Abstract
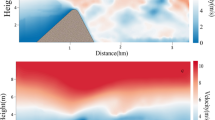
This paper studies the evolution of crescent-shaped dune under the influence of injected flux. A scaling law and a wind tunnel experiment are carried out for comparison. The experiment incorporates a novel image processing algorithm to recover the evolutionary process. The theoretical and experimental results agree well in the middle stage of dune evolution, but deviate from each other in the initial and final stages, suggesting that the crescent-shaped dune evolution is intrinsically scale-variant and that the crescent shape breaks down under unsaturated condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreotti B, Claudin P, Douady S. 2002. Selection of dune shapes and velocities. Part 1: Dynamics of sand, wind and barchans. The European Physical Journal B-Condensed Matter and Complex Systems, 28(3): 321–339.
Baas A C W. 2013. Modeling aeolian landscapes, In: Shroder J F. Treatise on Geomorphology. San Diego: Academic Press, 313–327.
Bagnold R A. 1941. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dune. New York: Methuen, 39–98.
Dauchot O, Lechénault F, Gasquet C, et al. 2002. “Barchan” dunes in the lab. Comptes Rendus Mécanique, 330(3): 185–191.
Duran O, Parteli E J R, Herrmann H J. 2010. A continuous model for sand dunes: review, new developments and application to barchans dunes and barchan dune fields. Earth Surface Processess & Landforms, 35(13): 1591–1600.
Ewing R C, Hayes A G, Lucas A. 2015. Sand dune patterns on Titan controlled by long-term climate cycles. Nature Geoscience, 8(1): 15–19.
Faria R, Ferreira A D, Sismeiro J L, et al. 2011. Wind tunnel and computational study of the stoss slope effect on the aeolian erosion of transverse sand dunes. Aeolian Research, 3(3): 303–314.
Franklin E M, Charru F. 2011. Subaqueous barchan dunes in turbulent shear flow. Part1. Dune motion. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 675(5): 199–222.
Gao X, Zhang D, Rozier O, et al. 2014. Transport capacity and saturation mechanism in a real-space cellular automaton dune model. Advances in Geosciences, 37: 47–55.
Groh C, Wierschem A, Aksel N, et al. 2008. Barchan dunes in two dimensions: experimental tests for minimal models. Physical Review E, 78(2): 021304.
Guignier L, Niiya H, Nishimori H, et al. 2013. Sand dunes as migrating strings. Physical Review E, 87(5): 052206.
Herrmann H J, Kroy K, Sauermann G. 2001. Saturation transients in saltation and their implications on dune shapes. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 302(1–4): 244–254.
Hersen P, Douady S, Andreotti B. 2002. Relevant length scale of barchan dunes. Physical Review Letters, 89(26): 264301.
Hersen P. 2005. Flow effects on the morphology and dynamics of aeolian and subaqueous barchan dunes. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 11(F4): F04S07.
Katsuki A, Nishimori H, Endo N, et al. 2005. Collision dynamics of two barchan dunes simulated using a simple model. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(2): 538–541.
Kok J F, Parteli E J R, Michaels T I, et al. 2012. The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Reports on Progress in Physics, 75(10): 106901.
Kroy K, Sauermann G, Herrmann H J. 2002. Minimal model for aeolian sand dunes. Physical Review E, 66(3): 031302.
Lima A R, Sauermann G, Herrmann H J, et al. 2002. Modeling a dune field. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 310(3–4): 487–500.
Narteau C, Zhang D, Rozler O, et al. 2009. Setting the length and time scales of a cellular automaton dune model from the analysis of superimposed bed forms. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 114(F3): F03006.
Parteli E J R, Duran O, Herrmann H J. 2007. Minimal size of a barchan dune. Physical Review E, 75(1): 011301.
Parteli E J R, Kroy K, Tsoar H, et al. 2014. Morphodynamic modeling of aeolian dunes: Review and future plans. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 223(11): 2269–2283.
Pye K, Tsoar H. 2009. Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Sauermann G, Kroy K, Herrmann H J. 2001. Continuum saltation model for sand dunes. Physical Review E, 64(3): 031305.
Schwämmle V, Herrmann H J. 2004. Modeling transverse dunes. Earth Surface Processes & Landforms, 29(6): 769–784.
Werner B T. 1995. Eolian dunes: computer simulations and attractor interpretation. Geology, 23(12): 1107–1110.
Zheng X J, Bo T L, Zhu W. 2009. A scale-coupled method for simulation of the formation and evolution of aeolian dune field. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences and Numerical Simulation, 10(3): 387–396.
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11402190), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M552443), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2013JQ2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, X. et al. Evolution of crescent-shaped sand dune under the influence of injected sand flux: scaling law and wind tunnel experiment. J. Arid Land 9, 270–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0005-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0005-7