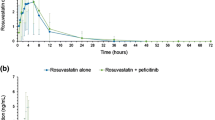
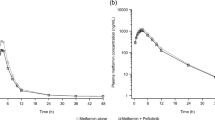
Abstract
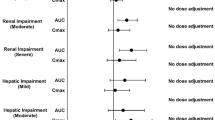
The introduction of novel, small-molecule Janus kinase inhibitors namely tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib has provided an alternative treatment option for patients with rheumatoid arthritis outside of traditional drugs and expensive biologics. This review aimed to critically assess the drug–drug interaction potential of tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib and provide a balanced perspective for choosing the most appropriate Janus kinase inhibitor based on the needs of patients with rheumatoid arthritis including co-medications and renal/hepatic impairment status. Based on the critical assessment, all three approved Janus kinase inhibitors generally provide a favourable opportunity for co-prescription with a plethora of drugs. While cytochrome P450 3A4-related inhibition or induction altered the exposures (area under the curve) of tofacitinib and upadacitinib, it did not impact the exposure of baricitinib. Transporter drug–drug interaction studies revealed that the disposition of baricitinib was altered with certain transporter inhibitors as compared with either tofacitinib or upadacitinib. Adjustment of tofacitinib or baricitinib dosages but not that of upadacitinib is required with the progression of renal impairment from a mild to a severe condition. While the dosage of tofacitinib needs to be adjusted for patients with moderate hepatic impairment status, it is not the case for either baricitinib or upadacitinib. Assessment of the drug–drug interaction potential suggests that tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib generally show a favourable disposition with no perpetrator activity; however, as victim drugs, they show subtle pharmacokinetic differences that may be considered during polypharmacy. Moreover, careful choice of the three drugs could be made in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with varying degrees of renal/hepatic impairments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D, Nossent J, Pavlos NJ, Xu J. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018;6:15.
Klareskog L, Catrina AI, Paget S. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2009;373(9664):659–72.
Zhang JM, An J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2007;45(2):27–37.
Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: strategies, opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(5):276–89.
Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(1):1–26.
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–77.
Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR, Bykerk V, Dougados M, Emery P, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: 2014 update of the recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(1):3–15.
Taylor PC, Moore A, Vasilescu R, Alvir J, Tarallo M. A structured literature review of the burden of illness and unmet needs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a current perspective. Rheumatol Int. 2016;36(5):685–95.
Taylor PC, Abdul Azeez M, Kiriakidis S. Filgotinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017;26(10):1181–7.
Yamanaka H, Seto Y, Tanaka E, Furuya T, Nakajima A, Ikari K, et al. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: the 2012 perspective. Mod Rheumatol. 2013;23(1):1–7.
Vaddi K, Luchi M. JAK inhibition for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a new era in oral DMARD therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012;21(7):961–73.
Schwartz DM, Kanno Y, Villarino A, Ward M, Gadina M, O’Shea JJ. JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(12):843–62.
Magyari L, Varszegi D, Kovesdi E, Sarlos P, Farago B, Javorhazy A, et al. Interleukins and interleukin receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: research, diagnostics and clinical implications. World J Orthop. 2014;5(4):516–36.
Seif F, Khoshmirsafa M, Aazami H, Mohsenzadegan M, Sedighi G, Bahar M. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15(1):23.
Bechman K, Yates M, Galloway JB. The new entries in the therapeutic armamentarium: the small molecule JAK inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. 2019;147:104392.
Krishnaswami S, Boy M, Chow V, Chan G. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of single oral doses of tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2015;4(2):83–8.
Gupta P, Stock TC, Wang R, Alvey C, Choo HW, Krishnaswami S. A phase 1 study to estimate the absolute oral bioavailability of tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;51(9):1348.
CDER. Tofacitinib. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2012/203214Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Xeljanz® package insert. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/203214s018lbl.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Niwa Y, Iio A, Niwa G, Sakane T, Tsunematsu T, Kanoh T. Serum-albumin metabolism in rheumatic diseases: relationship to corticosteroids and peptic-ulcer. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1990;31(1):11–6.
