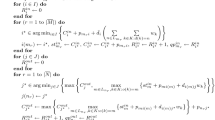Abstract
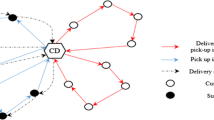
Cross-docking is a logistic strategy that can transport goods directly from suppliers or manufacturers to retailers or customers. In daily life, the requirements for timeliness of goods distribution have been continuously improved. Cross-docking can realize the rapid transshipment of goods and improve the process efficiency of distribution greatly. Meanwhile, during the cross-docking process, goods are deposited in the temporary storage area, which reduces the storage cost. This paper focuses on the analysis of reasonable vehicle scheduling and dock door allocation problems in cross-docking. The goal is to minimize the working time of cross-docks by the research on this combinatorial optimization problem. This paper proposes the genetic algorithm (GA) and the hybrid particle swarm optimization to solve the three-scale (small, medium and large) cross-docks. Optimal completion time, average completion time and average solution time are considered as factors to evaluate the efficiency of two algorithms on three scales. And then the concept of mixed-mode dock door is introduced. GA is used to conduct numerical experiments with mixed dock doors on different scales. Finally, by comparing the utilization rate of mixed dock doors, we can analyze the influence of mixed dock door on vehicles’ waiting time.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhen, L., Chew, E.P., Lee, L.H.: An integrated model for berth template and yard template planning in transshipment hubs. Transp. Sci. 45, 483–504 (2011)
Zhen, L.: Modeling of yard congestion and optimization of yard template in container ports. Transp. Res. Part B 90, 83–104 (2016)
Zhen, L.: Tactical berth allocation under uncertainty. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 247, 928–944 (2015)
Dondo, R., Cerdá, J.: A monolithic approach to vehicle routing and operations scheduling of a cross-dock system with multiple dock doors. Comput. Chem. Eng. 63, 184–205 (2014)
Bao, H.S., Wu, B., Dong, M.: Cross-docking scheduling problem based on fruit fly drosophila optimization algorithm. Comput. Eng. Des. 37, 3295–3298 (2016)
Samir, T., Abdessamad, C., Aziz, S.: Bio-Inspired routing control in a ‘smart-cross-dock’: simulation approach. IFAC Pap. 50, 2266–2271 (2017)
Philippe, G., Michel, G., Fabien, L.: A heuristic based on large neighborhood search for the vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. Comput. Oper. Res. 84, 116–126 (2017)
Guemri, O., Nduwayo, P., Todosijević, R., Hanafi, S., Glover, F.: Probabilistic tabu search for the cross-docking assignment problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 277, 875–885 (2019)
Qiang, R., Miu, C.W.: Research on the distribution of warehouse ports in the transit center of supply network. J. Manag. Eng. 25, 209–215 (2011)
Qiu, J.R.: Two-stage material delivery in cross-docking and heuristic algorithm. Mech. Eng. 9, 17–19 (2016)
Miao, Z.W., Zhang, J., Lan, Y.Q., Su, R.Z.: A two-stage genetic algorithm for the truck-door assignment problem with limited capacity vehicles and storage area. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 28, 285–298 (2019)
Li, X., Sun, J., Chen, X.: Research on three-stage cross-docking vehicle sequencing and algorithm. Logist. Technol. 47, 113–116 (2018)
Cóccola, M., Méndez, C.A., Dondo, R.G.: A branch-and-price approach to evaluate the role of cross-docking operations in consolidated supply chains. Comput. Chem. Eng. 80, 15–29 (2015)
Peter, B., Rene, K., Kaveh, A.: Scheduling trucks in a cross-dock with mixed service mode dock doors. Transp. Sci. 51, 112–131 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Tang, RY., MuRong, LW. et al. Collaborative Optimization of Dock Door Assignment and Vehicle Scheduling in Cross-Docking. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China 8, 493–514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40305-019-00266-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40305-019-00266-9