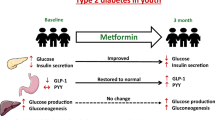
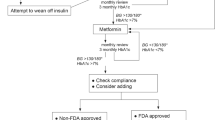
Abstract
The incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) among children and adolescents has been rising. This condition is associated with obesity, and it's prevalence is higher among minority or female youth. Lifestyle modification including diet and exercise is only successful in a small proportion of patients; therefore, pharmacotherapy approaches are needed to treat T2DM among youth. Currently, in the USA, only metformin and insulin are approved for the treatment of T2DM in children. However, several antihyperglycemic agents including exenatide, glimepiride, glyburide, liraglutide, pioglitazone, and rosiglitazone are also used off-label in this population. Moreover, a number of clinical trials are ongoing that are aimed at addressing the safety and efficacy of newer antihyperglycemic agents in this population. Little is known about the safety, efficacy, or pharmacokinetics of antihyperglycemic agents in children or adolescents. Our ability to predict the pharmacokinetics of these agents in youth is hampered first by the lack of information about the expression and activity of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in this population and second by the presence of comorbid conditions such as obesity and fatty liver disease. This article reviews the prevalence of obesity and T2DM in children and adolescents (youth). We then summarize published studies on safety and effectiveness of antihyperglycemic medications in youth. Drug disposition may be affected by age or puberty and thus the expression and activity of different pathways for drug metabolism and xenobiotic transporters are compared between youth and adults followed by a summary of pharmacokinetics studies of antihyperglycemic agents currently used in this population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenbloom AL, Joe JR, Young RS, Winter WE. Emerging epidemic of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(2):345–54.
Gaylor AS, Condren ME. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in the pediatric population. Pharmacotherapy. 2004;24(7):871–8.
Horta BL, Loret de Mola C, Victora CG. Long-term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104(467):30–7.
Whincup PH, Kaye SJ, Owen CG, Huxley R, Cook DG, Anazawa S, et al. Birth weight and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. JAMA. 2008;300(24):2886–97.
Mayer-Davis EJ. Type 2 diabetes in youth: epidemiology and current research toward prevention and treatment. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(4 Suppl 1):S45–51.
Copeland KC, Silverstein J, Moore KR, Prazar GE, Raymer T, Shiffman RN, et al. Management of newly diagnosed type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):364–82.
Hannon TS, Arslanian SA. The changing face of diabetes in youth: lessons learned from studies of type 2 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1353:113–37.
Society CP. Age limits and adolescents. Paediatr Child Health. 2003;8(9):577–8.
Schober E, Holl RW, Grabert M, Thon A, Rami B, Kapellen T, et al. Diabetes mellitus type 2 in childhood and adolescence in Germany and parts of Austria. Eur J Pediatrics. 2005;164(11):705–7.
May AL, Kuklina EV, Yoon PW. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors among US adolescents, 1999–2008. Pediatrics. 2012;129(6):1035–41.
Dabelea D, Bell RA, D’Agostino RB Jr, Imperatore G, Johansen JM, Linder B, et al. Incidence of diabetes in youth in the United States. JAMA. 2007;297(24):2716–24.
SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group, Liese AD, D’Agostino RB Jr, Hamman RF, Kilgo PD, Lawrence JM, et al. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics. 2006;118(4):1510–8.
Rotteveel J, Belksma EJ, Renders CM, Hirasing RA, Delemarre-Van de Waal HA. Type 2 diabetes in children in the Netherlands: the need for diagnostic protocols. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;157(2):175–80.
Fagot-Campagna A, Pettitt DJ, Engelgau MM, Burrows NR, Geiss LS, Valdez R, et al. Type 2 diabetes among North adolescents: an epidemiologic health perspective. J Pediatr. 2000;136(5):664–72.
Sinha R, Fisch G, Teague B, Tamborlane WV, Banyas B, Allen K, et al. Prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance among children and adolescents with marked obesity. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(11):802–10.