Dowty ME, Lin JY, Ryder TF, Wang WW, Walker GS, Vaz A, et al. The pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and clearance mechanisms of tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(4):759–73.
Dalvie D, Obach RS, Kang P, Prakash C, Loi CM, Hurst S, et al. Assessment of three human in vitro systems in the generation of major human excretory and circulating metabolites. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009;22(2):357–68.
Guo XC, Li W, Li QM, Chen Y, Zhao GD, Peng Y, et al. Tofacitinib is a mechanism-based inactivator of cytochrome P450 3A4. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(9):1791–800.
Veeravalli V, Dash RP. Tofacitinib is a mechanism-based inactivator of cytochrome P450 3A4: revisiting the significance of the epoxide intermediate and glutathione trapping. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020;33(2):281–2.
Abdulrahim H, Sharlala H, Adebajo AO. An evaluation of tofacitinib for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019;20(16):1953–60.
Bannwarth B, Kostine M, Poursac N. A pharmacokinetic and clinical assessment of tofacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Drug Met. 2013;9(6):753–61.
Lamba M, Wang R, Fletcher T, Alvey C, Kushner J, Stock TC. Extended-release once-daily formulation of tofacitinib: evaluation of pharmacokinetics compared with immediate-release tofacitinib and impact of food. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;56(11):1362–71.
Gupta P, Alvey C, Wang R, Dowty ME, Fahmi OA, Walsky RL, et al. Lack of effect of tofacitinib (CP-690,550) on the pharmacokinetics of the CYP3A4 substrate midazolam in healthy volunteers: confirmation of in vitro data. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;74(1):109–15.
Menon S, Riese R, Wang R, Alvey CW, Shi HH, Petit W, et al. Evaluation of the effect of tofacitinib on the pharmacokinetics of oral contraceptive steroids in healthy female volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2016;5(5):336–42.
Cohen SB, Pope J, Haraoui B, Irazoque-Palazuelos F, Korkosz M, Diehl A, et al. Methotrexate withdrawal in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who achieve low disease activity with tofacitinib modified-release 11 mg once daily plus methotrexate: a randomised non-inferiority phase 3B/4 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:260–1.
Gupta P, Chow V, Wang R, Kaplan I, Chan G, Alvey C, et al. Evaluation of the effect of fluconazole and ketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib in healthy adult subjects. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2014;3(1):72–7.
Klamerus KJ, Alvey C, Li L, Feng B, Wang R, Kaplan I, et al. Evaluation of the potential interaction between tofacitinib and drugs that undergo renal tubular secretion using metformin, an in vivo marker of renal organic cation transporter 2. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2014;3(6):499–507.
Xie RJ, Deng CH, Wang Q, Kanik KS, Nicholas T, Menon S. Population pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Int J Clin Pharm Ther. 2019;57(9):464–73.
Ruperto N, Brunner HI, Zuber Z, Tzaribachev N, Kingsbury DJ, Foeldvari I, et al. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of tofacitinib in children with polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis: results of a phase 1, open-label, multicenter study. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2017;15(1):86.
Lawendy N, Lamba M, Chan G, Wang R, Alvey CW, Krishnaswami S. The effect of mild and moderate hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib, an orally active Janus kinase inhibitor. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2014;3(6):421–7.
Krishnaswami S, Chow V, Boy M, Wang C, Chan G. Pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, in patients with impaired renal function and end-stage renal disease. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(1):46–52.
Krishnaswami S, Kudlacz E, Wang R, Chan G. A supratherapeutic dose of the Janus kinase inhibitor tasocitinib (CP-690,550) does not prolong QTc interval in healthy participants. J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;51(9):1256–63.
Shi JG, Chen XJ, Lee F, Emm T, Scherle PA, Lo Y, et al. The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of baricitinib, an oral JAK 1/2 inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(12):1354–61.
