Abstract
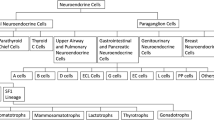
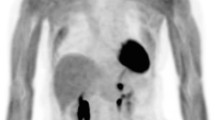
18F-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) is the radio-labelled analogue of DOPA, a precursor of dopamine and catecholamines. It is a multivalent molecule that is widely used for functional imaging of various neural crest tumors, documenting a better diagnostic accuracy compared to 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (123I-mIBG) scintigraphy and other conventional imaging modalities. Neuroblastoma (NB) is an embryonic tumor deriving from the peripheral sympathetic nervous system, commonly included into the vast group of neural crest tumors. So, it maintains the ability to produce and release biologically active amines and in most cases is characterized by an increased metabolism of catecholamines. 123I-mIBG scintigraphy represents a “cornerstone” in the assessment of NB at initial diagnosis, (re)staging and treatment response evaluation. Nevertheless this modality presents several drawbacks, thus leading the necessity to find “new” tools for the assessment of NB. 18F-DOPA is probably the most promising PET alternative to 123I-MIBG in NB and published data, although apparently limited, seem to support this hypothesis. For the current review we have performed a revision of the literature to find relevant published articles concerning the diagnostic and clinical significance of 18F-DOPA PET in the evaluation of patients with NB.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarvida ME, O’Dorisio MS (2011) Neuroendocrine tumors in children: rare or not so rare. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 40:65–80
Strenger V, Kerbl R, Dornbusch HJ et al (2007) Diagnostic and prognostic impact of urinary catecholamines in neuroblastoma patients. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48:504–509
Ley S, Ley-Zaporozhan J, Günther P et al (2011) Neuroblastoma imaging. Rofo 183(3):217–225
Lonergan GJ, Schwab CM, Suarez ES et al (2002) Neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 22:911–934
Schmidt ML, Lukens JN, Seeger RC et al (2000) Biologic factors determine prognosis in infants with stage IV neuroblastoma: a prospective Children’s Cancer Group Study. J Clin Oncol 18:1260–1268
Perez CA, Matthay KK, Atkinson JB et al (2000) Biologic Variables in the outcome of stage I and II Neuroblastoma treated with surgery as primary therapy: a Children’s Cancer Group study. J Clin Oncol 18:18–26
Ceschel S, Casotto V, Valsecchi MG et al (2006) Survival after relapse in children with solid tumors: a follow-up study from the Italian off-therapy registry. Pediatr Blood Cancer 47(5):560–566
Lopci E, Piccardo A, Nanni C, Altrinetti V, Garaventa A, Pession A, Cistaro A, Chiti A, Villavecchia G (2012) Fanti S 18F-DOPA PET/CT in neuroblastoma comparison of conventional imaging with CT/MR. Clin Nucl Med 37:e71–e78
Howman-Giles R, Shaw PJ, Uren RF et al (2007) Neuroblastoma and other neuroendocrine tumors. Semin Nucl Med 37:286–302
Tanabe M, Takahashi H, Ohnuma N et al (1993) Evaluation of bone marrow metastases of neuroblastoma and changes after chemotherapy by MRI. Med Pediatr Oncol 21:54–59
Sofka CM, Semelka RC, Kelekis NL et al (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging of neuroblastoma using current techniques. Magn Reson Imaging 17:193–198
Pfluger T, Schmied Cand C, Porn U et al (2002) Integrated imaging using MRI and 123I metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy to improve sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of pediatric neuroblastoma. Am J Roentgenol 181:1115–1124
Lebtahi N, Gudinchet F, Nenadov-Beck M et al (1997) Evaluating bone marrow metastasis of neuroblastoma with iodine-123-MIBG scintigraphy and MRI. J Nucl Med 38:1389–1392
Goo HW, Choi SH, Ghim T et al (2005) Whole-body MRI of paediatric malignant tumours: comparison with conventional oncological imaging methods. Pediatr Radiol 35:766–773
