Abstract
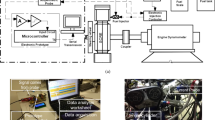
This work shows an electronic management system equipped with two microcontrollers for ethanol injection in the air intake pipe of a diesel engine. The aim was to reduce the NOx emissions, while increasing the amount of renewable fuel in the mixture. The system was specially developed to detect the high-pressure pulse in the diesel injection line and to trigger the ethanol injection. An intrusive pressure sensor was installed in the diesel injection pipe to allow the measurement. Through a security protocol, the timing and duration of injection can be adjusted. The system evaluates the temperature reduction caused by the ethanol injection using two NTC thermal sensors. The exhaust gas temperature was determined by a type K thermocouple. The system was tested in a single cylinder diesel generator with mechanical injection at 1,750, 1,800, and 1,850 rpm in order to verify the injection frequency, the injection delays, the NOx emissions and the intake air, and exhaust gas temperature variation. It was found that the injection delays were less than 850 \(\mu \)s. A reduction in the intake air and exhaust gas temperatures was observed as the ethanol content increased. Injections of 15 v/v% ethanol into the intake air pipe have shown a considerable reduction (60 %) in NOx emissions when compared to diesel-biodiesel blend composed of 70 v/v% mineral diesel and 30 v/v% soybean biodiesel. It was demonstrated that the addition of ethanol can be an important method to reduce the amount of NOx in the exhaust gas of Diesel engines.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Candeia, R. A., Silva, M. C. D., Filho, J. R., Carvalho Brasilino, M. G. A., Bicudo, T. C., & Santos, I. M. G. (2009). Influence of soybean biodiesel content on basic properties of biodiesel-diesel blends. Fuel, 88, 738–743.
Fang, Z. (Ed.) (2013). Biofuels—Economy environment and sustainability. (Chap. 14, pp. 357–386). InTech.
Guarieiro, L. L. N., Souza, A. F., Torres, E. A., & de Andrade, J. B. (2009). Emission profile of 18 carbonyl compounds, CO, \(\text{ CO }_2\), and NOx emitted by a diesel engine fuelled with diesel and ternary blends containing diesel, ethanol and biodiesel or vegetable oils. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 2754–2761.
Janaun, J., & Ellis, N. (2010). Perspectives on biodiesel as a sustainable fuel. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 14, 1312–1320.
Lapuerta, M., Armas, O., & Garcia-Contreras, R. (2007). Stability of diesel-bioethanol blends for use in diesel engines. Fuel, 86, 1351–1357.
Lapuerta, M., Armas, O., & Rodriguez-Fernandez, J. (2008). Effect of biodiesel fuels on diesel engine emissions. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 34, 198–223.
Lin, Y., Wu, Y. G., & Chang, C. (2007). Combustion characteristics of waste-oil produced biodiesel/diesel fuel blends. Fuel, 86, 1772–1780.
Lu, X., Ma, J., Ji, L., & Huang, Z. (2008). Simultaneous reduction of NOx emission and smoke opacity of biodiesel-fueled engines by port injection of ethanol. Fuel, 87, 1289–1296.
Mollenhauer, K., & Tschoeke, H. (2010). Handbook of diesel engines. Engines. Berlin: Springer.
Montero, G., & Stoytchevap, M. (2011). Biodiesel: Quality, emissions and by-products. Rijeka: Ed. Intec.
Randazzo, M. L., & Sodre, J. R. (2011). Exhaust emissions from a diesel powered vehicle fuelled by soybean biodiesel blends (B3–B20) with ethanol as an additive (B20E2–B20E5). Fuel, 90, 98–103.
Webster, J. (1999). The measurement instrumentation and sensor handbook. Piscataway: IEEE Press.
Zhu, L., Cheung, Z., & Huang, Z. (2011). Combustion performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with ethanol-biodiesel blend. Fuel, 90, 1743–1750.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, V.P., Achy, A.R.A., Pepe, I.M. et al. A New Electronic Ethanol Injection Management System for Diesel Engines. J Control Autom Electr Syst 25, 566–575 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-014-0132-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-014-0132-8