Abstract
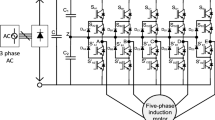
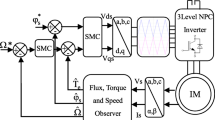
This paper presents experimental performance improvement of induction motor fed by five-leg AC–DC–AC converter with DC-link voltages offset compensation. In order to control the rectifier, a sliding mode control approach is proposed to track the DC-link voltage. The grid-side converter control is performed via a predictive power control, which minimizes the instantaneous input reactive power present in the system and compensates the undesirable harmonic contents of the grid current, under a unity power factor. In motor side, the inverter control is performed via a predictive torque control to achieve an accurate torque and flux references tracking with ripples reduction. The implementation of the proposed control architecture is achieved via a dSPACE 1104 card. The experimental results show that the proposed control strategy develops a faster active power response leading to low DC-link voltage variation, while the grid current is nearly sinusoidal with low total harmonic distortion. Experimental results reveal also that the drive system, associated with PTC technique, can effectively reduce flux and torque ripples with better dynamic and steady-state performance. Further, the proposed approaches minimize the average switching frequency.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, N. (2016). Power factor correction and harmonic filtering planning in electrical distribution network. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems. doi:10.1007/s40313-016-0247-1.
Benchouia, M. T., Ghadbane, I., Golea, A., Srairi, K., & Benbouzid, M. H. (2014). Design and implementation of sliding mode and PI controllers based control for three phase shunt active power filter. Energy Procedia, 50, 504–511. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2014.06.061.
Calle-Prado, A., Alepuz, S., Bordonau, J., Cortés, P., & Rodríguez-maroto, J. (2016). Predictive control of a back-to-back NPC converter-based wind power system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 0046(c), 1–12. doi:10.1109/TIE.2016.2529564.
Chihab, A. A., Giri, H. O. F., & Majdoub, K. El. (2015). Adaptive backstepping control of three-phase four-wire shunt active power filters for energy quality improvement. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems. doi:10.1007/s40313-015-0221-3.
Cortes, P., Rodriguez, J., Antoniewicz, P., & Kazmierkowski, M. (2008). Direct power control of an AFE using predictive control. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 23(5), 2516–2523. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2008.2002065.
Cortés, P., Rodríguez, J., Quevedo, D., & Silva, C. (2007). Predictive current control strategy with imposed load current spectrum. In Proceedings of EPE-PEMC 2006: 12th international power electronics and motion control conference (Vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 252–257). doi:10.1109/EPEPEMC.2006.283088.
Cortes, P., Rodriguez, J., Silva, C., & Flores, A. (2012). Delay compensation in model predictive current control of a three-phase inverter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 59(2), 1323–1325. doi:10.1109/TIE.2011.2157284.
Dannehl, J., Wessels, C., & Fuchs, F. W. (2009). Limitations of voltage-oriented PI current control of grid-connected PWM rectifiers with LCL filters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(2), 380–388. doi:10.1109/TIE.2008.2008774.
Diab, A. A. Z. (2014). Real-time implementation of full-order observer for speed sensorless vector control of induction motor drive. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems (pp. 639–648). doi:10.1007/s40313-014-0149-z.
Dida, A., & Benattous, D. (2015). Modeling and Control of DFIG through back-to-back five levels converters based on neuro-fuzzy controller. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems. doi:10.1007/s40313-015-0190-6.
Formentini, A., Trentin, A., Marchesoni, M., Zanchetta, P., & Wheeler, P. (2015). Speed finite control set model predictive control of a PMSM fed by matrix converter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(11), 6786–6796. doi:10.1109/TIE.2015.2442526.
Fuentes, E. J., Rodriguez, J., Silva, C., Diaz, S., & Quevedo, D. E. (2009). Speed control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor using predictive current control. In IPEMC ’09. IEEE 6th international power electronics and motion control conference, 2009 (pp. 390–395). doi:10.1109/IPEMC.2009.5157418.
Gayen, P. K., Chatterjee, D., & Goswami, S. K. (2015). Stator side active and reactive power control with improved rotor position and speed estimator of a grid connected DFIG (doubly-fed induction generator). Energy, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2015.05.111.
Habibullah, M., Lu, D. D.-C., Xiao, D., & Rahman, M. F. (2016). A simplified finite-state predictive direct torque control for induction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 0046(c), 1. doi:10.1109/TIE.2016.2519327.
Henrique, R., Palácios, C., Goedtel, A., Godoy, W. F., & Fabri, J. A. (2016). Fault identification in the stator winding of induction motors using PCA with artificial neural networks. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems. doi:10.1007/s40313-016-0248-0.
Lee, D., & Lim, D. (2002). AC voltage and current sensorless control of three-phase PWM rectifiers. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 17(6), 883–890.
Liu, X., Zhang, G., Mei, L., & Wang, D. (2016). Speed estimation with parameters identification of PMSM based on MRAS. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, (30). doi:10.1007/s40313-016-0253-3
Lopez, M., Rodriguez, J., Silva, C., & Rivera, M. (2015). Predictive torque control of a multidrive system fed by a dual indirect matrix converter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(5), 2731–2741. doi:10.1109/TIE.2014.2364986.
Monfared, M., Rastegar, H., & Madadi, H. (2010). High performance direct instantaneous power control of PWM rectifiers. Energy Conversion and Management, 51(5), 947–954. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2009.11.034.