Wabitsch M, Hauner H, Hertrampf M, Muche R, Hay B, Mayer H, et al. Type II diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in Caucasian children and adolescents with obesity living in Germany. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(2):307–13.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Lerner-Geva L, Copperman NM, Jacobson MS. Lipid and insulin levels in obese children: changes with age and puberty. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(11):2825–31.
Reinehr T. Clinical presentation of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005;29:S105–10.
Zdravkovic V, Daneman D, Hamilton J. Presentation and course of type 2 diabetes in youth in a large multi-ethnic city. Diabet Med. 2004;21(10):1144–8.
Kiess W, Böttner A, Raile K, Kapellen T, Müller G, Galler A, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents: a review from a European perspective. Horm Res. 2003;59(Suppl. 1):77–84.
Florez JC. The genetics of type 2 diabetes: a realistic appraisal in 2008. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(12):4633–42.
Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(23):2362–74.
Roth CL, Reinehr T. Roles of gastrointestinal and adipose tissue peptides in childhood obesity and changes after weight loss due to lifestyle intervention. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010;164(2):131–8.
Christensen ML, Franklin BE, Momper JD, Reed MD. Pediatric drug development programs for type 2 diabetes: a review. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;55(7):731–8.
Gungor N, Hannon T, Libman I, Bacha F, Arslanian S. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in youth: the complete picture to date. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2005;52(6):1579–609.
American Diabetes Association. Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2000;105(3 Pt 1):671–80.
Copeland KC, Zeitler P, Geffner M, Guandalini C, Higgins J, Hirst K, et al. Characteristics of adolescents and youth with recent-onset type 2 diabetes: the TODAY cohort at baseline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(1):159–67.
Gilliam LK, Brooks-Worrell BM, Palmer JP, Greenbaum CJ, Pihoker C. Autoimmunity and clinical course in children with type 1, type 2, and type 1.5 diabetes. J Autoimmun. 2005;25(3):244–50.
Rosenbloom AL, Silverstein JH, Amemiya S, Zeitler P, Klingensmith GJ. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2006–2007. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in the child and adolescent. Pediatr Diabetes. 2008;9(5):512–26.
Arslanian SA. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children: pathophysiology and risk factors. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2000;13(Suppl. 6):1385–94.
Flint A, Arslanian S. Treatment of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(Suppl. 2):S177–83.
International Diabetes Federation. Global IDF/ISPAD Guideline for Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence. 2011. http://c.ymcdn.com/sites/www.ispad.org/resource/resmgr/Docs/ispadlfac-pocketbook-final.pdf. Accessed Oct 2016.
Benavides S, Striet J, Germak J, Nahata MC. Efficacy and safety of hypoglycemic drugs in children with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy. 2005;25(6):803–9.
Jones KL, Arslanian S, Peterokova VA, Park J-S, Tomlinson MJ. Effect of metformin in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(1):89–94.
Yanovski JA, Krakoff J, Salaita CG, McDuffie JR, Kozlosky M, Sebring NG, et al. Effects of metformin on body weight and body composition in obese insulin-resistant children: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes. 2011;60(2):477–85.
Kelsey MM, Geffner ME, Guandalini C, Pyle L, Tamborlane WV, Zeitler PS, et al. Presentation and effectiveness of early treatment of type 2 diabetes in youth: lessons from the TODAY study. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016;17(3):212–21.
Kahn SE, Lachin JM, Zinman B, Haffner SM, Aftring RP, Paul G, et al. Effects of rosiglitazone, glyburide, and metformin on beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in ADOPT. Diabetes. 2011;60(5):1552–60.
Matthews DR, Cull CA, Stratton IM, Holman RR, Turner RC. UKPDS 26: sulphonylurea failure in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients over six years. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Diabet Med. 1998;15(4):297–303.
Kahn SE, Montgomery B, Howell W, Ligueros-Saylan M, Hsu CH, Devineni D, et al. Importance of early phase insulin secretion to intravenous glucose tolerance in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(12):5824–9.
Reinehr T. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. World J Diabetes. 2013;4(6):270–81.
