Singh A, Mithra SVA, Krishnamurthy SL, Parida SK, Jain S, Tiwari KK, Kumar P, Rao AR, Sharma SK, Khurana JP, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2015) Genome-wide association mapping of salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa). DNA Res 22:1–13
Lee SY, Ahn JH, Cha YS, Yun DW, Lee MC, Ko JC, Lee KS, Eun MY (2007) Mapping QTLs related to salinity tolerance of rice at the young seedling stage. Plant Breed 126:43–46
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu H, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004) QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 108:253–260
Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J (1995) Changes in plant response to NaCl during development of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties differing in salinity resistance. J Exp Bot 46:1843–1852
Meier U (2001) Growth stages of mono- and dicotyledonous plants. BBCH monograph. Blackwell Wissenschafts-Verlag, Berlin
Mohiti M, Ardalan MM, Torkashvand AM, Vahed HS (2011) The efficiency of potassium fertilization methods on the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under salinity stress. Afr J Biotechnol 10:15946–15952
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Platten JD, Egdane JA, Ismail AM (2013) Salinity tolerance, Na+ exclusion and allele mining of HKT1;5 in Oryza Sativa and O. Glaberrima: many sources, many genes, one mechanism? BMC Plant Biol 13:32
Qureshi RH, Aslam M, Mustafa G, Akhtar J (1991) Some aspects of physiology of salt tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Pak J Agric Sci 28:199–206
Rajendran K, Tester M, Roy SJ (2009) Quantifying the three main components of salinity tolerance in cereals. Plant Cell Environ 32:237–249
Ren Z, Zheng Z, Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Cui X, Iida K, Zhu JK (2010) RAS1, a quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance and ABA sensitivity in Arabidopsis. PNAS 107:5669–5674
Rengasamy P (2006) World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J Exp Bot 57:1017–1023
Saeed M, Dahab AHA, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ (2012) A cascade of recently discovered molecular mechanisms involved in abiotic stress tolerance of plants. OMICS 16:188–199
Senadhira D (1994) Rice and problem soils in South and Southeast Asia. In: IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 4. International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Manila, pp 1–2
Shannon MC, Rhoades JD, Draper JH, Scardaci SC, Spyres MD (1998) Assessment of salt tolerance in rice cultivars in response to salinity problems in California. Crop Sci 38:394–398
Tanksley SD (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Thomson MJ, Ocampo MD, Egdane J, Rahman MA, Sajise AG, Adorada DL, Raiz ET, Blumwald E, Seraj ZI, Singh RK, Gregorio GB, Ismail AM (2010) Characterizing the saltol quantitative trait locus for salinity tolerance in rice. Rice 3:148–160
Wang Z, Chen Z, Cheng J, Lai Y, Wang J, Bao Y, Huang J, Zhang H (2012) QTL Analysis of Na+ and K+ concentrations in roots and shoots under different levels of NaCl stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS One 7:e51202. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051202
White PJ, Karley AJ (2010) Potassium. In: Hell R, Mendel R-R (eds) Cell biology of metals and nutrients. Plant cell monographs 17. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 199–224
Yang H, Ren X, Weng Q, Zhu L, He G (2002) Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene. Hereditas 136:39–43
Yeo AR, Flowers TJ (1983) Varietal differences in the toxicity of sodium ions in rice leaves. Physiol Plant 59:189–195
Yeo AR, Caporn SJM, Flowers TJ (1985) The effect of salinity upon photosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.): gas exchange by individual leaves in relation to their salt content. J Exp Bot 36:1240–1248
Yuanlin D, Li Weiming, Weiren W, Runsen P, Yuanchang Z, Jianmin Q, Lihui L, Zhiwei C, Damei M, Huaqing L, Danfeng Z, Yongbiao X (2003) Genetic analysis and mapping of gene fzp(t) controlling spikelet differentiation in rice. Sci China (Ser C) 46:328–334
Zhang J, Wu YT, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ (2000) Fast screening of SSR markers in cotton with PAGE/silver staining. Cotton Sci 12:267–269
Zhang JL, Flowers TJ, Wang SM (2010) Mechanisms of sodium uptake by roots of higher plants. Plant Soil 326:45–60
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Acknowledgments
The first author was a PhD scholar on the prime minister’s scholarship programme financed by Government of Pakistan (Ministry of Education). This work is the output of his PhD research project. We are thankful to Punjab Agricultural Research Board (PARB), Lahore, Pakistan for providing financial support to construct salinity blocks and purchase instruments and chemicals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.S.K., Saeed, M. & Iqbal, J. Identification of quantitative trait loci for Na+, K+ and Ca++ accumulation traits in rice grown under saline conditions using F2 mapping population. Braz. J. Bot 38, 555–565 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-015-0160-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-015-0160-z