Abstract
Introduction
Mutational analysis of RAS is required for anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). However, most patients with KRAS wild-type tumors still do not respond. Other molecules downstream of the EGFR may also play a role in resistance to EGFR therapies.
Objective
Our objective was to investigate the clinical importance of biomarkers in relation to response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with mCRC receiving first-line treatment with anti-EGFR therapy plus chemotherapy.
Methods
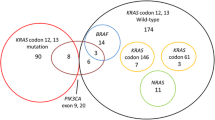
We studied the EGFR pathway [EGFR, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), amphiregulin (AREG), and epiregulin (EREG)] in 105 patients with mCRC KRAS codon 12 wild type. We analysed objective response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in molecularly defined subgroups of the patients receiving anti-EGFR therapy plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment.
Results
We found a significant association between RAS wild-type, BRAF wild-type, EREG, and AREG overexpression and response to anti-EGFR therapy (p = 0.003, p = 0.015, p = 0.05, and p = 0.009, respectively). Progression-free survival and overall survival were lower in patients with RAS (p = 0.36 and p ≤ 0.001, respectively) or BRAF (p = 0.003 and p = 0.002, respectively) mutant tumors. Patients with EREG and AREG messenger RNA (mRNA) expression had longer survival than those with low-expression tumors; progression-free survival and overall survival were significant for AREG (p = 0.001 and p = 0.05, respectively). Patients with EGFR amplification tumors responded better to treatment and had better survival rates, although this was not significant. PIK3CA and PTEN were not associated with either response or survival. The multivariate logistic regression model for response showed only BRAF as a significant predictor after adjustment for the other covariates (p = 0.04, odds ratio 8.3, 95 % confidence interval 0.81–86.0).
Conclusions
RAS, BRAF, AREG, and EREG predict for efficacy of first-line anti-EGFR therapy in patients with mCRC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Cutsem E, Dicato M, Arber N, Berlin J, Cervantes A, Ciardiello F, et al. Molecular markers and biological targeted therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer: expert opinion and recommendations derived from the 11th ESMO/world congress on gastrointestinal cancer, Barcelona, 2009. Ann. Oncol. 2010;21:vi1–10.
Allegra CJ, Jessup JM, Somerfield MR, Hamilton SR, Hammond EH, Hayes DF, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion: testing for KRAS gene mutations in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma to predict response to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2091–6.
Douillard J-Y, Siena S, Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, et al. Randomized, phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: the PRIME study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4697–705.
Van Cutsem E, Köhne C-H, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien C-R, Makhson A, et al. Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1408–17.
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Hartmann JT, de Braud F, Schuch G, Zubel A, et al. Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the OPUS study. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1535–46.
Schwartzberg L, Rivera F, Karthaus M, Fasola G, Canon JL, Yu H, et al. Analysis of KRAS/NRAS mutations in PEAK: a randomized phase II study of FOLFOX6 plus panitumumab (pmab) or bevacizumab (bev) as first-line treatment (tx) for wild-type (WT) KRAS (exon 2) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J Clin Oncol. 2013;31 (suppl 15); ASCO Annual meeting abstr 3631.
Stintzing S, Jung A, Rossius L, Modest D, Fischer von Weikersthal L, Decker T, et al. Analysis of KRAS/NRAS and BRAF mutations in FIRE-3: a randomized phase III study of FOLFIRI plus cetuximab or bevacizumab as first-line treatment for wild type (WT) KRAS (exon 2) metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Eur Cancer Congr. 2013:49 (suppl 3); ESMO abstract LBA17.
Douillard J-Y, Oliner KS, Siena S, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1023–34.
Bokemeyer C, Khone C, Ciardiello F, Lenz HJ, Heinemann V, Klinkhardt U, et al. Treatment outcome according to tumor RAS mutation status in OPUS study patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) randomized to FOLFOX4 with/without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:5s [2014 (suppl; abstr 3505)]..
Ciardiello F, Lenz HJ, Khone CH, Heinemann V, Tejpar S, Melezinek I, et al. Treatment outcome according to tumor RAS mutation status in CRYSTAL study patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) randomized to FOLFIRI with/without cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:5s [2014 (suppl; abstr 3506)].
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:753–62.
Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Nichelatti M, Molinari F, De Dosso S, Saletti P, et al. Multi-determinants analysis of molecular alterations for predicting clinical benefit to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies in colorectal cancer. PloS One. 2009;4:e7287.
