Abstract
Background
The evidence for adding small-molecule drugs to an ongoing biologic treatment is sparse, but combination therapies appear to be advantageous in appropriately selected patients with psoriasis. To our knowledge, efficacy and safety of combination therapy with apremilast and biologics has not previously been reviewed.
Materials and Methods
A literature search was performed on Medline (PubMed), Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library. Inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of psoriasis, age ≥ 18 years, concomitant treatment with apremilast and a specified biologic agent, and available safety and/or efficacy results. All papers written in English and published from database inception to August 2021 were included. No limit was set regarding study size.
Results
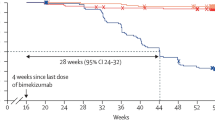
The literature search yielded 447 citations. Of these, 19 studies published from 2015 to 2020 were included in the review. All papers referred to retrospective studies, comprising case reports (n = 9), case series (n = 8), or cohort studies (n = 2). A total of 172 patients with psoriasis were identified. Clinical subtypes included plaque psoriasis (n = 164), palmoplantar pustulosis (n = 7), and acute pustular psoriasis (n = 1). The observation period ranged from 3 weeks to 24 months. Geographical origin of studies was North America (n = 11), Europe (n = 4), and Asia (n = 4). In general, apremilast-biologic combination therapy was reported to be safe; across papers, one serious adverse event was registered (hospitalization due to weight loss). Adverse events (AEs) were otherwise mostly mild and gastrointestinal. No differences in AEs were observed in studies comparing apremilast mono- and combination therapy. In several papers, sufficient information about AEs was not reported or could not be extracted. Clinical response to combination treatment was evaluated at various time points, and only few studies used validated scores. In the remaining papers, efficacy data were descriptive and/or in photographic form, or not available. In total, two patients discontinued therapy due to lack of efficacy.
Conclusion
Evidence for combined treatment with apremilast and biologics is limited and restricted to retrospective studies of various quality. Based on available data, apremilast may constitute an efficacious and safe add-on treatment to biologic therapy, but properly conducted clinical investigations are needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1029–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.057.
Egeberg A, Ottosen MB, Gniadecki R, et al. Safety, efficacy and drug survival of biologics and biosimilars for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:509–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.16102.
Armstrong AW, Bagel J, Van Voorhees AS, et al. Combining biologic therapies with other systemic treatments in psoriasis: evidence-based, best-practice recommendations from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:432–8. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.3456.
Loos AM, Liu S, Segel C, et al. Comparative effectiveness of targeted immunomodulators for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79(135–44): e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.027.
Robinson JK, Dellavalle RP, Bigby M, Callen JP. Systematic reviews: grading recommendations and evidence quality. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:97–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/archdermatol.2007.28.
AbuHilal M, Walsh S, Shear N. Use of apremilast in combination with other therapies for treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a retrospective study. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:313–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/1203475416631328.
Alomran A, Zancanaro P, Prussick L, et al. Apremilast in combination with an interleukin 17A inhibitor in the treatment of recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis: a chart review. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2018;3:122–5.
Aragón-Miguel R, González IM, González-Valle O, Aragón-Díez A. Combination therapy of apremilast and biologic agent as a step-up strategy option of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 83(6 supplement) (abstract) 2020.
Armesto S, Gonzalez Vela C, Sanchez J, et al. Treating multidrug-resistant psoriasis with brodalumab, apremilast, methotrexate and prednisone combination therapy in the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33: e14464. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.14464.
Danesh MJ, Beroukhim K, Nguyen C, et al. Apremilast and adalimumab: a novel combination therapy for recalcitrant psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21. https://doi.org/10.5070/D3216027825.
De A, Das S, Dhoot D, Sarda A. Apremilast coadministered with Secukinumab for safe and effective control of psoriasis with resultant reduction of maintenance dose of the biologic. Indian J Dermatol. 2019;64:239–41. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijd.IJD_548_18.
Galluzzo M, D’Adamio S, Campione E, et al. Treating a multidrug-resistant psoriatic HLA-C*18:01 allele carrier with combination Ustekinumab Apremilast therapy. Mol Diagn Ther. 2018;22:717–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-018-0354-8.
Georgakopoulos JR, Ighani A, Yeung J. Short- and long-term management of an acute pustular psoriasis flare: a case report. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:452–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/1203475417712499.
Hadi A, Lebwohl M. Secukinumab and apremilast combination therapy for recalcitrant psoriasis. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2017;2:59–61.
Ighani A, Georgakopoulos JR, Shear NH, et al. Maintenance of therapeutic response after 1 year of apremilast combination therapy compared with monotherapy for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: a multicenter, retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:953–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.04.043.
