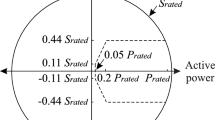
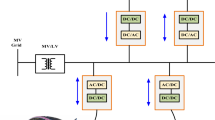
Abstract
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a promising solution to resolve the greenhouse emission issue as well as the fossil fuels scarcity problem in the future. However, as the number of EVs significantly increases, the excessive charging demand of EV parking lots (EVPLs) in the charging station may incur an instability problem to the electricity network. In this paper, the optimal allocation and sizing of EVPLs were carried out in order to minimize the costs of the EVPLs installation and EV users’ distance traveled and recharge. As a consequence, it encourages the participation of vehicle users in a demand response program related to smart charging and time of use tariffs. It is important to mention that the increasing inclusion of EVs negatively affects the voltage level and power losses of the distribution system. Therefore, this paper also performs the optimal allocation and sizing of distributed energy resources (DERs) in order to mitigate these problems. The non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) was applied to obtain the Pareto curve, which made it possible to minimize the objective functions for the IEEE 33-node test feeder and 25-node transportation network. Furthermore, it was considered a spatial distribution of EVs for the 24-h from the closeness centrality of graph theory. The optimal planning of EVPLs and DERs promoted a 35%, 23.14% and 34.11% reduction of the travel distance, voltage deviation and power losses, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, M., Hosseini, S., & Farsadi, M. (2021). Optimal allocation of electric vehicles parking lots and optimal charging and discharging scheduling using hybrid metaheuristic algorithms. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00634-z
Battapothula, G., Yammani, C., & Maheswarapu, S. (2019). Multi-objective simultaneous optimal planning of electrical vehicle fast charging stations and DGs in distribution system. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, 7(4), 923–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40565-018-0493-2
Celli, G., Ghiani, E., Mocci, S., et al. (2005). A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for the sizing and siting of distributed generation. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 20(2), 750–757. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2005.846219
Cheng, C. S., & Shirmohammadi, D. (1995). A three-phase power flow method for real-time distribution system analysis. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 10(2), 671–679. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.387902
Chen, L., Xu, C., Song, H., et al. (2021). Optimal sizing and sitting of evcs in the distribution system using metaheuristics: A case study. Energy Reports, 7, 208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.12.032
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., Rivest, R. L., et al. (2009). Introduction to algorithms (3rd ed.). The MIT Press.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., et al. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 6(2), 182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Dong, J., Liu, C., & Lin, Z. (2014). Charging infrastructure planning for promoting battery electric vehicles: An activity-based approach using multiday travel data. pp. 44–55, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2013.11.001.
Fan, X., Sun, H., Yuan, Z., et al. (2020). High voltage gain DC/DC converter using coupled inductor and vm techniques. IEEE Access, 8, 131,975-131,987. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3002902
Faridimehr, S., Venkatachalam, S., & Chinnam, R. B. (2019). A stochastic programming approach for electric vehicle charging network design. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 20(5), 1870–1882. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2018.2841391
Fernandez Savari, G., Krishnasamy, V., Kuppusamy, S., et al. (2020). Optimal dynamic scheduling of electric vehicles in a parking lot using particle swarm optimization and shuffled frog leaping algorithm. Energies, 13, 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13236384
Ferraz, R. S. F., Ferraz, R. S. F., Rueda-Medina, A. C., et al. (2020). Genetic optimisation-based distributed energy resource allocation and recloser-fuse coordination. IET Generation Transmission and Distribution, 14(20), 4501–4508. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2020.0664
Garcia-Osorio, V. A., Rueda-Medina, A. C., Melo, J. D., et al. (2013). Optimal charging of electric vehicles considering constraints of the medium voltage distribution network. In 2013 IEEE PES Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT Latin America), pp 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISGT-LA.2013.6554390.
Hodgson, M. J. (1990). A flow-capturing location-allocation model. Geographical Analysis, 22(3), 270–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-4632.1990.tb00210.x
IEEE. (2018). IEEE standard for interconnection and interoperability of distributed energy resources with associated electric power systems interfaces. IEEE Std 1547-2018 (Revision of IEEE Std 1547-2003) pp. 1–138. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.2018.8332112.
