Abstract
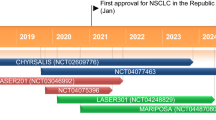
Furmonertinib mesylate (hereafter furmonertinib) [Ivesa®] is a selective epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) being developed by Allist Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In March 2021, furmonertinib received its first approval in China for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with confirmed EGFR T790M mutation whose disease has progressed during or after EGFR TKI therapy. Furmonertinib (as monotherapy and/or combination therapy) continues to be assessed in phase I/II and phase III trials for NSCLC with EGFR mutation in China, and its clinical development is also underway/planned in China and elsewhere for NSCLC with various EGFR mutations. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of furmonertinib leading to this first approval for EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee SM. Is EGFR expression important in non-small cell lung cancer? Thorax. 2006;61(2):98–9.
Pacini L, Jenks AD, Vyse S, et al. Tackling drug resistance in EGFR exon 20 insertion mutant lung cancer. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021;14:301–17.
Khaddour K, Jonna S, Deneka A, et al. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in EGFR-mutated lung cancer: current and emerging therapies. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(13):3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133164.
Le T, Gerber DE. Newer-generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer: how are they best used? Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(3):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030366.
National Medical Products Administration. The State Food and Drug Administration has conditionally approved the listing of vometinib mesylate tablets. 2021. https://www.nmpa.gov.cn. Accessed 3 Aug 2021.
Shanghai Allist Pharmaceutical Technology Co Ltd. Furmonertinib mesilate: Chinese prescribing information. Shanghai: Shanghai Allist Pharmaceutical Technology Co Ltd; 2021.
Hogan Lovells. The China Food and Drug Administration pushes forward on conditional approval and compassionate use of new drugs. 2018. https://www.engage.hoganlovells.com/knowledgeservices/news/the-china-food-and-drug-administration-pushes-forward-on-conditional-approval-and-compassionate-use-of-new-drugs. Accessed 3 Aug 2021.
ArriVent Biopharma. ArriVent Biopharma launches with up to $150M in Series A financing and strategic licensing agreement for clinical-stage oncology asset [media release]. 30 June 2021. https://www.arrivent.com.
Liu X, Li W, Zhang Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of alflutinib and its active metabolite in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019;176: 112735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.06.032.
Zhu S, Deng J, Tang Q, et al. A randomized, open, single-centre, crossed study of the effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of one oral dose of alflutinib mesylate tablets (AST2818) in healthy male subjects. Iranian J Pharm Res. 2020;19(3):24–33.
Liu XY, Guo ZT, Chen ZD, et al. Alflutinib (AST2818), primarily metabolized by CYP3A4, is a potent CYP3A4 inducer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(10):1366–76.
Meng J, Zhang H, Bao JJ, et al. Metabolic disposition of the EGFR covalent inhibitor furmonertinib in humans. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00667-8.
Heng J, Tang Q, Chen X, et al. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetic effects of itraconazole on alflutinib (AST2818): an open-label, single-center, single-sequence, two-period randomized study in healthy volunteers. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;162: 105815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2021.105815.
Zhu YT, Zhang YF, Jiang JF, et al. Effects of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of alflutinib, a selective third-generation EGFR kinase inhibitor, and its metabolite AST5902 in healthy volunteers. Invest New Drugs. 2021;39(4):1011–8.
Wu YL, Xue YR, Guo ZT, et al. Furmonertinib (alflutinib, AST2818) is a potential positive control drug comparable to rifampin for evaluation of CYP3A4 induction in sandwich-cultured primary human hepatocytes. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00692-7.
Shi Y, Hu X, Zhang S, et al. Efficacy, safety, and genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2b, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;26:1–11.
Shi Y, Zhang S, Hu X, et al. Safety, clinical activity and pharmacokinetics of alflutinib (AST2818) in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR T790M mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15(6):1015–26.
Shi Y, Hu X, Liao W, et al. CNS efficacy of AST2818 in patients with T790M-positive advanced NSCLC: data from a phase I-II dose-expansion study [abstract no. P76.65]. J Thoracic Oncol. 2021;16(3 Suppl):S616.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Emma Deeks is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deeks, E.D. Furmonertinib: First Approval. Drugs 81, 1775–1780 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01588-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01588-w