Abstract
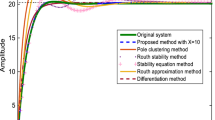
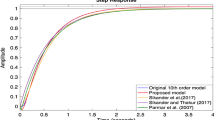
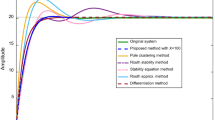
In this paper, mixed method of linear, time-invariant system model reduction method is suggested. A novel clustering algorithm based on Lehmer measure is utilized in the proposed method to obtain the reduced-order denominator polynomial. The selection of poles to form cluster center is based on the viewpoint of important poles contributing to the system is preserved by dominant pole algorithm. Having obtained the denominator polynomial of the reduced model, the coefficient of the numerator is found using the frequency response matching method. The reduction algorithm is fully computer oriented. The reduced model is stable if the original model is stable. Moreover, this method gives a good quality approximation in both the transient and the steady-state responses of the original system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appiah, R. K. (1979). Pade methods of Hurwitz polynomial approximation with application to linear system reduction. International Journal of Control, 29(1), 39–48.
Bistritz, Y., & Langholz, G. (1979). Model reduction by Chebyshev polynomial techniques. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 24(5), 741–747.
Bultheel, A., & Barel, M. V. (1986). Padé techniques for model reduction in linear system theory: A survey. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 14, 401–438.
Chahlaoui, Y., & Van Dooren, P. (2005). Benchmark examples for model reduction of linear time-invariant dynamical systems. In P. Benner, V. Mehrmann, & Sorensen (Eds.), Dimension reduction of large-scale systems (pp. 379–392). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Chen, C. F., & Shieh, L. S. (1970). An algebraic method for control systems design. International Journal of Control, 11(5), 717–739.
Chen, T. C., Chang, C. Y., & Han, K. W. (1979). Reduction of transfer functions by the stability-equation method. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 308(4), 389–404.
Chen, T. C., Chang, C. Y., & Han, K. W. (1980a). Model reduction using the stability-equation method and the continued-fraction method. International Journal of Control, 32(1), 81–94.
Chen, T. C., Chang, C. Y., & Han, K. W. (1980b). Model reduction using the stability-equation method and the Padé approximation method. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 309(6), 473–490.
Chuang, S. C. (1976). Homographic transformation for the simplification of continuous-time transfer functions by Padé approximation. International Journal of Control, 23(6), 821–826.
Desai, S. R., & Prasad, R. (2013). A new approach to order reduction using stability equation and big bang big crunch optimization. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 1(1), 20–27.
Hutton, M., & Friedland, B. (1975). Routh approximations for reducing order of linear, time-invariant systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 20(3), 329–337.
Komarasamy, R., Albhonso, N., & Gurusamy, G. (2011). Order reduction of linear systems with an improved pole clustering. Journal of Vibration and Control, 18(12), 1876–1885.
Krishnamurthi, V., & Seshadri, V. (1976). A simple and direct method of reducing order of linear systems using routh approximations in the frequency domain. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 21(5), 797–799.
Krishnamuthy, V., & Seshadri, V. (1978). Model reduction using the Routh stability criterion. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 23, 729–731.
Langhoz, G., & Bistrltz, Y. (1980). Model reduction of dynamic systems over a frequency interval\(\dagger \). International Journal of Control, 31(1), 51–62.
Lin, P. L., & Wu, Y. C. (1982). Reduction of transfer functions from the stability-equation method and complex curve fitting. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 314(2), 109–121.
Lucas, T. (1983). Factor division: A useful algorithm in model reduction. Control Theory and Applications., 130(6), 1981–1983.
Martins, N., & Quintão, P. E. M. (2003). Computing dominant poles of power system multlvariable transfer functions. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 11(1), 152–159.
Mittal, A. K., Prasad, R., & Sharama, S. P. (2004). Reduction of linear dynamic system using an error minimization technique. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (India), 84, 201–204.
Mukherjee, S., & Mittal, R. C. (2005). Model order reduction using response-matching technique. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 342(5), 503–519.
