Abstract
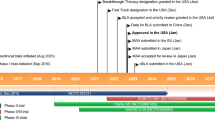
Melphalan flufenamide (melflufen, Pepaxto®) is a peptide conjugated alkylating drug developed by Oncopeptides for the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM) and amyloid light-chain amyloidosis. It is an ethyl ester of a lipophilic dipeptide consisting of melphalan and para-fluoro-l-phenylalanine. Due to its lipophilicity, melphalan flufenamide is rapidly transported across the cell membrane and almost immediately hydrolyzed by aminopeptidases in the cytoplasm to yield more hydrophilic alkylating molecules, such as melphalan and desethyl-melflufen. Like other nitrogen mustard drugs, melphalan flufenamide exerts antitumor activity through DNA crosslinking. In February 2021, melphalan flufenamide, in combination with dexamethasone, received its first approval in the USA for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory (r/r) MM who have received at least four prior lines of therapy and whose disease is refractory to at least one proteasome inhibitor (PI), one immunomodulatory agent, and one CD38-directed monoclonal antibody. A multinational clinical study of melphalan flufenamide in amyloid light-chain amyloidosis is underway across several countries, and preclinical studies for various haematological and solid cancers are underway. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of melphalan flufenamide leading to this first approval.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richardson PG. Melflufen-a novel agent in the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. US Oncol Hematol Rev. 2020;16(1):12–4.
Mateos MV, Bladé J, Bringhen S, et al. Melflufen: a peptide-drug conjugate for the treatment of multiple myeloma. J Clin Med. 2020;9(10):1–16.
Hitzerd SM, Verbrugge SE, Ossenkoppele G, et al. Positioning of aminopeptidase inhibitors in next generation cancer therapy. Amino Acids. 2014;46(4):793–808.
Nanus DM. Of peptides and peptidases: the role of cell surface peptidases in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(17):6307–9.
Lehmann F, Wennerberg J. Evolution of nitrogen-based alkylating anticancer agents. Processes. 2021;9(377):1–10.
Wickström M, Nygren P, Larsson R, et al. Melflufen: a peptidase-potentiated alkylating agent in clinical trials. Oncotarget. 2017;8(39):66641–55.
Miettinen JJ, Kumari R, Traustadottir GA, et al. Aminopeptidase expression in multiple myeloma associates with disease progression and sensitivity to melflufen. Cancers (Basel). 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071527.
US Food & Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to melphalan flufenamide for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma [media release]. 26 Feb 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-melphalan-flufenamide-relapsed-or-refractory-multiple-myeloma.
Oncopeptides AB. PEPAXTO® (melphalan flufenamide): US prescribing information. 2021. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/214383s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2021.
Berglund Å, Ullén A, Lisyanskaya A, et al. First-in-human, phase I/IIa clinical study of the peptidase potentiated alkylator melflufen administered every three weeks to patients with advanced solid tumor malignancies. Invest New Drugs. 2015;33(6):1232–41.
Gullbo J, Wickström M, Tullberg M, et al. Activity of hydrolytic enzymes in tumour cells is a determinant for anti-tumour efficacy of the melphalan containing prodrug J1. J Drug Target. 2003;11(6):355–63.
Wickstrom M, Viktorsson K, Lundholm L, et al. The alkylating prodrug J1 can be activated by aminopeptidase N, leading to a possible target directed release of melphalan. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79(9):1281–90.
Chauhan D, Ray A, Viktorsson K, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of a novel alkylating agent, melphalan-flufenamide, against multiple myeloma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(11):3019–31.
Delforoush M, Strese S, Wickström M, et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of melflufen (J1)in lymphoma. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:263.
Strese S, Hassan SB, Velander E, et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-leukemic activity of the peptidase-potentiated alkylator melflufen in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 2017;8(4):6341–52.
Slipicevic A, Munawar U, Stuhmer T, et al. Melflufen efficacy in multiple myeloma with TP53 aberrations. Cancer Res. 2020;80(16 Suppl):2.
Flanagan K, Majumder MM, Kumari R, et al. In vitro and invivo activity of melflufen in amyloidosis. Blood. 2019;134(Suppl 1):6.
Schepsky A, Traustadottir GA, Joelsson JP, et al. Melflufen, a peptide-conjugated alkylator, is an efficient anti-neo-plastic drug in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Med. 2020;9(18):6726–38.
Byrgazov K, Besse L, Kraus M, et al. Melflufen is a highly effective antineoplastic agent in bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma models [abstract no. EP915]. HemaSphere. 2020;4(Suppl 1):412–3.
Richardson PG, Oriol A, Larocca A, et al. Melflufen and dexamethasone in heavily pretreated relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(7):757–67.
Richardson PG, Bringhen S, Voorhees P, et al. Melflufen plus dexamethasone in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (O-12-M1): a multicentre, international, open-label, phase 1–2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(5):e395–407.
Bringhen S, Voorhees PM, Plesner T, et al. Melflufen plus dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: long-term survival follow-up from the phase II study O-12-M1. Br J Haematol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17302.
Ocio EM, Efebera YA, Hajek R, et al. ANCHOR (OP-104): Melflufen plus dexamethasone (dex) and daratumumab (dara) or bortezomib (BTZ) in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) refractory to an IMiD and/or a proteasome inhibitor (PI): updated efficacy and safety [abstract no. 417]. Blood. 2020;136(Suppl 1):9–10.
Schjesvold F, Robak P, Pour L, et al. OCEAN: a randomized Phase III study of melflufen + dexamethasone to treat relapsed refractory multiple myeloma. Future Oncol. 2020;16(11):631–41.
Mateos MV, Ocio EM, Sonneveld P, et al. Lighthouse (OP-108): a phase 3 study of melflufen in combination with daratumumab versus daratumumab in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma [abstract no. PB2018]. HemaSphere. 2020;4(Suppl 1):916.
Palladini G, Schonland SO, Lentzsch S, et al. OP201: A phase 1/2 study of melflufen and dexamethasone in patients with immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Blood. 2019;134(Suppl 1):3163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Sohita Dhillon is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhillon, S. Melphalan Flufenamide (Melflufen): First Approval. Drugs 81, 963–969 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01522-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01522-0