Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate clinical and radiographic outcomes of vital pulp therapy (VPT) in deeply carious young permanent first molars (PFM) affected with MIH over 24 months.
Methods
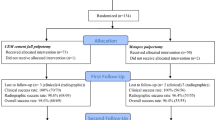
In this prospective randomized clinical trial, n = 50 children with deeply carious young PFM affected with MIH, and diagnosed with reversible or irreversible pulpitis were randomized into 2 groups: indirect pulp treatment (IPT) and pulpotomy (partial or complete). Teeth were followed up clinically and radiographically for 24 months. Statistical analysis was done using Chi-square test; P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
A total of n = 50 teeth/patients (n = 26 females (52%), n = 24 males (48%)) were included, and 14 upper and 36 lower PFM were treated. Mean age was 11 ± 3.2 years. Clinical and radiographic success rates were: 96% for IPT, 90% for PP and 82% for CP (and 86% for both types of pulpotomy combined) over 24 months. There were no significant differences in outcomes between treatment groups. Age, gender and tooth location/jaw were found to have no statistically significant difference in outcomes among treatment groups, nor did pulpal status or root maturity, regardless of type of VPT and follow up period.
Conclusions
VPT is a valid treatment option in deeply carious young permanent first molars affected with MIH over 24 months. IPT had a higher clinical and radiographic success rate (96%) than partial or cervical pulpotomy (total 86%), but the difference was not statistically significant. Future randomized clinical trials on VPT for teeth affected with MIH are recommended with larger sample size and longer follow-up.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAE glossary of endodontic terms, 9th edition. 2019. https://www.aae.org/specialty/clinical-resources/glossary-endodontic-terms/. Accessed 22 Mar 2022.
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Pulp therapy for primary and immature permanent teeth. The reference manual of pediatric dentistry. Chicago: American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry; 2021. pp. 399–407. https://www.aapd.org/media/Policies_Guidelines/BP_PulpTherapy.pdf. Accessed 22 Mar 2022.
Aguilar P, Linsuwanont P. Vital pulp therapy in vital permanent teeth with cariously exposed pulp: a systematic review. J Endod. 2011;37(5):581–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2010.12.004.
Alqaderi HE, Al-Mutawa SA, Qudeimat MA. MTA pulpotomy as an alternative to root canal treatment in children’s permanent teeth in a dental public health setting. J Dent. 2014;42(11):1390–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2014.06.007.
Barrieshi-Nusair KM, Qudeimat MA. A prospective clinical study of mineral trioxide aggregate for partial pulpotomy in cariously exposed permanent teeth. J Endod. 2006;32(8):731–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2005.12.008.
Calişkan MK. Pulpotomy of carious vital teeth with periapical involvement. Int Endod J. 1995;28(3):172–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.1995.tb00293.x.
Costa CA, Ribeiro AP, Giro EM, Randall RC, Hebling J. Pulp response after application of two resin modified glass ionomer cements (RMGICs) in deep cavities of prepared human teeth. Dent Mater. 2011;27(7):e158–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2011.04.002.
Discepolo K, Sultan M. Investigation of adult stainless steel crown longevity as an interim restoration in pediatric patients. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2017;27(4):247–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.12255.
Donly KJ, Sasa I, Contreras CI, Mendez MJC. Prospective randomized clinical trial of primary molar crowns: 24-month results. Pediatr Dent. 2018;40(4):253–8.
El-Meligy OA, Avery DR. Comparison of mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide as pulpotomy agents in young permanent teeth (apexogenesis). Pediatr Dent. 2006;28(5):399–404.
European Society of Endodontology (ESE) developed by: Duncan HF, et al., European Society of Endodontology position statement: Management of deep caries and the exposed pulp. Int Endod J. 2019;52(7):923–934. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.13080.
Gatón-Hernandéz P, Serrano CR, da Silva LAB, de Castañeda ER, da Silva RAB, Pucinelli CM, Manton D, Ustrell-Torrent JM, Nelson-Filho P. Minimally interventive restorative care of teeth with molar incisor hypomineralization and open apex-A 24-month longitudinal study. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2020;30(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.12581.
Ghanim AM, Manton DJ, Morgan MV, Mariño RJ, Bailey DL. Trends of oral health care and dental treatment needs in relation to molar incisor hypomineralisation defects: a study amongst a group of Iraqi schoolchildren. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2012;13(4):171–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262866.
Gruythuysen RJ, van Strijp AJ, Wu MK. Long-term survival of indirect pulp treatment performed in primary and permanent teeth with clinically diagnosed deep carious lesions. J Endod. 2010;36(9):1490–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2010.06.006 (Erratum in: J Endod. 2010;36(12):2015. Gruythuysen, René [corrected to Gruythuysen, René J M]; van Strijp, Guus [corrected to van Strijp, A J P]).
Hamama HH, Yiu CK, Burrow MF. Viability of intratubular bacteria after chemomechanical caries removal. J Endod. 2014;40(12):1972–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2014.07.025.
Hargreaves KM, Cohen S. Cohen’s pathways of the pulp. 10th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Inc; 2010.
Ismail AI, Sohn W, Tellez M, Amaya A, Sen A, Hasson H, Pitts NB. The International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS): an integrated system for measuring dental caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2007;35(3):170–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0528.2007.00347.x.
Jälevik B, Klingberg GA. Dental treatment, dental fear and behaviour management problems in children with severe enamel hypomineralization of their permanent first molars. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2002;12(1):24–32.
Kotsanos N, Kaklamanos EG, Arapostathis K. Treatment management of first permanent molars in children with molar-incisor hypomineralisation. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2005;6(4):179–84.
