Abstract
Purpose
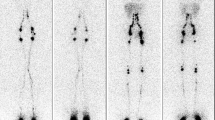
Lymphoscintigraphy is the imaging of choice in diagnosis of lymphedema. Diagnosis is made on the basis of qualitative assessment of tracer distribution at specified time points. A sound knowledge of the anatomy and function of the lymphatic system combined with understanding of tracer propagation and distribution through the lymphatic system is necessary for accurate diagnosis of lymphedema.
Technique and image findings
Lymphoscintigraphy at Aga Khan University Hospital (AKUH) is performed by intradermal injection of Tc 99m nanocolloid with planar imaging performed at 5, 15 min and 1½ h for reproducibility. Images are analyzed mainly by qualitative parameters that relate to tracer kinetics within the lymphatic system. We describe different image appearances which represent the various patterns of tracer distribution in normal lymphatics and with lymphedema.
Conclusion
Lymphoscintigraphy is a highly accurate and reproducible technique for the evaluation of the lymphedema. A thorough knowledge of the various imaging appearances on lymphoscintigraphy is necessary for proper interpretation of images. Addition of quantitative parameters would increase the accuracy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moshiri M, Katz DS, Boris M, Yung E (2002) Using lymphoscintigraphy to evaluate suspected lymphedema of the extremities. Am J Roentgenol 178(2):405–412
Keeley V (2006) The use of lymphoscintigraphy in the management of chronic oedema. J Lymphoed 1(1):42–57
Moffatt C, Franks P, Doherty D, Williams A, Badger C, Jeffs E et al (2003) Lymphoedema: an underestimated health problem. QJM 96(10):731–738
Weissleder H, Weissleder R (1988) Lymphedema: evaluation of qualitative and quantitative lymphoscintigraphy in 238 patients. Radiology 167(3):729–735
Scarsbrook A, Ganeshan A, Bradley K (2007) Pearls and pitfalls of radionuclide imaging of the lymphatic system. Part 2: evaluation of extremity lymphoedema. Br J Radiol 80(951):219–226
Mohler ER, Mondry TE (2011) Lymphedema: prevention and treatment. UpToDate. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/lymphedema-prevention-and-treatment?source=see_link. Accessed 10 Sept 2016
Tartaglione G, Pagan M, Morese R, Cappellini GA, Zappalà AR, Sebastiani C et al (2010) Intradermal lymphoscintigraphy at rest and after exercise: a new technique for the functional assessment of the lymphatic system in patients with lymphoedema. Nucl Med Commun 31(6):547–551
Williams WH, Witte CL, Witte MH, McNEILL GC (2000) Radionuclide lymphangioscintigraphy in the evaluation of peripheral lymphedema. Clin Nucl Med 25(6):451–464
Szuba A, Rockson SG (1998) Lymphedema: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Vasc Med 3(2):145–156
Ter S-E, Alavi A, Kim CK, Merli G (1993) Lymphoscintigraphy A reliable test for the diagnosis of lymphedema. Clin Nucl Med 18(8):646–654
Andersson HC, Parry DM, Mulvihill JJ (1995) Lymphangiosarcoma in late-onset hereditary lymphedema: case report and nosological implications. Am J Med Genet 56(1):72–75
Szczesny G, Olszewski WL, Gorecki A (2005) Lymphoscintigraphic monitoring of the lower limb lymphatic system response to bone fracture and healing. Lymph Res Biol 3(3):137–145
Shenoy R (2008) Clinical and pathological aspects of filarial lymphedema and its management. Korean J Parasitol 46(3):119–125
Mohler ER et al (2013) Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of lymphedema. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-features-and-diagnosis-of-peripheral-lymphedema. Accessed 12 Dec 2016
Warren AG, Brorson H, Borud LJ, Slavin SA (2007) Lymphedema: a comprehensive review. Ann Plast Surg 59(4):464–472
Rijke AM, Croft BY, Johnson RA, de Jongste AB, Camps J (1990) Lymphoscintigraphy and lymphedema of the lower extremities. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med 31(6):990
Sapienza MT, Endo IS, Ferraro GC, Tavares MG, Neto C, de Carvalho G, Guedes Neto HJ, Lewin S, Marone MM (2006) Criteria for semi-quantitative analysis of lymphoscintigraphy in lower limb lymphedema. J Vasc Bras 5(4):288–294
Kramer EL (2004) Lymphoscintigraphy: defining a clinical role. Lymph Res Biol 2(1):32–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
Verbal and written informed consent was obtained from the patients or next of kin. The standard protocol including dosage, route of radiotracer injection and time to imaging were not altered. Potential patient identifiers were not used.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nganga, E.C., Gitau, S. & Makhdomi, K. Lower limb lymphoscintigraphy patterns among patients with lower limb lymphedema: a pictorial essay. Clin Transl Imaging 6, 135–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-018-0266-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-018-0266-y