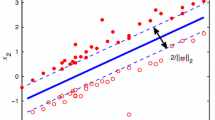
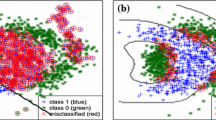
Abstract
Logistic regression has been proved as a promising method for machine learning, which focuses on the problem of classification. In this paper, we present an \(\ell _{1}\hbox {-}\ell _{2}\)-regularized logistic regression model, where the \(\ell _{1}\)-norm is responsible for yielding a sparse logistic regression classifier and the \(\ell _{2}\)-norm for keeping better classification accuracy. To solve the \(\ell _{1}\hbox {-}\ell _{2}\)-regularized logistic regression model, we develop an alternating direction method of multipliers with embedding limited-Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno (L-BFGS) method. Furthermore, we implement our model for binary classification problems by using real data examples selected from the University of California, Irvine Machines Learning Repository (UCI Repository). We compare our numerical results with those obtained by the well-known LIBSVM and SVM-Light software. The numerical results show that our \(\ell _{1}\hbox {-}\ell _{2}\)-regularized logistic regression model achieves better classification and less CPU Time.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neumaier, A.: Solving ill-conditioned and singular linear systems: a tutorial on regularization. SIAM Rev. 40(3), 636–666 (1998)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer, New York (2006)
Bai, Y.Q., Zhu, Z.Y., Yan, W.L.: Sparse proximal support vector machine with a specialized interior-point method. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China. 3(1), 1–15 (2015)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theo. 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
Epifanio, B., Takio, K., Masakatsu, H.: Adapting SVM image classifiers to changes in imaging conditions using incremental svm: an application to car detection. Computer Vision-AACV (2009)
Liang, Y., Liu, C., Xu, Z.B.: Sparse logistic regression with a \({L}_{\frac{1}{2}}\) penalty for gene selection in cancer classification. BMC Bioinform. (2013). doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-198
Bai, Y.Q., Niu, B.L., Chen, Y.: New sdp models for protein homology detection with semi-supervised (svm). Optimization 62(4), 561–572 (2013)
Bai, Y.Q., Han, X., Chen, T., Yu, H.: Quadratic kernel-free least squares support vector machine for target diseases classification. J. Comb. Optim., doi:10.1007/s10878-015-9848-z
Bai, Y.Q., Shen, Y.J., Shen, K.J.: Consensus proximal support vector machine for classification problems with sparse solutions. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China. 2(1), 57–74 (2014)
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, New York (2004)
Zou, H., Hastie, T.: Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. 67, 301–320 (2005)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E.: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 3(1), 1–122 (2011)
Bazaraa, M.S., Sherali, H.D., Shetty, C.M.: Nonlinear Programming: Theory and Algorithms. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New Jersey (2006)
Chang, C.C., Lin, C.J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/ (2014)
Joachims, T.: SVM-Light support vector machine. http://svmlight.joachims.org/svm_perf.html (2009)
Minka, T.P.: A comparison of numerical optimizers for logistic regression. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.85.7017rep=rep1type=pdf (2013)
Eckstein, J., Bertsekas, D.P.: On the Douglasrachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math. Program. 55(1–3), 293–318 (1992)
Eckstein, J., Ferris, M.C.: Operator-splitting methods for monotone affine variational inequalities, with a parallel application to optimal control. INFORMS J. Comput. 10(2), 218–235 (1998)
Asuncion, A., Newman, D.: UCI machine learning repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11371242).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, YQ., Shen, KJ. Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers for \(\ell _{1}\hbox {-}\ell _{2}\)-Regularized Logistic Regression Model. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China 4, 243–253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40305-015-0090-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40305-015-0090-2
Keywords
- Classification problems
- Logistic regression model
- Sparsity
- Alternating direction method of multipliers