Abstract
Background and Objective
Veliparib (ABT-888) is a potent oral inhibitor of Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase enzyme that is currently in development for the treatment of non-hematologic and hematologic malignancies. This analysis characterizes the population pharmacokinetics of veliparib, including developing a structural pharmacokinetic model and testing patient demographics and covariates for potential influence on veliparib pharmacokinetics in patients with non-hematologic malignancies.
Methods
The analysis dataset included 3,542 veliparib concentration values from 325 patients with non-hematologic malignancies enrolled in three phase I and one phase II studies. Population pharmacokinetic modeling was performed using NONMEM. The likelihood ratio test was used for comparison of nested models, and visual predictive check was employed for model qualification. Covariates tested included body size measures, creatinine clearance (CLCR), formulation, age, sex, race, liver function tests, and coadministration with temozolomide.
Results
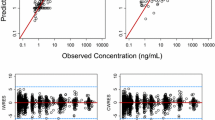
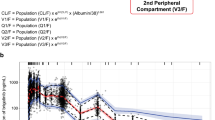
A one-compartment model with first-order absorption and elimination adequately described veliparib pharmacokinetics. The final model included fixed effects for CLCR on veliparib oral clearance (CL/F) and lean body mass (LBM) on volume of distribution (V d/F). CL/F and V d/F were 20.9 L/h (for a CLCR of 100 mL/min) and 173 L (for an LBM of 56 kg), respectively.
Conclusion
Only LBM and CLCR were found to be determinants of veliparib V d/F and CL/F, respectively. Dosage adjustments of veliparib on the basis of body size, age, sex, race, liver function, and temozolomide coadministration are not necessary in patients with non-hematologic malignancies. This is the first study to characterize the population pharmacokinetics of veliparib, and the developed model will be used to conduct simulations and evaluate veliparib exposure-response relationships.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiarugi A. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase: killer or conspirator? The ‘suicide hypothesis’ revisited. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002;23(3):122.
Virág L, Szabó C. The therapeutic potential of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54(3):375–429.
Wielckens K, Garbrecht M, Kittler M, Hilz H. ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins in normal lymphocytes and in low-grade malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Eur J Biochem/FEBS. 1980;104(1):279.
Tomoda T, Kurashige T, Moriki T, Yamamoto H, Fujimoto S, Taniguchi T. Enhanced expression of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase gene in malignant lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 1991;37(4):223–7.
Shiobara M, Miyazaki M, Ito H, Togawa A, Nakajima N, Nomura F, et al. Enhanced polyadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation in cirrhotic liver and carcinoma tissues in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;16(3):338–44.
Hirai K, Ueda K, Hayaishi O. Aberration of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) metabolism in human colon adenomatous polyps and cancers. Cancer Res. 1983;43(7):3441–6.
Palma JP, Wang YC, Rodriguez LE, Montgomery D, Ellis PA, Bukofzer G, et al. ABT-888 confers broad in vivo activity in combination with temozolomide in diverse tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(23):7277–90.
Penning TD, Zhu G-D, Gandhi VB, Gong J, Liu X, Shi Y, et al. Discovery of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor 2-[(R)-2-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-1 H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide (ABT-888) for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. 2008;52(2):514–23.
Donawho CK, Luo Y, Penning TD, Bauch JL, Bouska JJ, Bontcheva-Diaz VD, et al. ABT-888, an orally active poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor that potentiates DNA-damaging agents in preclinical tumor models. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(9):2728–37.
Kummar S, Ji J, Morgan R, Lenz HJ, Puhalla SL, Belani CP, et al. A phase I study of veliparib in combination with metronomic cyclophosphamide in adults with refractory solid tumors and lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(6):1726–34.
Kummar S, Chen A, Ji J, Zhang Y, Reid JM, Ames M, et al. Phase I study of PARP inhibitor ABT-888 in combination with topotecan in adults with refractory solid tumors and lymphomas. Cancer Res. 2011;71(17):5626–34.
