Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate and compare the protective effect of fluoride varnish (Enamelast™, Ultradent Inc., Cologne, Germany), casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate fluoride/CPP-ACPF (MI Paste Plus, GC Corp., Tokyo, Japan) and self-assembling P11-4 peptide (Curodont™ Protect, Credentis AG, Windisch, Switzerland), against acidic erosion of primary teeth.
Methods
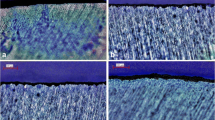
Forty primary anterior teeth were randomly assigned to four groups (n = 10): group 1: control, group 2: fluoride varnish, group 3: CPP-ACPF and group 4: self-assembling P11-4 peptide. After applying remineralising agents, except for the control group, all specimens underwent an erosive challenge of carbonated soft drink and artificial saliva for 15 cycles of 6 s each at 6-h intervals for a day. Groups were compared in terms of surface microhardness, roughness readings, and surface scanning with an extra-oral scanner (D800; 3Shape A/S) before and after the erosive process.
Results
All experimental groups showed superior results than the control group regarding microhardness, surface roughness, and substance loss. The fluoride varnish group showed significantly favourable results in microhardness change. There was no significant difference between the experimental groups regarding surface roughness and enamel loss measurements.
Conclusion
5% NaF fluoride varnish, CPP-ACPF and self-assembling P11-4 peptide protect the enamel of primary teeth against erosion compared to artificial saliva alone.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper. Should any raw data files be needed in another format they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abou Neel EA, Aljabo A, Strange A, Ibrahim S, Coathup M, Young AM, Bozec L, Mudera V. Demineralization-remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone. Int J Nanomed. 2016. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S107624.
Alessandri-Bonetti G, D’Antò V, Stipa C, Rongo R, Incerti-Parenti S, Michelotti A. Dentoskeletal effects of oral appliance wear in obstructive sleep apnoea and snoring patients. Eur J Orthod. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjw078.
Alexandria AK, Vieira TI, Pithon MM, da Silva Fidalgo TK, Fonseca-Gonçalves A, Valença AM, Cabral LM, Maia LC. In vitro enamel erosion and abrasion-inhibiting effect of different fluoride varnishes. Arch Oral Biol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.01.010.
Attin T, Becker K, Wiedemeier DB, Schmidlin PR, Wegehaupt FJ. Anti-erosive effect of a self-assembling peptide gel. Swiss Dent J. 2017. https://doi.org/10.5167/uzh-143887.
Bud ES, Bocanet VI, Muntean MH, Vlasa A, Păcurar M, Zetu IN, Soporan BI, Bud A. Extra-oral three-dimensional (3D) scanning evaluation of three different impression materials—an in vitro study. Polymers. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12495.
Ceci M, Mirando M, Beltrami R, Chiesa M, Colombo M, Poggio C. Effect of self-assembling peptide P11–4 on enamel erosion: AFM and SEM studies. Scanning. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.21276.
Field J, Waterhouse P, German M. Quantifying and qualifying surface changes on dental hard tissues in vitro. J Dent. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2010.01.002.
Fujii M, Kitasako Y, Sadr A, Tagami J. Roughness and pH changes of enamel surface induced by soft drinks in vitro-applications of stylus profilometry, focus variation 3D scanning microscopy and micro pH sensor. Dent Mater J. 2011. https://doi.org/10.4012/dmj.2010-204.
Ganss C, Schlueter N, Klimek J. Retention of KOH-soluble fluoride on enamel and dentine under erosive conditions—a comparison of in vitro and in situ results. Arch Oral Biol. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2006.07.004.
Hannig M. The protective nature of the salivary pellicle. Int Dent J. 2002;52:417–23.
Jayarajan J, Janardhanam P, Jayakumar P, Deepika. Efficacy of CPP-ACP and CPP-ACPF on enamel remineralization—an in vitro study using scanning electron microscope and DIAGNOdent®. Indian J Dent Res. 2011;22:77–82.
Johansson AK, Sorvari R, Birkhed D, Meurman JH. Dental erosion in deciduous teeth—an in vivo and in vitro study. J Dent. 2001. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-5712(01)00029-X.
Lione R, Huanca Ghislanzoni LT, Defraia E, Franchi L, Cozza P. Bonded versus banded rapid palatal expander followed by facial mask therapy: analysis on digital dental casts. Eur J Orthod. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjv038.
