Abstract
Background
BCR-ABL1/ABL1 p210 measurement by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) is used worldwide to monitor the molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients. Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) seems to show a greater sensitivity than qPCR, probably due to the high number of replicates analyzed in ddPCR for the comparison. Additionally, in a recently published comparison, ddPCR measurements were not adequately transformed into International Scale (IS).
Method
We have analyzed 50 CML patients and ten non-CML donors in parallel by qPCR and ddPCR. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparing both techniques under similar conditions, with BCR-ABL1/ABL1 measurements performed via both techniques transformed into IS.
Results
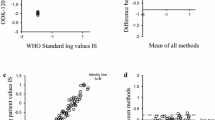
Qualitative and quantitative comparisons showed excellent results. The qualitative correlation showed a Kappa index of 0.94 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.90–0.98) (P < 0.001). In the quantitative comparison, the absolute intra-class correlation coefficient was 0.868 (95% CI 0.734–0.937; P < 0.001), and Lin’s concordance correlation coefficient was 0.863. The Passing-Bablock test indicated a slight proportional difference between qPCR and ddPCR. A quantitative and qualitative subanalysis including 40 patients with a molecular response of 3.0 or deeper showed similar results in every test. In addition, the proportional difference in the Passing-Bablock test disappeared. There were no differences in the sensitivity for BCR-ABL1 detection between qPCR and ddPCR (McNemar test, P = 0.5).
Conclusions
In conclusion, our results show very good quantitative and qualitative correlations between BCR-ABL1/ABL1 p210 results obtained by qPCR and by ddPCR and confirm previous scarce data regarding the lack of an increase in sensitivity of ddPCR over qPCR in this setting.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chereda B, Melo JV. Natural course and biology of CML. Ann Hematol. 2015;94(Suppl 2):S107–21.
Apperley JF. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet Lond Engl. 2015;385:1447–59.
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–17.
Branford S, Fletcher L, Cross NCP, Müller MC, Hochhaus A, Kim D-W, et al. Desirable performance characteristics for BCR-ABL measurement on an international reporting scale to allow consistent interpretation of individual patient response and comparison of response rates between clinical trials. Blood. 2008;112:3330–8.
White HE, Matejtschuk P, Rigsby P, Gabert J, Lin F, Lynn Wang Y, et al. Establishment of the first World Health Organization International Genetic Reference Panel for quantitation of BCR-ABL mRNA. Blood. 2010;116:e111–7.
Cross NCP, White HE, Ernst T, Welden L, Dietz C, Saglio G, et al. Development and evaluation of a secondary reference panel for BCR-ABL1 quantification on the International Scale. Leukemia. 2016;30:1844–52.
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 2013;122:872–84.
Cross NCP, Hochhaus A, Müller MC. Molecular monitoring of chronic myeloid leukemia: principles and interlaboratory standardization. Ann Hematol. 2015;94(Suppl 2):S219–25.
Bizouarn F. Introduction to digital PCR. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2014;1160:27–41.
Morley AA. Digital PCR: a brief history. Biomol Detect Quantif. 2014;1:1–2.
White RA, Blainey PC, Fan HC, Quake SR. Digital PCR provides sensitive and absolute calibration for high throughput sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:116.
Jennings LJ, George D, Czech J, Yu M, Joseph L. Detection and quantification of BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts by droplet digital PCR. J Mol Diagn JMD. 2014;16:174–9.
Maier J, Lange T, Cross M, Wildenberger K, Niederwieser D, Franke G-N. Optimized digital droplet PCR for BCR-ABL. J Mol Diagn JMD. 2019;21:27–37.
Wang W-J, Zheng C-F, Liu Z, Tan Y-H, Chen X-H, Zhao B-L, et al. Droplet digital PCR for BCR/ABL(P210) detection of chronic myeloid leukemia: a high sensitive method of the minimal residual disease and disease progression. Eur J Haematol. 2018;101:291–6.
Alikian M, Whale AS, Akiki S, Piechocki K, Torrado C, Myint T, et al. RT-qPCR and RT-digital PCR: a comparison of different platforms for the evaluation of residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Chem. 2017;63:525–31.
Coccaro N, Anelli L, Zagaria A, Casieri P, Tota G, Orsini P, et al. Droplet digital PCR is a robust tool for monitoring minimal residual disease in adult Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Mol Diagn JMD. 2018;20:474–82.
Kjaer L, Skov V, Andersen MT, Aggerholm A, Clair P, Gniot M, et al. Variant-specific discrepancy when quantitating BCR-ABL1 e13a2 and e14a2 transcripts using the Europe Against Cancer qPCR assay. Eur J Haematol. 2019;103:26–34.
Franke G-N, Maier J, Wildenberger K, Cross M, Giles FJ, Muller MC, et al. Comparison of real-time quantitative PCR and digital droplet PCR for BCR-ABL1 monitoring in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. J Mol Diagn JMD. United States. 2020;22:81–9.
Delgado Rodríguez Miguel, Llorca Díaz Javier DMJM. Estudios para pruebas diagnósticas y factores pronósticos. Signo, editor. Barcelona; 2012.
Chung HJ, Hur M, Yoon S, Hwang K, Lim HS, Kim H, et al. Performance evaluation of the QXDx BCR-ABL %IS droplet digital PCR assay. Ann Lab Med. 2020;40:72–5.
Yan Z, Sun Q, Zhang H, Han Y, Qiao J, Niu M, et al. Advantages of digital PCR in the detection of low abundance BCR-ABL1 gene in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncol Lett. 2019;18:5139–44.
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VHJ, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N, et al. Standardization and quality control studies of “real-time” quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia—a Europe Against Cancer program. Leukemia. 2003;17:2318–57.
Beillard E, Pallisgaard N, van der Velden VHJ, Bi W, Dee R, van der Schoot E, et al. Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using “real-time” quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR)—a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia. 2003;17:2474–86.
Cross NCP, White HE, Colomer D, Ehrencrona H, Foroni L, Gottardi E, et al. Laboratory recommendations for scoring deep molecular responses following treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:999–1003.
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 2009;55:611–22.
Huggett JF, Foy CA, Benes V, Emslie K, Garson JA, Haynes R, et al. The digital MIQE guidelines: minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Digital PCR Experiments. Clin Chem. 2013;59:892–902.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res. 1999;8:135–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Incyte S.L.
Conflicts of interest
Juan Manuel Alonso-Dominguez received research funding from Incyte Corporation, Pfizer International and Celgene International. AAR, SO, JSL, DLG, TC, RI, JLLL, AG, MA, RNSS, CBL, MGA, and PLS have no conflicts to declare.
Ethics approval
The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee for Clinical Research of the institution (FJD-HEMPCR-16-01). Informed consent was not required according to the Ethics Committee for Clinical Research of the institution. Samples were collected in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of the current version of this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortés, A.A., Olmedillas, S., Serrano-López, J. et al. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR versus qPCR Measurements on the International Scale for the Molecular Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Mol Diagn Ther 24, 593–600 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-020-00485-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-020-00485-4