Abstract
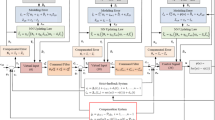
In this work, the trajectory tracking control scheme is the framework of optimal control and robust integral of the sign of the error (RISE); sliding mode control technique for an uncertain/disturbed nonlinear robot manipulator without holonomic constraint force is presented. The sliding variable combining with RISE enables to deal with external disturbance and reduced the order of closed systems. The adaptive reinforcement learning technique is proposed by tuning simultaneously the actor–critic network to approximate the control policy and the cost function, respectively. The convergence of weight as well as tracking control problem was determined by theoretical analysis. Finally, the numerical example is investigated to validate the effectiveness of proposed control scheme.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhasin, S., Kamalapurkar, R., Johnson, M., Vamvoudakis, K. G., Lewis, F. L., & Dixon, W. E. (2013). A novel actor-critic-identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica, 49(1), 82–92.
Binh, N. T., Tung, N. A., Nam, D. P., & Quang, N. H. (2019). An adaptive backstepping trajectory tracking control of a tractor trailer wheeled mobile robot. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 17(2), 465–473.
Dupree, K., Patre, P. M., Wilcox, Z. D., & Dixon, W. E. (2011). Asymptotic optimal control of uncertain nonlinear Euler–Lagrange systems. Automatica, 1, 99–107.
Galicki, M. (2015). Finite-time control of robotic manipulators. Automatica, 51, 49–54.
Guo, Y., Huang, B., Li, A., & Wang, C. (2019). Integral sliding mode control for Euler-Lagrange systems with input saturation. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 29(4), 1088–1100.
He, W., Xue, C., Yu, X., Li, Z., & Yang, C. (2020). Admittance-Based Controller Design for Physical Human-Robot Interaction in the Constrained Task Space. In IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering,Early Access, (pp 1–13).
He, W., & Dong, Y. (2017). Adaptive fuzzy neural network control for a constrained robot using impedance learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29(4), 1174–1186.
He, W., Chen, Y., & Yin, Z. (2015). Adaptive neural network control of an uncertain robot with full-state constraints. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 46(3), 620–629.
He, W., Dong, Y., & Sun, C. (2015). Adaptive neural impedance control of a robotic manipulator with input saturation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 46(3), 334–344.
Hu, X., Wei, X., Zhang, H., Han, J., & Liu, X. (2019). Robust adaptive tracking control for a class of mechanical systems with unknown disturbances under actuator saturation. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 6(29), 1893–1908.
Huang, J., Ri, S., Fukuda, T., & Wang, Y. (2018). A disturbance observer based sliding mode control for a class of underactuated robotic system with mismatched uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 64(6), 2480–2487.
Li, S., Ding, L., Gao, H., Liu, Y.-J., Huang, L., & Deng, Z. (2020). ADP-based online tracking control of partially uncertain time-delayed nonlinear system and application to wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 50(7), 3182–3194.
Liu, Y., Dao, N., & Zhao, K. Y. (2020). On robust control of nonlinearteleoperators under dynamic uncertainties with variable time delays and without relative velocity. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 16(2), 1272–1280.
Lu, M., Liu, L., & Feng, G. (2019). Adaptive tracking control of uncertain Euler–Lagrange systems subject to external disturbances. Automatica, 104, 207–219.
Lv, Y., Na, J., Yang, Q., Wu, X., & Guo, Y. (2016). Online adaptive optimal control for continuous-time nonlinear systems with completely unknown dynamics. International Journal of Control, 89(1), 99–112.
Madani, T., Daachi, B., & Djouani, K. (2016). Modular controller design based fast terminal sliding mode for articulated exoskeleton systems. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 25(3), 1133–1140.
Mondal, S., & Mahanta, C. (2014). Adaptive second order terminal sliding mode controller for robotic manipulators. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 351(4), 2356–2377.
Nguyena, T., Hoang, T., Pham, M., & Dao, N. (2019). A Gaussian wavelet network-based robust adaptive tracking controller for a wheeled mobile robot with unknown wheel slips. International Journal of Control, 92(11), 2681–2692.
Sun, Z., Xia, Y., Dai, L., Liu, K., & Ma, D. (2017). Disturbance rejection MPC for tracking of wheeled mobile robot. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 22(6), 2576–2587.
Sun, Z., Dai, L., Xia, Y., & Liu, K. (2017). Event-based model predictive tracking control of nonholonomic systems with coupled input constraint and bounded disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 63(2), 608–615.
Vamvoudakis, K. G., Vrabie, D., & Lewis, F. L. (2014). Online adaptive algorithm for optimal control with integral reinforcement learning. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 24(17), 2686–2710.
Wang, H., Pan, Y., Li, S., & Yu, H. (2018). Robust sliding mode control for robots driven by compliant actuators. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 27(3), 1259–1266.
Yang, L., & Yang, J. (2011). Nonsingular fast terminal sliding-mode control for nonlinear dynamical systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 21(16), 1865–1879.
Yang, H., Guo, M., Xia, Y., & Sun, Z. (2020). Dual closed-loop tracking control for wheeled mobile robots via active disturbance rejection control and model predictive control. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 30(1), 80–89.
Yu, X., He, W.I, Li, H., & Sun, J. (2020). Adaptive fuzzy full-state and output-feedback control for uncertain robots with output constraint. In IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems,Early Acess, (pp 1–14).
Yu, Y, Dai, L., Sun, Z., & Xia, Y. (2018). Robust Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Robot Manipulators with Disturbances. The 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), 3629–3633.
Zhu, Y., Zhao, D., & Li, X. (2016). Using reinforcement learning techniques to solve continuous-time non-linear optimal tracking problem without system dynamics. IET Control Theory and Applications, 10(12), 1339–1347.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Ministry of Education and Training, Vietnam, under Grant B2020-BKA-05.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vu, V.T., Dao, P.N., Loc, P.T. et al. Sliding Variable-based Online Adaptive Reinforcement Learning of Uncertain/Disturbed Nonlinear Mechanical Systems. J Control Autom Electr Syst 32, 281–290 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-020-00674-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-020-00674-w