Abstract
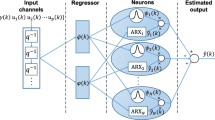
In this paper, an online identification algorithm for instrumental variable-based evolving neuro-fuzzy modeling applied to dynamic systems in noisy environment is proposed. The adopted methodology is based on neuro-fuzzy inference system with Takagi–Sugeno evolving structure, which employs an adaptive distance norm based on the maximum likelihood criterion with instrumental variable recursive parameter estimation. The application and performance analysis of the proposed algorithm is based on black-box modeling of a 2DOF Helicopter with errors in variables.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acampora, G., Pedrycz, W., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). Efficient modeling of MIMO systems through timed automata based neuro-fuzzy inference engine. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 55(6), 1336–1356. (Neuro-fuzzy systems; Timed Automata based Fuzzy Systems).
Angelov, P. (2013). Autonomous learning systems: From data streams to knowledge in real-time. In IEEE press series on computational intelligence. Willey, ISBN 9781119951520.
Angelov, P., Filev, D., & Kasabov, N. (2010). Evolving intelligent systems: Methodology and applications. In IEEE press series on computational intelligence. Willey-Blackwell, ISBN 9780470287194.
Arya, V., & Rathy, R. K. (2014). An efficient neuro-fuzzy approach for classification of Iris dataset. In International conference on reliability, optimization and information technology (pp. 161–165). doi:10.1109/ICROIT.2014.6798304.
Babuska, R., Schutter, B., Lendek, Zs, & Guerra, T. M. (2010). Stability analysis and nonlinear observer design using Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy models (Vol. 262). Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-16776-8.
Babuska, R. (1998). Fuzzy modeling control. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Baruah, R. D., & Angelov, P. (2012). Evolving local means method for clustering of streaming data. In IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2012 (pp. 1–8). doi:10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2012.6251366.
Baruah, R. D., Angelov, P., & Baruah, D. (2014). Dynamically evolving clustering for data streams. In IEEE conference on evolving and adaptive intelligent systems (EAIS)2014 (pp. 1–6). doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2264938.
Bodyanskiy, Y., Tyshchenko, O., & Kopliani, D. (2015). An evolving neuro-fuzzy system for online fuzzy clustering. In Computer science and information technologies (pp. 158–161). doi:10.1109/STC-CSIT.2015.7325456.
Bodyanskiy, Y., Vynokurova, O., Setlak, G., & Pliss, I. (2015). Hybrid neuro-neo-fuzzy system and its adaptive learning algorithm. In Computer science and information technologies (pp. 111–114). doi:10.1109/STC-CSIT.2015.7325445.
Bordignon, F., & Gomide, F. (2014). Uninorm based evolving neural networks and approximation capabilities. Neurocomputing, 127, 13–20. (ELSEVIER).
Costa, B. S., Angelov, P. P., & Guedes, L. A. (2015). Fully unsupervised fault detection and identification based on recursive density estimation and self-evolving cloud-based classifier. Neurocomputing, 150(A), 289–303. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2014.05.086.
Dovzan, D., Logar, V., & Skrjanc, I. (2015). Implementation of an evolving fuzzy model (eFuMo) in a monitoring system for a waste-water treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 23(5), 1761–1776. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2379252.
Han, L., Yi, D., Lifan, Z., & Ding, L. (2015). Neuro-fuzzy control based on online least square support vector machines. In Proceedings of the 34th Chinese control conference (pp. 3411–3416).
Lemos, A., Caminhas, W., & Gomide, F. (2011). Multivariable Gaussian evolving fuzzy modeling system. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 19(1), 91–104. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2010.2087381.
Liu, Y., Zhang, W., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Data driven modeling of human welder intelligence: A neuro-fuzzy approach. In IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering (pp. 663–668). doi:10.1109/CoASE.2013.6653890.
Liu, X., Wang, J., & Zheng, W. X. (2011). Convergence analysis of refined instrumental variable method for continuous-time system identification. IET Control Theory and Applications, 5(7), 868–877.
Lughofer, E. (2011). Evolving fuzzy systems: Methodologies, advanced concepts and applications. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 9783642180866.
Lughofer, E., Cernuda, C., Kindermann, S., & Pratama, M. (2015). Generalized smart evolving fuzzy systems. Evolving Systems, 6(4), 269–292. doi:10.1007/s12530-015-9132-6.
Lughofer, E., & Sayed-Mouchaweh, M. (2015). Autonomous data stream clustering implementing incremental split-and-merge techniques–towards a plug-and-play approach. Information Sciences, 204(C), 54–79. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2015.01.010.