Pereira, W. C. A., Paula, G. T., & Almeida, T. E. P. (2016). Vector control of induction motor using an integral sliding mode controller with anti-windup. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems. doi:10.1007/s40313-016-0228-4.
Perez, M. a, Fuentes, E., & Rodriguez, J. (2010). Predictive current control of ac-ac modular multilevel converters. In 2010 IEEE international conference on industrial technology (ICIT) (pp. 1289–1294). doi:10.1109/ICIT.2010.5472536.
Pichan, M., Rastegar, H., & Monfared, M. (2013). Two fuzzy-based direct power control strategies for doubly-fed induction generators in wind energy conversion systems. Energy, 51, 154–162. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.12.047.
Preindl, M., & Bolognani, S. (2013). Model predictive direct torque control with finite control set for PMSM drive systems, part 1?: Maximum torque per ampere operation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(c), 1912–1921. doi:10.1109/TII.2012.2227265.
Quevedo, D. E., Aguilera, R. P., Perez, M. A., Cortes, P., & Lizana, R. (2012). Model predictive control of an AFE rectifier with dynamic references. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 27(7), 3128–3136. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2011.2179672.
Rahoui, A., Bechouche, A., Seddiki, H., Abdeslam, D. O., & Member, S. (2017). Grid voltages estimation for three-phase PWM rectifiers control without AC voltage sensors. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, PP(99), 1–13. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2017.2669146.
Riar, B., Geyer, T., & Madawala, U. (2015). Model predictive direct current control of modular multilevel converters: Modelling, analysis and experimental evaluation. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, PP(1), 1-1. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2014.2301438.
Rivera, M., Vargas, R., Espinoza, J., Rodríguez, J., Wheeler, P., & Silva, C. (2008). Current control in matrix converters connected to polluted AC voltage supplies. PESC Record IEEE Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 2, 412–417. doi:10.1109/PESC.2008.4591964.
Rodriguez, J., Kazmierkowski, M. P., Espinoza, J. R., Zanchetta, P., Abu-Rub, H., Young, H. A., et al. (2013). State of the art of finite control set model predictive control in power electronics. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(2), 1003–1016. doi:10.1109/TII.2012.2221469.
Rodríguez, J., Pontt, J., Correa, P., Lezana, P., & Cortés, P. (2005). Predictive power control of an AC/DC/AC converter. Conference Record IAS Annual Meeting (IEEE Industry Applications Society), 2(1), 934–939. doi:10.1109/IAS.2005.1518458.
S. Muller, U. Ammann, & Rees, S. (2003). New modulation strategy for a matrix converter with a very small mains filter. In IEEE 34th annual power electronics specialist conference (Vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1275–1280). doi:10.1109/PESC.2003.1216772
Vargas, R., Rodriguez, J., Ammann, U., & Wheeler, P. W. (2008). Predictive current control of an induction machine fed by a matrix converter with reactive power control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 55(12), 4362–4371. doi:10.1109/TIE.2008.2006947.
Verne, S. A., & Valla, M. I. (2010). Predictive control of a back to back motor drive based on diode clamped multilevel converters. In IECON 2010 36th annual conference on IEEE industrial electronics society (pp. 2972–2977). doi:10.1109/IECON.2010.5674940.
Xia, C., Liu, T., Shi, T., & Song, Z. (2014). A simplified finite-control-set model-predictive control for power converters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 10(2), 991–1002. doi:10.1109/TII.2013.2284558.
Zhang, Y., & Yang, H. (2015). Model-predictive flux control of induction motor drives with switching instant optimization. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 30(3), 1–10. doi:10.1109/TEC.2015.2423692.
Zhang, Y., & Yang, H. (2016). Two-vector-based model predictive torque control without weighting factors for induction motor drives. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 31(2), 1381–1390. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2015.2416207.
Zhang, Z., Hackl, C., Wang, F., Chen, Z., & Kennel, R. (2013a). Encoderless model predictive control of back-to-back converter direct-drive permanent-magnet synchronous generator wind turbine systems. In 2013 15th European conference on power electronics and applications (EPE) (pp. 1–9). doi:10.1109/EPE.2013.6632002.
Zhang, Z., Hackl, C., Wang, F., Chen, Z., & Kennel, R. (2013b). Encoderless model predictive control of back-to-back converter direct-drive permanent-magnet synchronous generator wind turbine systems. In 2013 15th European conference on power electronics and applications (EPE). doi:10.1109/EPE.2013.6632002
Zhang, Z., Xu, H., Xue, M., Chen, Z., Sun, T., Kennel, R., et al. (2015). Predictive control with novel virtual-flux estimation for back-to-back power converters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(5), 2823–2834. doi:10.1109/TIE.2014.2361802.
Zhi, D. Z. D., Xu, L. X. L., & Williams, B. W. (2009). Improved direct power control of grid-connected DC/AC converters. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 24(5), 1280–1292. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2009.2012497.
Zhou, D., Zhao, J., & Li, Y. (2016). Model predictive control scheme of five-leg AC–DC–AC converter fed induction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 46, 1–10. doi:10.1109/TIE.2016.2541618.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chebaani, M., Goléa, A., Benchouia, M.T. et al. Sliding Mode Predictive Control of Induction Motor Fed by Five-Leg AC–DC–AC Converter with DC-Link Voltages Offset Compensation. J Control Autom Electr Syst 28, 597–611 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-017-0334-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-017-0334-y