Padwal RS, Gabr RQ, Sharma AM, Langkaas LA, Birch DW, Karmali S, et al. Effect of gastric bypass surgery on the absorption and bioavailability of metformin. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(6):1295–300.
Gottschalk M, Danne T, Vlajnic A, Cara JF. Glimepiride versus metformin as monotherapy in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, single-blind comparative study. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(4):790–4.
Group TS, Zeitler P, Hirst K, Pyle L, Linder B, Copeland K, et al. A clinical trial to maintain glycemic control in youth with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(24):2247–56.
Food and Drug Administration of the United States. Statistical Review and Evaluation, Clinical Studies (Glucovance); 2004. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/DevelopmentResources/UCM445509.pdf. Accessed Oct 2016.
Micale SJ, Kane MP, Hogan E. Off-label use of liraglutide in the management of a pediatric patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Case Rep Pediatr. 2013;2013:703925.
Klein DJ, Battelino T, Chatterjee D, Jacobsen LV, Hale PM, Arslanian S. Liraglutide’s safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics in pediatric type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16(10):679–87.
Schwimmer JB. Clinical advances in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2016;63(5):1718–25.
Dostalek M, Court MH, Yan B, Akhlaghi F. Significantly reduced cytochrome P450 3A4 expression and activity in liver from humans with diabetes mellitus. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163(5):937–47.
Dostalek M, Court MH, Hazarika S, Akhlaghi F. Diabetes mellitus reduces activity of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B7 in liver and kidney leading to decreased formation of mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide metabolite. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(3):448–55.
Dostalek M, Akhlaghi F, Puzanovova M. Effect of diabetes mellitus on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(8):481–99.
Gwilt PR, Nahhas RR, Tracewell WG. The effects of diabetes mellitus on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991;20(6):477–90.
Hanley MJ, Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010;49(2):71–87.
Clarke JD, Cherrington NJ. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in precision medicine: unraveling the factors that contribute to individual variability. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;151:99–106.
Kearns GL, Abdel-Rahman SM, Alander SW, Blowey DL, Leeder JS, Kauffman RE. Developmental pharmacology–drug disposition, action, and therapy in infants and children. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(12):1157–67.
Anderson GD. Children versus adults: pharmacokinetic and adverse-effect differences. Epilepsia. 2002;43(s3):53–9.
Harskamp-van Ginkel MW, Hill KD, Becker K, Testoni D, Cohen-Wolkowiez M, Gonzalez D, et al. Drug dosing and pharmacokinetics in children with obesity: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(7):678–85.
Stewart C, Hampton E. Effect of maturation on drug disposition in pediatric patients. Clin Pharm. 1987;6(7):548–64.
Morselli PL, Franco-Morselli R, Bossi L. Clinical pharmacokinetics in newborns and infants. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980;5(6):485–527.
Kennedy M. Hormonal regulation of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme activity during adolescence. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008;84(6):662–73.
Linday LA, Greenblatt DJ, Warren MP, Harmatz JS, DeCresce R, Cicalese C, et al. Changes in salivary antipyrine pharmacokinetics during adolescence, correlated with age, hormonal levels and Tanner stage. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1991;16(4):194–202.
Lasker JM, Wester MR, Aramsombatdee E, Raucy JL. Characterization of CYP2C19 and CYP2C9 from human liver: respective roles in microsomal tolbutamide, S-mephenytoin, and omeprazole hydroxylations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;353(1):16–28.
Wester MR, Lasker JM, Johnson EF, Raucy JL. CYP2C19 participates in tolbutamide hydroxylation by human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28(3):354–9.
Hadama A, Ieiri I, Morita T, Kimura M, Urae A, Irie S, et al. P-hydroxylation of phenobarbital: relationship to (S)-mephenytoin hydroxylation (CYP2C19) polymorphism. Ther Drug Monit. 2001;23(2):115–8.
Kobayashi K, Kogo M, Tani M, Shimada N, Ishizaki T, Numazawa S, et al. Role of CYP2C19 in stereoselective hydroxylation of mephobarbital by human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001;29(1):36–40.