Jaiswal, S., & Ballal, M. S. (2017). Optimal load management of plug-in electric vehicles with demand side management in vehicle to grid application. In 2017 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference (ITEC-India), pp. 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1109/ITEC-India.2017.8356942.
Janga Reddy, M., & Kumar, D. N. (2007). An efficient multi-objective optimization algorithm based on swarm intelligence for engineering design. Engineering Optimization. https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150600930493
Khaksari, A., Tsaousoglou, G., Makris, P., et al. (2021). Sizing of electric vehicle charging stations with smart charging capabilities and quality of service requirements. Sustainable Cities and Society, 70(102), 872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.102872
Li, S., Xie, F., Huang, Y., et al. (2020). Optimizing workplace charging facility deployment and smart charging strategies. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 87(102), 481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102481
Metcalf, L., & Casey, W. (2016). Chapter 5-graph theory. In L. Metcalf & W. Casey (Eds.), Cybersecurity and Applied Mathematics (pp. 67–94). Boston: Syngress. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804452-0.00005-1
Muthukannan, S., & Karthikaikannan, D. (2022). Multiobjective planning strategy for the placement of electric-vehicle charging stations using hybrid optimization algorithm. IEEE Access, 10, 48,088-48,101. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3168830
Pal, A., Bhattacharya, A., & Chakraborty, A. (2021). Placement of electric vehicle charging station and solar dg in distribution system considering uncertainties. Scientia Iranica, 30(1), 183–206. https://doi.org/10.24200/SCI.2021.56782.4908
Porta, S., Latora, V., Wang, F., et al. (2012). Street centrality and the location of economic activities in Barcelona. Urban Studies, 49, 1471–1488. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098011422570
Qian, K., Zhou, C., Allan, M., et al. (2011). Modeling of load demand due to EV battery charging in distribution systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 26(2), 802–810. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2010.2057456
Rueda-Medina, A. C., Franco, J. F., Rider, M. J., et al. (2013). A mixed-integer linear programming approach for optimal type, size and allocation of distributed generation in radial distribution systems. Electric Power Systems Research, 97, 133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2012.12.009
Sadeghi-Barzani, P., Rajabi-Ghahnavieh, A., & Kazemi-Karegar, H. (2014). Optimal fast charging station placing and sizing. Applied Energy, 125, 289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.077
Swarnkar, A., Gupta, N., & Niazi, K. (2011). Adapted ant colony optimization for efficient reconfiguration of balanced and unbalanced distribution systems for loss minimization. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 1(3), 129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2011.05.004
Xiao, D., An, S., Cai, H., et al. (2020). An optimization model for electric vehicle charging infrastructure planning considering queuing behavior with finite queue length. Journal of Energy Storage, 29(101), 317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101317
Yang, X. S. (2014). Chapter 14-multi-objective optimization. In X. S. Yang (Ed.), Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms (pp. 197–211). Oxford: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416743-8.00014-2
Yang, Z., Huang, X., Gao, T., et al. (2022). Real-time energy management strategy for parking lot considering maximum penetration of electric vehicles. IEEE Access, 10, 5281–5291. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3141377
Yao, L., Lim, W. H., & Tsai, T. S. (2017). A real-time charging scheme for demand response in electric vehicle parking station. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 8(1), 52–62. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2016.2582749
Yilmaz, M., & Krein, P. T. (2013). Review of battery charger topologies, charging power levels, and infrastructure for plug-in electric and hybrid vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 28(5), 2151–2169. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2012.2212917
Zhu, Z., Gao, Z., Zheng, J. F., et al. (2017). Charging station planning for plug-in electric vehicles. Journal of Systems Science and Systems Engineering, 27, 24–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11518-017-5352-6
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Espírito Santo – Brazil (FAPES) - Number 012/2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ferraz, R.S.F., Ferraz, R.S.F., Rueda-Medina, A.C. et al. Multi-objective Optimization Approach for Allocation of Electric Vehicles Parking Lots and Smart Charging with Distributed Energy Resource. J Control Autom Electr Syst 34, 1070–1079 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-023-01027-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-023-01027-z