Olumiant® package insert. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/207924s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Mogul A, Corsi K, McAuliffe L. Baricitinib: the second FDA-approved JAK inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Pharmacother. 2019;53(9):947–53.
CDER. Baricitinib. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2018/207924Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Payne C, Zhang X, Shahri N, Williams W, Cannady E. AB0492 evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions with baricitinib. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1063.
Markham A. Baricitinib: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77(6):697–704.
Posada MM, Cannady EA, Payne CD, Zhang X, Bacon JA, Pak YA, et al. Prediction of transporter-mediated drug-drug interactions for baricitinib. Clin Transl Sci. 2017;10(6):509–19.
Al-Salama ZT, Scott LJ. Baricitinib: a review in rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs. 2018;78(7):761–72.
Mohamed MEF, Camp HS, Jiang P, Padley RJ, Asatryan A, Othman AA. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of ABT-494, a novel selective JAK 1 inhibitor, in healthy volunteers and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(12):1547–58.
Klunder B, Mittapalli RK, Mohamed MEF, Friedel A, Noertersheuser P, Othman AA. Population pharmacokinetics of upadacitinib using the immediate-release and extended-release formulations in healthy subjects and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis: analyses of phase I–III clinical trials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019;58(8):1045–58.
Klunder B, Mohamed MEF, Othman AA. Population pharmacokinetics of upadacitinib in healthy subjects and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis: analyses of phase I and II clinical trials. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2018;57(8):977–88.
Mohamed MEF, Zeng JW, Jiang P, Hosmane B, Othman AA. Use of early clinical trial data to support thorough QT study waiver for upadacitinib and utility of food effect to demonstrate ECG assay sensitivity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018;103(5):836–42.
Rinvoq® package insert. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/211675s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
CDER. Upadacitinib. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2019/211675Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Mohamed MEF, Trueman S, Feng T, Friedman A, Othman AA. The JAK1 inhibitor upadacitinib has no effect on the pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel and ethinylestradiol: a study in healthy female subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;59(4):510–6.
Zhang H, Cui D, Wang B, Han YH, Balimane P, Yang Z, et al. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions involving 17alpha-ethinylestradiol: a new look at an old drug. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(2):133–57.
Mohamed MEF, Jungerwirth S, Asatryan A, Jiang P, Othman AA. Assessment of effect of CYP3A inhibition, CYP induction, OATP1B inhibition, and high-fat meal on pharmacokinetics of the JAK1 inhibitor upadacitinib. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83(10):2242–8.
Mohamed MEF, Zeng JW, Marroum PJ, Song IH, Othman AA. Pharmacokinetics of upadacitinib with the clinical regimens of the extended-release formulation utilized in rheumatoid arthritis phase 3 trials. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2019;8(2):208–16.
Trueman S, Mohamed MEF, Feng T, Lacerda AP, Marbury T, Othman AA. Characterization of the effect of hepatic impairment on upadacitinib pharmacokinetics. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;59(9):1188–94.
Mohamed MEF, Trueman S, Feng T, Anderson J, Marbury TC, Othman AA. Characterization of the effect of renal impairment on upadacitinib pharmacokinetics. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;59(6):856–62.
Abbasi M, Mousavi MJ, Jamalzehi S, Alimohammadi R, Bezvan MH, Mohammadi H, et al. Strategies toward rheumatoid arthritis therapy; the old and the new. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):10018–31.
Mazouyes A, Clay M, Bernard AC, Gaudin P, Baillet A. Efficacy of triple association methotrexate, sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine in early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with insufficient response to methotrexate: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Jt Bone Spine. 2017;84(5):563–70.
Curtis JR, Singh JA. Use of biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: current and emerging paradigms of care. Clin Ther. 2011;33(6):679–707.
McInnes IB, Byers NL, Higgs RE, Lee J, Macias WL, Na SQ, et al. Comparison of baricitinib, upadacitinib, and tofacitinib mediated regulation of cytokine signaling in human leukocyte subpopulations. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):183.
McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205–19.