Saridaki Z, Tzardi M, Papadaki C, Sfakianaki M, Pega F, Kalikaki A, et al. Impact of KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA mutations, PTEN, AREG, EREG expression and skin rash in ≥2 line cetuximab-based therapy of colorectal cancer patients. PloS One. 2011;6:e15980.
Mao C, Zhou J, Yang Z, Huang Y, Wu X, Shen H, et al. KRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA Mutations and the Loss of PTEN Expression in Chinese Patients with Colorectal Cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36653.
Yang Z-Y, Wu X-Y, Huang Y-F, Di M-Y, Zheng D-Y, Chen J-Z, et al. Promising biomarkers for predicting the outcomes of patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(8):1914–25.
Jacobs B, Roock WD, Piessevaux H, Oirbeek RV, Biesmans B, Schutter JD, et al. Amphiregulin and epiregulin mRNA expression in primary tumors predicts outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5068–74.
Khambata-Ford S, Garrett CR, Meropol NJ, Basik M, Harbison CT, Wu S, et al. Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and K-ras mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3230–7.
Kuramochi H, Nakajima G, Kaneko Y, Nakamura A, Inoue Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Amphiregulin and Epiregulin mRNA expression in primary colorectal cancer and corresponding liver metastases. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:88.
Baker JB, Dutta D, Watson D, Maddala T, Munneke BM, Shak S, et al. Tumour gene expression predicts response to cetuximab in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;104:488–95.
Moroni M, Veronese S, Benvenuti S, Marrapese G, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, et al. Gene copy number for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and clinical response to antiEGFR treatment in colorectal cancer: a cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:279–86.
Laurent-Puig P, Cayre A, Manceau G, Buc E, Bachet J-B, Lecomte T, et al. Analysis of PTEN, BRAF, and EGFR status in determining benefit from cetuximab therapy in wild-type KRAS metastatic colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5924–30.
Sartore-Bianchi A, Moroni M, Veronese S, Carnaghi C, Bajetta E, Luppi G, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number and clinical outcome of metastatic colorectal cancer treated with panitumumab. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3238–45.
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, et al. Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5705–12.
Loupakis F, Pollina L, Stasi I, Ruzzo A, Scartozzi M, Santini D, et al. PTEN expression and KRAS mutations on primary tumors and metastases in the prediction of benefit from cetuximab plus irinotecan for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2622–9.
Bokemeyer C, Van Cutsem E, Rougier P, Ciardiello F, Heeger S, Schlichting M, et al. Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:1466–75.
Souglakos J, Philips J, Wang R, Marwah S, Silver M, Tzardi M, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of common mutations for treatment response and survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:465–72.
Sartore-Bianchi A, Martini M, Molinari F, Veronese S, Nichelatti M, Artale S, et al. PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 2009;69:1851–7.
Bardelli A, Siena S. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1254–61.
Perrone F, Lampis A, Orsenigo M, Di Bartolomeo M, Gevorgyan A, Losa M, et al. PI3KCA/PTEN deregulation contributes to impaired responses to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:84–90.
Phipps AI, Buchanan DD, Makar KW, Burnett-Hartman AN, Coghill AE, Passarelli MN, et al. BRAF mutation status and survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis according to patient and tumor characteristics. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012;21:1792–8.
Van Cutsem E, Köhne C-H, Láng I, Folprecht G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, et al. Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2011–9.
Mao C, Liao R-Y, Qiu L-X, Wang X-W, Ding H, Chen Q. BRAF V600E mutation and resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:2219–23.
Prenen H, Schutter JD, Jacobs B, Roock WD, Biesmans B, Claes B, et al. PIK3CA mutations are not a major determinant of resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:3184–8.
Huang L, Liu Z, Deng D, Tan A, Liao M, Mo Z, et al. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody-based therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the effect of PIK3CA mutations in KRAS wild-type patients. Arch Med Sci AMS. 2014;10:1–9.
Jonker DJ, Karapetis CS, Harbison C, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Simes RJ, et al. Epiregulin gene expression as a biomarker of benefit from cetuximab in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(3):648–55.
Karapetis CS, Jonker D, Daneshmand M, Hanson JE, O’Callaghan CJ, Marginean C, et al. PIK3CA, BRAF, and PTEN Status and benefit from cetuximab in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer-results from NCIC CTG/AGITG CO.17. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:744–53.