Luyk NH, Beck FM, Weaver JM. A visual analogue scale in the assessment of dental anxiety. Anesth Prog. 1988;35(3):121–3.
Lygidakis NA, Garot E, Somani C, Taylor GD, Rouas P, Wong FSL. Best clinical practice guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with molar-incisor-hypomineralisation (MIH): an updated European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry policy document. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022;23(1):3–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-021-00668-5.
Maltz M, et al. Partial removal of carious dentine: a multicenter randomized controlled trial and 18-month follow-up results. Caries Res. 2013;47(2):103–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000344013.
Maltz M, et al. Partial caries removal in deep caries lesions: a 5-year multicenter randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(3):1337–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2221-0.
Mejàre IA, Axelsson S, Davidson T, Frisk F, Hakeberg M, Kvist T, Norlund A, Petersson A, Portenier I, Sandberg H, Tranaeus S, Bergenholtz G. Diagnosis of the condition of the dental pulp: a systematic review. Int Endod J. 2012;45(7):597–613. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.2012.02016.x.
Murray PE, Smith AJ, Windsor LJ, Mjör IA. Remaining dentine thickness and human pulp responses. Int Endod J. 2003;36(1):33–43. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0143-2885.2003.00609.x.
Qudeimat MA, Alyahya A, Hasan AA. Mineral trioxide aggregate pulpotomy for permanent molars with clinical signs indicative of irreversible pulpitis: a preliminary study. Int Endod J. 2017;50(2):126–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12614.
Ricucci D, Loghin S, Siqueira JF Jr. Correlation between clinical and histologic pulp diagnoses. J Endod. 2014;40(12):1932–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2014.08.010.
Rodd HD, Boissonade FM, Day PF. Pulpal status of hypomineralized permanent molars. Pediatr Dent. 2007;29(6):514–20.
Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D, for the CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials.
Schwendicke F, Dörfer CE, Paris S. Incomplete caries removal: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent Res. 2013;92(4):306–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034513477425 (Erratum in: J Dent Res. 2013;92(8):759).
Somani C, Taylor GD, Garot E, Rouas P, Lygidakis NA, Wong FSL. An update of treatment modalities in children and adolescents with teeth affected by molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH): a systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022;23(1):39–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-021-00635-0.
Steffen R, van Waes H. Therapy of molar-incisor-hypominerlisation under difficult circumstances. A concept for therapy. Quintessenz. 2011;62:1613–23.
Steffen R, Krämer N, Bekes K. The Würzburg MIH concept: the MIH treatment need index (MIH TNI): A new index to assess and plan treatment in patients with molar incisior hypomineralisation (MIH). Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2017;18(5):355–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-017-0301-0.
Taha NA, Abdulkhader SZ. Full pulpotomy with biodentine in symptomatic young permanent teeth with carious exposure. J Endod. 2018;44(6):932–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2018.03.003.
Taha NA, Khazali MA. Partial pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth with clinical signs indicative of irreversible pulpitis: a randomized clinical trial. J Endod. 2017;43(9):1417–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2017.03.033.
Taha NA, Ahmad MB, Ghanim A. Assessment of mineral trioxide aggregate pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth with carious exposures. Int Endod J. 2017;50(2):117–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12605.
Takahashi K. Changes in the pulpal vasculature during inflammation. J Endod. 1990;16(2):92–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0099-2399(06)81570-0.
Taylor GD, Vernazza CR, Abdulmohsen B. Success of endodontic management of compromised first permanent molars in children: a systematic review. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2020;30(3):370–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.12599.
Torabinejad M, Hong CU, McDonald F, Pitt Ford TR. Physical and chemical properties of a new root-end filling material. J Endod. 1995;21(7):349–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0099-2399(06)80967-2.
Uesrichai N, Nirunsittirat A, Chuveera P, Srisuwan T, Sastraruji T, Chompu-Inwai P. Partial pulpotomy with two bioactive cements in permanent teeth of 6- to 18-year-old patients with signs and symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis: a noninferiority randomized controlled trial. Int Endod J. 2019;52(6):749–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.13071.
Walia T, Salami AA, Bashiri R, Hamoodi OM, Rashid F. A randomised controlled trial of three aesthetic full-coronal restorations in primary maxillary teeth. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2014;15(2):113–8.
Weerheijm KL, et al. Judgement criteria for molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH) in epidemiologic studies: a summary of the European meeting on MIH held in Athens, 2003. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2003;4(3):110–3.
Witherspoon DE, Small JC, Harris GZ. Mineral trioxide aggregate pulpotomies: a case series outcomes assessment. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006;137(5):610–8. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.2006.0256.
Zhao D, Dong B, Yu D, Ren Q, Sun Y. The prevalence of molar incisor hypomineralization: evidence from 70 studies. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2018;28(2):170–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.12323.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Deanship of Research, at Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid 22110, Jordan (Research Grant no: 20170181). The authors would like to thank Nessrin Taha, Professor of Endodontics at Jordan University of Science and Technology for her consultation efforts during the study period.
Funding
This project was supported by the Deanship of Research, at Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid 22110, Jordan (Research Grant no: 20170181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OA contributed to the study conception and methodology/design. Funding acquisition, material preparation and analysis were performed by OA, data collection was done by IA and OA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by OA. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or non-financial interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board at Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) (Ref #4/105/2017). Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT03735069.
Informed consent
After examination and explanation of study objectives, risks and benefits, informed consent was obtained from all parents for their childrens’ participation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Batayneh, O.B., Abdelghani, I.M. Outcome of vital pulp therapy in deeply carious molars affected with molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH) defects: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 23, 587–599 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-022-00722-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-022-00722-w