Ouyang, M., Liaw, C., & Pan, C. (1987). Model reduction by power decomposition and frequency response matching. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 32(1), 59–62.
Pal, J. (1983). Improved Pade approximants using stability equation method. Electronics Letters, 19(11), 3–4.
Parmar, G., Mukherjee, S., & Prasad, R. (2007a). Reduced order modelling of linear multivariable systems using particle swarm optimisation technique. International Journal of Innovative Computing and Applications, 1(2), 128.
Parmar, G., Mukherjee, S., & Prasad, R. (2007b). System reduction using factor division algorithm and eigen spectrum analysis. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 31(11), 2542–2552.
Parthasarathy, R., & John, S. (1978). System reduction using Cauer continued fraction expansion about \(s=0\) and \(s=\infty \) alternately. Electronics Letters, 18(23), 9–10.
Philip, B., & Pal, J. (2010). An evolutionary computation based approach for reduced order modelling of linear systems. IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, 2010, 1–8.
Prasad, R., & Pal, J. (1991). Use of continued fraction expansion for stable reduction of linear multivariable systems. Institution of Engineers India Part Electrical Engineering Division, 72, 43–43.
Rao, S. V., & Lammba, S. S. (1974). A new frequency domain technique for the simplification of linear dynamic systems. International Journal of Control, 20(1), 71–79.
Reddy, A. S. S. R. (1976). A method for frequency domain simplification of transfer functions. International Journal of Control, 23(3), 403–408.
Saadvandi, M., Meerbergen, K., & Jarlebring, E. (2012). On dominant poles and model reduction of second order time-delay systems. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 62(1), 21–34.
Shamash, Y. (1980a). Failure of the Routh–Hurwitz method of reduction. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 25(2), 313–314.
Shamash, Y. (1980b). Stable biased reduced order models using the Routh method of reduction. International Journal of Systems Science, 11(5), 641–654.
Singh, J., Vishwakarma, C. B., & Chattterjee, K. (2016). Biased reduction method by combining improved modified pole clustering and improved Pade approximations. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 40(2), 1418–1426.
Sinha, A. K., & Pal, J. (1990). Simulation based reduced order modelling using a clustering technique. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 16(3), 159–169.
Skogestad, S., & Postlethwaite, I. (2007). Multivariable feedback control: Analysis and design (Vol. 2). New York: BOOK, Wiley.
Soloklo, H. N., & Farsangi, M. M. (2013). Chebyshev rational functions approximation for model order reduction using harmony search, 20, 771–777.
Soloklo, H. N., & Farsangi, M. M. (2015). Model order reduction by using Legendre expansion and harmony search algorithm. Majlesi Journal of Electrical Engineering, 9(1), 25–35.
Soloklo, H. N., Hajmohammadi, R., & Farsangi, M. M. (2015). Model order reduction based on moment matching using Legendre wavelet and harmony search algorithm. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, 39(E1), 39–54.
Soloklo, H. N., Nali, O., & Farsangi, M. M. (2014). Model reduction by Hermite polynomials and genetic algorithm. Journal of Mathematics and Computer Science, 9, 188–202.
Stolarsky, K. B. (1996). Holder means, Lehmer Means, and \(\text{ x }^{-1}\) log cosh x. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 202, 810–818.
Vishwakarma, C. B., & Prasad, R. (2008). Clustering method for reducing order of linear system using Pade approximation. IETE Journal of Research., 54(5), 326–330.
Vishwakarma, C. B., & Prasad, R. (2009). MIMO system reduction using modified pole clustering and genetic algorithm. Modelling and Simulation in Engineering, 2009, 1–5.
Wan, B.-W. (1981). Linear model reduction using Mihailov criterion and Padé approximation technique. International Journal of Control, 33(6), 1073–1089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, S.K., Kaur, G. Model Reduction by New Clustering Method and Frequency Response Matching. J Control Autom Electr Syst 28, 78–85 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0282-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0282-y