Custodio A, Feliu J. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers for epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy in colorectal cancer: beyond KRAS mutations. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013;85:45–81.
Romero A, Martín M, Cheang MCU, López García-Asenjo JA, Oliva B, He X, et al. Assessment of Topoisomerase II α status in breast cancer by quantitative PCR, gene expression microarrays, immunohistochemistry, and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:1453–60.
Frattini M, Saletti P, Romagnani E, Martin V, Molinari F, Ghisletta M, et al. PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2007;97:1139–45.
Lièvre A, Bachet J-B, Boige V, Cayre A, Le Corre D, Buc E, et al. KRAS mutations as an independent prognostic factor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:374–9.
De Roock W, De Vriendt V, Normanno N, Ciardiello F, Tejpar S. KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, and PTEN mutations: implications for targeted therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:594–603.
Richman SD, Seymour MT, Chambers P, Elliott F, Daly CL, Meade AM, et al. KRAS and BRAF mutations in advanced colorectal cancer are associated with poor prognosis but do not preclude benefit from oxaliplatin or irinotecan: results from the MRC FOCUS trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5931–7.
Yokota T. Are KRAS/BRAF mutations potent prognostic and/or predictive biomarkers in colorectal cancers? Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012;12:163–71.
Seymour MT, Brown SR, Middleton G, Maughan T, Richman S, Gwyther S, et al. Panitumumab and irinotecan versus irinotecan alone for patients with KRAS wild-type, fluorouracil-resistant advanced colorectal cancer (PICCOLO): a prospectively stratified randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:749–59.
Yuan Z-X, Wang X-Y, Qin Q-Y, Chen D-F, Zhong Q-H, Wang L, et al. The prognostic role of BRAF mutation in metastatic colorectal cancer receiving anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: a meta-analysis. PloS One. 2013;8:e65995.
Lièvre A, Bachet J-B, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile J-F, et al. KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3992–5.
Tural D, Batur S, Erdamar S, Akar E, Kepil N, Mandel NM, et al. Analysis of PTEN, BRAF and PI3K status for determination of benefit from cetuximab therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients refractory to chemotherapy with wild-type KRAS. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:1041–9.
Cappuzzo F, Finocchiaro G, Rossi E, Jänne PA, Carnaghi C, Calandri C, et al. EGFR FISH assay predicts for response to cetuximab in chemotherapy refractory colorectal cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:717–23.
Scartozzi M, Bearzi I, Mandolesi A, Pierantoni C, Loupakis F, Zaniboni A, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) gene copy number (GCN) correlates with clinical activity of irinotecan-cetuximab in K-RAS wild-type colorectal cancer: a fluorescence in situ (FISH) and chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) analysis. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:303.
Personeni N, Fieuws S, Piessevaux H, De Hertogh G, De Schutter J, Biesmans B, et al. Clinical usefulness of EGFR gene copy number as a predictive marker in colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab: a fluorescent in situ hybridization study. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5869–76.
Yang Z-Y, Shen W-X, Hu X-F, Zheng D-Y, Wu X-Y, Huang Y-F, et al. EGFR gene copy number as a predictive biomarker for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: a meta-analysis. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:52.
Pentheroudakis G, Kotoula V, De Roock W, Kouvatseas G, Papakostas P, Makatsoris T, et al. Biomarkers of benefit from cetuximab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: interaction of EGFR ligand expression with RAS/RAF, PIK3CA genotypes. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
JS, JSO, TC, ED-R, AC and EA belong to Centres affiliated to the Red Tematica de Investigacion Cooperativa (RD12/0036/006, RD12/0036/0038/, RD12/0036/0073), Instituto Carlos III, Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitivity, Madrid, Spain.
Conflict of interest
All authors state they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and informed consent
Ethical approval was received from the Comité ético de investigación Clínica Hospital Clínico San Carlos (CEIC), E-09/124.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llovet, P., Sastre, J., Ortega, J.S. et al. Prognostic Value of BRAF, PI3K, PTEN, EGFR Copy Number, Amphiregulin and Epiregulin Status in Patients with KRAS Codon 12 Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Receiving First-Line Chemotherapy with Anti-EGFR Therapy. Mol Diagn Ther 19, 397–408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-015-0165-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-015-0165-0