Ighani A, Georgakopoulos JR, Walsh S, et al. A comparison of apremilast monotherapy and combination therapy for plaque psoriasis in clinical practice: a Canadian multicenter retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:623–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2017.09.060.
Kishimoto M, Komine M, Hioki T, et al. Real-world use of apremilast for patients with psoriasis in Japan. J Dermatol. 2018;45:1345–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.14617.
Masuda K, Kanehisa F, Katoh N. Combination therapy of apremilast and biological product in a patient with psoriasis. In: Acta dermato-venereologica conference 5th world psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis conference, p 392018.
Mayba J, Gooderham M. Treatment of palmoplantar pustulosis with the combination of ustekinumab and apremilast: a case report. Arc Cas Rep CMed. 2016;2:128.
Metyas S, Tomassian C, Messiah R, et al. Combination therapy of apremilast and biologic agent as a safe option of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2019;15:234–7. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573397115666181130094455.
Mikhailitchenko AL, Crowley EL, Gooderham M. Eight-patient case series of palmoplantar pustulosis treated successfully with apremilast. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2019;4:7–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/24755303.
Nisar MK. Combining secukinumab and apremilast to successfully treat refractory psoriatic skin and joint disease: A novel approach. Eur J Rheumatol. 2019;6:60–1. https://doi.org/10.5152/eurjrheum.2018.17188.
Rothstein BE, McQuade B, Greb JE, et al. Apremilast and secukinumab combined therapy in a patient with recalcitrant plaque psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:648–9.
Sacchelli L, Patrizi A, Loi C, Bardazzi F. Combination therapy of apremilast and secukinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe, recalcitrant plaque psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:e243–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.14000.
Takamura S, Sugai S, Taguchi R, Teraki Y. Combination therapy of apremilast and biologics in patients with psoriasis showing biologic fatigue. J Dermatol. 2020;47:290–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.15193.
Crowley J, Thaci D, Joly P, et al. Long-term safety and tolerability of apremilast in patients with psoriasis: pooled safety analysis for >/=156 weeks from 2 phase 3, randomized, controlled trials (ESTEEM 1 and 2). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77(310–7): e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2017.01.052.
Abignano G, Fadl N, Merashli M, et al. Apremilast for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis: a single-centre real-life experience. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57:578–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex454.
Yiu ZZN, Mason KJ, Hampton PJ, et al. Drug survival of adalimumab, ustekinumab and secukinumab in patients with psoriasis: a prospective cohort study from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register (BADBIR). Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.18981.
Peng T, Qi B, He J, et al. Advances in the development of phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2020;63:10594–617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02170.
Schafer PH, Truzzi F, Parton A, et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 in inflammatory diseases: effects of apremilast in psoriatic blood and in dermal myofibroblasts through the PDE4/CD271 complex. Cell Signal. 2016;28:753–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.01.007.
Li H, Zuo J, Tang W. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1048. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
None.
Conflict of interest
M. Gyldenløve: None. F. Alinaghi: None. C. Zachariae: Investigator for AbbVie, Sanofi, Janssen Cilag, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Regeneron, and LEO Pharma. Paid speaker for Eli Lilly, Novartis, CSL, and LEO Pharma. Consultant and/or advisory board member for AbbVie, Janssen Cilag, Novartis, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma, UCB, Almirall, Takeda, Amgen, and CSL. L. Skov: Received research funding from Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, the Danish National Psoriasis Foundation, the LEO Foundation, and the Kgl Hofbundtmager Aage Bang Foundation. Honoraria as consultant and/or speaker for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, LEO Pharma, Janssen Cilag, UCB, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Sanofi. Investigator for AbbVie, Pfizer, Sanofi, Janssen Cilag, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Regeneron, Galderma, and LEO Pharma. A. Egeberg: Received research funding from Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, the Danish National Psoriasis Foundation, the Simon Spies Foundation, and the Kgl Hofbundtmager Aage Bang Foundation. Honoraria as consultant and/or speaker from AbbVie, Almirall, Leo Pharma, Zuellig Pharma Ltd., Galápagos NV, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd., Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, Union Therapeutics, Galderma, Dermavant, UCB, Mylan, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Ethics approval, informed consent, and code availability
Not applicable.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributions (credit taxonomy)
Conceptualization (MG), methodology (MG and FA), literature search and data extraction (MG, FA, and AE), resources (FA, CZ, and LS), writing—original draft (MG), writing—review and editing (FA, AE, LS, and CZ).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gyldenløve, M., Alinaghi, F., Zachariae, C. et al. Combination Therapy with Apremilast and Biologics for Psoriasis: A Systematic Review. Am J Clin Dermatol 23, 605–613 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-022-00703-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-022-00703-1