Tateishi T, Nakura H, Asoh M, Watanabe M, Tanaka M, Kumai T, et al. A comparison of hepatic cytochrome P450 protein expression between infancy and postinfancy. Life Sci. 1997;61(26):2567–74.
Blanco JG, Harrison PL, Evans WE, Relling MV. Human cytochrome P450 maximal activities in pediatric versus adult liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28(4):379–82.
Naraharisetti SB, Lin YS, Rieder MJ, Marciante KD, Psaty BM, Thummel KE, et al. Human liver expression of CYP2C8: gender, age, and genotype effects. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(6):889–93.
Prasad B, Gaedigk A, Vrana M, Gaedigk R, Leeder JS, Salphati L, et al. Ontogeny of hepatic drug transporters as quantified by LC-MS/MS proteomics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;100(4):362–70.
Gao X, Christensen M, Burghen G, Velasquez-Mieyer P, Moore K, Donahue S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of metformin in pediatric type 2 diabetic and healthy adult subjects [abstract]. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003;73(2):P46.
Sánchez-Infantes D, Díaz M, López-Bermejo A, Marcos MV, de Zegher F, Ibáñez L. Pharmacokinetics of metformin in girls aged 9 years. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50(11):735–8.
Brill MJ, Diepstraten J, van Rongen A, van Kralingen S, van den Anker JN, Knibbe CA. Impact of obesity on drug metabolism and elimination in adults and children. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(5):277–304.
Turner KC, Christensen M, Connor JD, Moore KT, Gao X, Donahue SR. Pharmacokinetics of a glyburide/metformin combination tablet in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003;73(2):P66.
Christensen ML, Meibohm B, Capparelli EV, Velasquez-Mieyer P, Burghen GA, Tamborlane WV. Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of pioglitazone in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;45(10):1137–44.
Malloy J, Capparelli E, Gottschalk M, Guan X, Kothare P, Fineman M. Pharmacology and tolerability of a single dose of exenatide in adolescent patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus being treated with metformin: a randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind, dose-escalation, crossover study. Clin Ther. 2009;31(4):806–15.
Fineman M, Flanagan S, Taylor K, Aisporna M, Shen LZ, Mace KF, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of exenatide extended-release after single and multiple dosing. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50(1):65–74.
Petri KC, Jacobsen LV, Klein DJ. Comparable liraglutide pharmacokinetics in pediatric and adult populations with type 2 diabetes: a population pharmacokinetic analysis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015;54(6):663–70.
Tirucherai GS, LaCreta F, Ismat FA, Tang W, Boulton DW. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dapagliflozin in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18(7):678–84.
Miyagi SJ, Milne AM, Coughtrie MW, Collier AC. Neonatal development of hepatic UGT1A9: implications of pediatric pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012;40(7):1321–7.
Hines RN. The ontogeny of drug metabolism enzymes and implications for adverse drug events. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;118(2):250–67.
Salem F, Johnson TN, Abduljalil K, Tucker GT, Rostami-Hodjegan A. A re-evaluation and validation of ontogeny functions for cytochrome P450 1A2 and 3A4 based on in vivo data. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53(7):625–36.
Novo Nordisk A/S. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide in combination with metformin compared to metformin alone, in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes (Ellipse™). [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01541215]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 19 Oct 2016.
AstraZeneca. Safety and efficacy study of exenatide once weekly in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01554618]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 19 Oct 2016.
Acknowledgements
Use of the University of Washington Drug Interaction Database is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Support received from Grant # R15 GM101599 from the National Institutes of Health is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of interest
Fatemeh Akhlaghi, Kelly L. Matson, Amir Hooshang Mohammadpour, Meghan Kelly, and Asieh Karimani declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhlaghi, F., Matson, K.L., Mohammadpour, A.H. et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antihyperglycemic Medications in Children and Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin Pharmacokinet 56, 561–571 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-016-0472-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-016-0472-6