Braduer GM, Pritchacrd J, Berthold F, Carlsen NL, Castel V, Castelberry RP et al (1993) Revision of international criteria for neuroblastoma diagnosis, staging, and response to treatment. J Clin Oncol 11:1466–1477
Bomanji J, Levison DA, Flatman WD, Horne T, Bouloux PM, Ross G et al (1987) Uptake of iodine-123 MIBG by pheochromocytomas, paragangliomas, and neuroblastomas: a histopathological comparison. J Nucl Med 28:973–978
Jacobson AF, Deng H, Lombard J, Lessig HJ, Black RR (2010) 123Imeta-iodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy for the detection of neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma: results of a metaanalysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:2596–2606
Piccardo A, Lopci E, Conte M, Garaventa A, Foppiani L, Altrinetti V et al (2012) Comparison of (18)F-dopa PET/CT and (123)I-MIBG scintigraphy in stage 3 and 4 neuroblastoma: a pilot study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:57–61
Minn H, Kauhanen S, Seppänen M, Nuutila P (2009) 18F-FDOPA: a multiple-target molecule. J Nucl Med 50(12):1915–1918
Fottner C, Helisch A, Anlauf M, Rossmann H, Musholt TJ, Kreft A et al (2010) 6-18F-fluoro-L-dihydroxyphenylalanine positron emission tomography is superior to 123I-metaiodobenzyl-guanidine scintigraphy in the detection of extraadrenal and hereditary pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas: correlation with vesicular monoamine transporter expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(6):2800–2810
LaBrosse EH, Comoy E, Bohuon C, Zucker JM, Schweisguth O (1976) Catecholamine metabolism in neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 57:633–638
Brodeur GM (1991) Neuroblastoma and other peripheral neuroectodermal tumors. In: Fernbach DJ, Vietti TJ (eds) Clinical pediatric oncology, 4th edn. CV Mosby, St. Louis, p 337
Timmers HJ, Chen CC, Carrasquillo JA, Whatley M, Ling A, Havekes B et al (2009) Comparison of 18F-fluoro-L-DOPA, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, and 18F-fluorodopamine PET and 123I-MIBG scintigraphy in the localization of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(12):4757–4767
Fiebrich HB, Brouwers AH, Kerstens MN, Pijl ME, Kema IP, de Jong JR et al (2009) 6-[F-18]Fluoro-L-dihydroxyphenylalanine positron emission tomography is superior to conventional imaging with (123) I-metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy, computer tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging in localizing tumors causing catecholamine excess. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(10):3922–3930
Lu MY, Liu YL, Chang HH, Jou ST, Yang YL, Lin KH, Lin DT, Lee YL, Lee H, Wu PY, Luo TY, Shen LH, Huang SF, Liao YF, Hsu WM, Tzen KY, National Taiwan University Neuroblastoma Study Group (2013) Characterization of neuroblastic tumors using 18F-FDOPA PET. J Nucl Med 54(1):42–49
Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC, Stram DO, Harris RE, Ramsay NK et al (1999) Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bonemarrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. Children’s Cancer Group. N Engl J Med 341:1165–1173
Pearson AD, Pinkerton CR, Lewis IJ, Imeson J, Ellershaw C, Machin D et al (2008) High-dose rapid and standard induction chemotherapy for patients aged over 1 year with stage 4 neuroblastoma: a randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 9:247–256
Zage PE, Kletzel M, Murray K, Marcus R, Castleberry R, Zhang Y et al (2008) Outcomes of the POG 9340/9341/9342 trials for children with high-risk neuroblastoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 51:747–753
London WB, Castel V, Monclair T, Ambros PF, Pearson AD, Cohn SL et al (2011) Clinical and biologic features predictive of survival after relapse of neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Project. J Clin Oncol 29:3286–3292
Papathanasiou ND, Gaze MN, Sullivan K, Aldridge M, Waddington W, Almuhaideb A et al (2011) 18F-FDG PET/CT and 123Imetaiodobenzylguanidine imaging in high-risk neuroblastoma: diagnostic comparison and survival analysis. J Nucl Med 52:519–525