Maciel, L., Gomide, F., & Ballini, R. (2012). MIMO evolving participatory learning fuzzy modeling. In IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2012 (pp. 1–8). doi:10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2012.6251170.
Petelin, D., & Kocijan, J. (2014). Evolving Gaussian process models for predicting chaotic time-series. In IEEE conference on evolving and adaptive intelligent systems (EAIS), 2014 (pp. 1–8). doi:10.1109/EAIS.2014.6867476.
Pratama, M., Anavatti, S. G., & Lughofer, E. (2014). GENEFIS: Toward an effective localist network. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 22(3), 547–562.
Rajab, S., & Sharma, V. (2015). Performance evaluation of ANN and neuro-fuzzy system in business forecasting. In 2nd international conference on computing for sustainable global development (INDIACom), 2015 (pp. 749–754).
Sayed-Mouchaweh, M., & Lughofer, E. (2012). Learning in non-stationary environments: Methods and applications. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 9781441980199.
Serra, G. (2012). Frontiers in advanced control systems, InTech, ISBN 9789535106777. doi:10.5772/1267.
Serra, G., & Bottura, C. (2007). An IV–QR algorithm for neuro-fuzzy multivariable online identification. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 15(2), 200–210. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2006.879997.
Serra, G., & Bottura, C. (2009). Fuzzy instrumental variable approach for nonlinear discrete-time systems identification in a noisy environment. Science direct: Fuzzy sets and systems, 160(4), 500–520. doi:10.1016/j.fss.2008.06.020. (ELSEVIER).
Silva, A., Caminhas, W., Lemos, A., & Gomide, F. (2014). Real-time nonlinear modeling of a twin rotor MIMO system using evolving neuro-fuzzy network. In IEEE symposium on computational intelligence in control and automation (CICA), 2014 (pp. 1–8). doi:10.1109/CICA.2014.7013229.
Skrjanc, I., Dovzan, D., & Gomide, F. (2014). Evolving fuzzy-madel-based on c-regression clustering. In IEEE conference on evolving and adaptive intelligent systems (EAIS), 2014 (pp. 1–7). doi:10.1109/EAIS.2014.6867481.
Skrjanc, I. (2015). Evolving fuzzy-model-based design of experiments with supervised hierarchical clustering. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 23(4), 861–871. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2014.2329711.
Soleimani-B, H., Lucas, C., & Arrabi, N. (2010). Recursive Gath–Geva clustering as basis for evolving neuro-fuzzy modeling. In IEEE conference on fuzzy systems 2010 (Vol. 1, pp. 1–7). doi:10.1109/ICSSSM.2014.6874031.
Sun, Z., Mao, K. Z., Tang, W., Mak, L. O., Xian, K., & Liu, Y. (2014). Knowledge-based evolving clustering algorithm for data stream. In 11th international conference on service systems and service management (ICSSSM), 2014 (pp. 1–6).
Tsumura, K. (2012). Optimal quantization of signals for system identification. In IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2009 (Vol. 54(12), pp. 2909–2915). doi:10.1109/TAC.2009.2033859.
Tsumura, K., & Maciejowski, J. (2003). Optimal quantization of signals for system identification. In European control conference (ECC), Cambridge, UK (pp. 785–790).
Tsumura, K., & Oishi, Y. (1999). Optimal length of data for identification of time varying system, decision and control, 1999. In Proceedings of the 38th IEEE conference on Phoenix, AZ, 1999 (Vol. 4, pp. 3224-3229). doi:10.1109/CDC.1999.827766.
Vishnupriyan, J., Manoharan, P. S., & Ramalakshmi, A. P. S. (2014). Uncertainty modeling of nonlinear 2-DOF helicopter model. In 2014 international conference on computer communication and informatics (ICCCI -2014) (pp. 1–6). doi:10.1109/ICCCI.2014.6921840.
Yilmaz, S., & Oysal, Y. (2014). Nonlinear system modeling with dynamic adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. In IEEE international symposium on innovations in intelligent systems and applications (INISTA) proceedings, 2014 (pp. 205–211). doi:10.1109/INISTA.2014.6873619.
Young, P. (2015). Refined instrumental variable estimation: Maximum likelihood optimization of a unified Box–Jenkings model. Automatica, 52, 35–46. doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.126. (ELSEVIER).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FAPEMA and encouraged by Ph.D. Program in Electrical Engineering of Federal University of Maranhao (PPGEE/UFMA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, O., Serra, G. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Black-Box Modeling Based on Instrumental Variable Evolving Algorithm. J Control Autom Electr Syst 28, 50–67 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0285-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0285-8