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9617):987–97.
Mohamed MEF, Feng T, Enejosa JV, Fisniku O, Othman AA. Effects of upadacitinib coadministration on the pharmacokinetics of sensitive cytochrome P450 probe substrates: a study with the modified cooperstown 5+1 cocktail. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;60(1):86–95.
Giri P, Patel H, Srinivas NR. Use of cocktail probe drugs for indexing cytochrome p450 enzymes in clinical pharmacology studies: review of case studies. Drug Metab Lett. 2019;13(1):3–18.
Lee JS, Kim SH. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib in rats: influence of hepatic and intestinal first-pass metabolism. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(7):318.
Namour F, Desrivot J, Van der Aa A, Harrison P, Tasset C, van’t Klooster G. Clinical confirmation that the selective JAK1 inhibitor filgotinib (GLPG0634) has a low liability for drug-drug interactions. Drug Metab Lett. 2016;10(1):38–48.
Lilly. FDA approves Olumiant® (baricitinib) 2-mg tablets for the treatment of adults with moderately-to-severely active rheumatoid arthritis. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/fda-approves-olumiantr-baricitinib-2-mg-tablets-treatment-adults. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Westhovens R. Clinical efficacy of new JAK inhibitors under development. Just more of the same? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(Suppl 1):i27–i33.
Gilead. Gilead submits filgotinib new drug application to U.S. Food and Drug Administration under priority review for rheumatoid arthritis treatment [press release]. https://www.gilead.com/news-and-press/press-room/press-releases/2019/12/gilead-submits-filgotinib-new-drug-application-to-us-food-and-drug-administration-under-priority-review-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-treatment. Accessed 31 Mar 2020.
Gilead. European Medicines Agency validates marketing application for filgotinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [press release]. https://www.gilead.com/news-and-press/press-room/press-releases/2019/8/european-medicines-agency-validates-marketing-application-for-filgotinib-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis. Accessed 31 Mar 2020.
Gilead. Gilead and Eisai enter into agreement in Japan for the co-promotion of the investigational rheumatoid arthritis therapy filgotinib, pending regulatory approval [press release]. https://www.gilead.com/news-and-press/press-room/press-releases/2019/12/gilead-and-eisai-enter-into-agreement-in-japan-for-the-copromotion-of-the-investigational-rheumatoid-arthritis-therapy-filgotinib-pending-regulatory. Accessed on 31 Mar 2020.
thepharmaletter. Oral JAK inhibitor Smyraf approved in Japan for RA. https://www.thepharmaletter.com/article/oral-jak-inhibitor-smyraf-approved-in-japan-for-ra. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Tanaka S, Kawakami A, Iwasaki M, Song YW, et al. Efficacy and safety of peficitinib (ASP015K) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to conventional DMARDs: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial (RAJ3). Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(10):1320–32.
PMDA. Report on the deliberation results. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000153609.pdf. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
AbbVie. AbbVie receives FDA approval of RINVOQ™ (upadacitinib), an oral JAK inhibitor for the treatment of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. https://news.abbvie.com/news/press-releases/abbvie-receives-fda-approval-rinvoq-upadacitinib-an-oral-jak-inhibitor-for-treatment-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis.htm. Accessed 13 Dec 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation of this article.
Conflict of interest
Vijayabhaskar Veeravalli, Ranjeet P. Dash, Jennifer A. Thomas, R. Jayachandra Babu, Lakshmi Mohan Vamsi Madgula and Nuggehally R. Srinivas have no conflicts of interest or competing interests that are directly relevant to the content of this article. Ranjeet P. Dash is currently an employee of Charles River Laboratories, Ashland, OH, USA.
Data Sharing
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veeravalli, V., Dash, R.P., Thomas, J.A. et al. Critical Assessment of Pharmacokinetic Drug–Drug Interaction Potential of Tofacitinib, Baricitinib and Upadacitinib, the Three Approved Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Drug Saf 43, 711–725 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-020-00938-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-020-00938-z