Messina JA, Cheng SC, Franc BL, CharronM Shulkin B, To B et al (2006) Evaluat ion of semi-quanti t a tive scor ing system for metaiodobenzylguanidine (mIBG) scans in patients with relapsed neuroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 47:865–874
Lewington V, Bar Sever Z, Giammarile F, Lynch T, McEwan A, Shulkin B et al (2009) Development of a semi-quantitative I-123 mIBG reporting method in high risk neuroblastoma. J Nucl Med 50:1379
Matthay KK, Edeline V, Lumbroso J, Tanguy ML, Asselain B, Zucker JM et al (2003) Correlation of early metastatic response by123Imetaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy with overall response and event-free survival in stage IV neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol 21:2486–2491
Piccardo A, Puntoni M, Lopci E, Conte M, Foppiani L, Sorrentino S, Morana G, Naseri M, Cistaro A, Villavecchia G, Fanti S, Garaventa A (2014) Prognostic value of 18F-DOPA PET/CT at the time of recurrence in patients affected by neuroblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41:1046–1056
Sharp SE, Shulkin BL, Gelfand MJ, Salisbury S, Furman WL (2009) 123IMIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG PET in neuroblastoma. J Nucl Med 50:1237–1243
Taggart DR, Han MM, Quach A, Groshen S, Ye W, Villablanca JG et al (2009) Comparison of iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scan and [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to evaluate response after iodine-131 MIBG therapy for relapsed neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:5343–5349
Piccardo A, Lopci E, Conte M, Foppiani L, Garaventa A, Cabria M, Villavecchia G, Fanti S, Cistaro A (2013) PET/CT imaging in neuroblastoma. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 57:29–39
Giammarile F, Lumbroso J, Ricard M et al (1995) Radioiodinated metaiodobenzylguanidine in neuroblastoma: influence of high dose on tumour site detection. Eur J Nucl Med 22:1180Y1183
Piccardo A, Lopci E, Conte M, Cabria M, Cistaro A, Garaventa A, Villavecchia G (2014) Bone and lymph node metastases from neuroblastoma detected by 18F-DOPA-PET/CT and confirmed by posttherapy 131I-MIBG but negative on diagnostic 123I-MIBG scan. Clin Nucl Med 39:e80–e83
Matthay KK, Brisse H, Couanet D et al (2003) Central nervous system metastases in neuroblastoma: radiologic, clinical, and biologic features in 23 patients. Cancer 98:155–165
D’Ambrosio N, Lyo JK, Young R et al (2010) Imaging of metastatic CNS neuroblastoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1223–1229
Piccardo A, Morana G, Massollo M, Pescetto M, Conte M, Garaventa A (2015) Brain metastasis from neuroblastoma depicted by (18)F-DOPA PET/CT. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49(3):241–242
Piccardo A, Lopci E, Foppiani L, Morana G, Conte M (2014) (18)F-DOPA PET/CT for assessment of response to induction chemotherapy in a child with high-risk neuroblastoma. Pediatr Radiol 44(3):355–361
Brisse HJ, McCarville MB, Granata C, Krug KB, Wootton-Gorges SL, Kanegawa K, International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Project et al (2011) Guidelines for imaging and staging ofneuroblastic tumors: consensus report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Project. Radiology 261:243–257
Lopci E, D’Ambrosio D, Nanni C, Chiti A, Pession A, Marengo M et al (2012) Feasibility of carbidopa premedication in pediatric patients: a pilot study. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27(10):729–733
Huang YY, Tzen KY, Liu YL, Chiu CH, Tsai CL, Wen HP et al (2015) Impact of residual (18)F-fluoride in (18)F-FDOPA for the diagnosis of neuroblastoma. Ann Nucl Med 29(6):489–498
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piccardo, A., Lopci, E. Potential role of 18F-DOPA PET in neuroblastoma. Clin Transl Imaging 4, 79–86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-016-0162-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-016-0162-2