Abstract
Objective
The goal of this study was to determine plasma levels of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) in patients with pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH), and to explore the diagnostic value of plasma HGF for PAH.
Methods
Sixty subjects were divided into a control group of healthy individuals (N = 15) and a PAH group (N = 45). The PAH group was divided into three groups (N = 15 each) according to disease severity: mild PAH (group L), moderate PAH (group M), and severe PAH (group H). Plasma HGF levels in PAH patients were collected on the morning after admission to the hospital. Mean pulmonary arterial pressure was measured by right heart catheterization.
Results
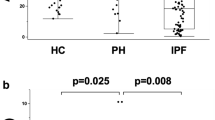
Plasma HGF levels were significantly higher in the PAH group than in the control group (P < 0.001), and significantly higher in group H than in group M (P < 0.001) and group L (P < 0.001). There was no statistically significant difference in plasma HGF levels between patients with PAH of idiopathic etiology and those with PAH of secondary etiology (P = 0.595). The HGF level was positively correlated with mean pulmonary arterial pressure (Pearson correlation coefficient 0.967, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Plasma levels of HGF in PAH patients with mild disease were significantly higher than those in healthy controls, suggesting that plasma HGF has potential utility as a diagnostic biomarker for early PAH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun PM. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2004;109(2):159–65.
McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Circulation. 2009;119(16):2250–94.
Bazan IS, Fares WH. Pulmonary hypertension: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11:1221–33.
Cordier JF, Chabot F, Dromer C, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in France: results from a national registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:1023–30.
Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:34–41.
Kiatchoosakun S, Wongvipaporn C, Nanagara R, Hoit BD. Right ventricular systolic pressure assessed by echocardiography: a predictive factor of mortality in patients with scleroderma. Clin Cardiol. 2011;34:488–93.
Fisher MR, Forfia PR, Chamera E, et al. Accuracy of Doppler echocardiography in the hemodynamic assessment of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:615–21.
Giannakoulas G, Dimopoulos K, Bolger AP, et al. Usefulness of natriuretic peptide levels to predict mortality in adults with congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2010;105:869–73.
Takatsuki S, Wagner BD, Ivy DD. B-type natriuretic peptide and amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in pediatric patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Congenit Heart Dis. 2012;7:259–67.
Dimitri Y, Chirgadze JH, Byrd Andrew, et al. Insights into the structur of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF) and implications for receptor activation. FEBS Lett. 1998;430:126–9.
Ware LB, Matthay MA. Keratinocyte and hepatocyte growth factors in the lung: roles in lung development, inflammation, and repair. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;282(5):924–40.
Yanagita Kimihiko, Matsumoto Kunio, Sekiguchin Kiyoshi, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor may act as a pulmotrophic factor on lung regeneration after acute lung injury. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:212–7.
Traniyama Y, Morishita R, Aoki M, et al. Therepeutic angiogenesis induced by human hepatocyte growth factor gene in rat and rabbit hindlimb ischemia models preclinical study for treatment of peripheral arterial disease. Gene Ther. 2001;8:181–9.
Michalopoulos GK, Zarnegav R. Hepatocyte growth factor. Hepatology. 1992;15(1):149–55.
Comoglio PM. Structure, biosynthesis and biochemical properties of the HGF receptor in normal and malignant cells. EXS. 1993;65:131–65.
Ono K, Matsumori A, Shioi T, et al. Enhanced expression of hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met by myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in a rat model. Circulation. 1997;95:2552–8.
Ramadori G, Neubauer K, Odenthal M, et al. The gene of hepatocyte growth factor is expressed in fat-storing cells of rat liver and is downregulated during cell growth and by transforming growth factor-beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;183:739–42.
Miyazawa K, Kitamura A, Kitamura N. Structural organization and the transcription ination site of the human hepatocyte growth factor gene. Biochemistry. 1991;30:9170–6.
Price LC, Caramori G, Perros F, et al. Nuclear factor κ-B is activated in the pulmonary vessels of patients with end-stage idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. PloS One. 2013;8:e75415.
Bigatto V, De Bacco F, Casanova E, et al. TNF-α promotes invasive growth through the MET signaling pathway. Mol Oncol. 2015;9:377–88.
Rychli K, Richter B, Hohensinner PJ, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor is a strong predictor of mortality in patients with advanced heart failure. Heart. 2011;97:1158–63.
Karabulut S, Tas F, Akyüz F, et al. Clinical significance of serum hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) levels in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:2327–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Mingting Liang, Ying Pang, Shuguang Zhang, and Mei Zhang declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Funding
The authors have no funding to declare.
Ethical approval and informed consent
All patients provided informed consent, and the studies were approved by the local ethics committee at Liaocheng City People’s Hospital.
Additional information
M. Liang and Y. Pang contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, M., Pang, Y., Zhang, S. et al. Utility of Hepatocyte Growth Factor as a Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Pulmonary Artery Hypertension. Mol Diagn Ther 20, 463–468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-016-0214-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-016-0214-3