Kummar S, Kinders R, Gutierrez ME, Rubinstein L, Parchment RE, Phillips LR, et al. Phase 0 clinical trial of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor ABT-888 in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(16):2705–11.
Li X, Delzer J, Voorman R, de Morais SM, Lao Y. Disposition and drug-drug interaction potential of veliparib (ABT-888), a novel and potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(7):1161–9.
Muscal JA, Thompson PA, Giranda VL, Dayton BD, Bauch J, Horton T, et al. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of ABT-888 after oral administration in non-human primates. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010;65(3):419–25.
Lindbom L, Pihlgren P, Jonsson N. PsN-Toolkit—a collection of computer intensive statistical methods for non-linear mixed effect modeling using NONMEM. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2005;79(3):241–57.
Beal S, Sheiner L, Boeckmann A, Bauer R. NONMEM user’s guide. Ellicott City: Icon Development Solutions; 1989–2009.
Jonsson EN, Karlsson MO. Xpose–an S-PLUS based population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model building aid for NONMEM. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1999;58(1):51–64.
Cheymol G. Effects of obesity on pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000;39(3):215–31.
Duffull SB, Dooley MJ, Green B, Poole SG, Kirkpatrick CM. A standard weight descriptor for dose adjustment in the obese patient. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004;43(15):1167–78.
Janmahasatian S, Duffull SB, Ash S, Ward LC, Byrne NM, Green B. Quantification of lean bodyweight. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(10):1051–65.
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41.
Mosteller R. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med. 1987;317(17):1098.
Savic RM, Karlsson MO. Importance of shrinkage in empirical bayes estimates for diagnostics: problems and solutions. AAPS J. 2009;11(3):558–69.
Bergstrand M, Hooker AC, Wallin JE, Karlsson MO. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J. 2011;13(2):143–51.
Anderson BJ, Holford NH. Mechanistic basis of using body size and maturation to predict clearance in humans. Drug Metabol Pharmacokinet. 2009;24(1):25–36.
Ekhart C, Rodenhuis S, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH, Huitema AD. Carboplatin dosing in overweight and obese patients with normal renal function, does weight matter? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009;64(1):115–22.
Prado CM, Lima IS, Baracos VE, Bies RR, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, et al. An exploratory study of body composition as a determinant of epirubicin pharmacokinetics and toxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67(1):93–101.
Morgan D, Bray K. Lean body mass as a predictor of drug dosage: implications for drug therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994;26(4):292.
Roche A, Heymsfield S, Lohman T, editors. Human body composition. Champaign (IL): Human Kinetics Press; 1996.
Kikuchi R, Lao Y, Bow DA, Chiou WJ, Andracki ME, Carr RA, et al. Prediction of clinical drug–drug interactions of veliparib (ABT-888) with human renal transporters (OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2K). J Pharm Sci. 2013;102(12):4426–32.
Mehta MP, Curran WJ, Wang D, Wang F, Kleinberg L, Brade A, et al. Phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of veliparib in combination with whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in patients (PTS) with brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;84(3S):S269.
Middleton M, Friedlander P, Hamid O, Daud A, Plummer R, Schuster R, et al. Efficacy of veliparib (ABT-888) plus temozolomide versus temozolomide alone: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with metastatic melanoma. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:8.
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by AbbVie, who contributed to the study design, research, and interpretation of data, and writing, reviewing, and approving the publication. Ahmed Hamed Salem, Vincent L. Giranda, and Nael M. Mostafa are employees of AbbVie. The authors would like to thank Teresa Turner (AbbVie) for medical writing support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salem, A.H., Giranda, V.L. & Mostafa, N.M. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Veliparib (ABT-888) in Patients with Non-Hematologic Malignancies. Clin Pharmacokinet 53, 479–488 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-013-0130-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-013-0130-1