Lippert F. Fluoride release from fluoride varnishes under acidic conditions. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2014. https://doi.org/10.17796/jcpd.39.1.b45805v0v17407gl.
Maden EA, Acar Ö, Altun C, Polat GG. The effect of casein phosphopeptide-Amorf calcium phosphate and acidulated phosphate fluoride gel on dental erosion in primary teeth: an in vitro study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2017. https://doi.org/10.17796/1053-4628-41.4.275.
Manton DJ, Cai F, Yuan Y, Walker GD, Cochrane NJ, Reynolds C, Brearley-Messer LJ, Reynolds EC. Effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate added to acidic beverages on enamel erosion in vitro. Aust Dent J. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1834-7819.2010.01234.x.
Maude S, Ingham E, Aggeli A. Biomimetic self-assembling peptides as scaffolds for soft tissue engineering. Nanomedicine (lond). 2013. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.13.65.
Moazzez R, Bartlett D, Anggiansah A. Dental erosion, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and saliva: how are they related? J Dent. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2004.03.004.
Nekrashevych Y, Stösser L. Protective influence of experimentally formed salivary pellicle on enamel erosion. An in vitro study. Caries Res. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1159/000070449.
Pindborg JJ. Pathology of the dental hard tissues. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1970.
Rallan M, Chaudhary S, Goswami M, Sinha A, Arora R, Kishor A. Effect of various remineralising agents on human eroded enamel of primary teeth. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-013-0085-9.
Reynolds EC. Remineralization of enamel subsurface lesions by casein phosphopeptide-stabilized calcium phosphate solutions. J Dent Res. 1997. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345970760091101.
Sar Sancakli H, Austin RS, Al-Saqabi F, Moazzez R, Bartlett D. The influence of varnish and high fluoride on erosion and abrasion in a laboratory investigation. Aust Dent J. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1111/adj.12271.
Soares LE, De Carvalho Filho AC. Protective effect of fluoride varnish and fluoride gel on enamel erosion: roughness, SEM-EDS, and µ-EDXRF studies. Microsc Res Tech. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22467.
Soares GG, Magalhães PA, Fonseca ABM, Tostes MA, Silva EMD, Coutinho TCL. Preventive effect of CPP-ACPF paste and fluoride toothpastes against erosion and erosion plus abrasion in vitro—a 3D profilometric analysis. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2017a. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.ohpd.a38160.
Soares R, De Ataide IN, Fernandes M, Lambor R. Assessment of enamel remineralisation after treatment with four different remineralising agents: a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017b. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/23594.9758.
Somani R, Jaidka S, Singh DJ, Arora V. Remineralizing potential of various agents on dental erosion. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2014.05.001.
Sorvari R, Meurman JH, Alakuijala P, Frank RM. Effect of fluoride varnish and solution on enamel erosion in vitro. Caries Res. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1159/000261970.
Taji S, Seow WK. A literature review of dental erosion in children. Aust Dent J. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1834-7819.2010.01255.x.
Üstün N, Güven Y. Effect of three different remineralizing agents on artificial erosive lesions of primary teeth. Aust Dent J. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/adj.12922.
Wierichs RJ, Carvalho TS, Wolf TG. Efficacy of a self-assembling peptide to remineralize initial caries lesions—a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2021.103652.
Yilmaz N, Baltaci E, Baygin O, Tüzüner T, Ozkaya S, Canakci A. Effect of the usage of Er, Cr:YSGG laser with and without different remineralization agents on the enamel erosion of primary teeth. Lasers Med Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-020-03015-0.
Zawaideh FI, Owais AI, Mushtaha S. Effect of CPP-ACP or a potassium nitrate sodium fluoride dentifrice on enamel erosion prevention. JOCPD. 2017;41(2):135–40.
Acknowledgements
We would like to give our sincere gratitude to Dr. Ufuk Ilgen for his contributions to statistical analysis.
Funding
None to be declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EB conceived the ideas and carried out the literature search and manuscript writing. CB and OO, carried out experiments and data analysis. NO took part in the manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to this article’s content.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baltaci, E., Bilmenoglu, C., Ozgur, O. et al. Effect of three different remineralising agents on prevention against acidic erosion of primary teeth: an in vitro study. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 24, 651–659 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-023-00834-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-023-00834-x