Abstract
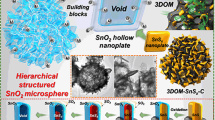
A designed solution route was developed to fabricate size tunable SnO2 hollow microspheres based on the sol-gel theory. The hydrolysis of SnSO4 released protons to form SnO2 particulates and induced the decrease of pH value. To minimize the high surface energy, the SnO2 particulates tended to assemble into large particles, the size of which was affected by the electrolyte concentration or pH value. Elevating SnSO4 content aroused the decrease of the pH value that directed to the shrinkage of the aggregated particle size of SnO2. Size tunable SnO2 hollow microspheres were then rationally fabricated under solvothermal conditions via Ostwald ripening by simply adjusting the SnSO4 concentration. The in situ pH decrease directed to the shrinkage of the particle size from 270 nm to 112 nm. The formation mechanism was confirmed and rationally elucidated by the time dependant morphology evolution. Charge-discharge tests revealed that the reduced particle size aroused an improved lithium ion battery performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lou X. W., Archer L. A., Yang Z. C., Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 3987
Zhang Q., Wang W. S., Goebl J., Yin Y. D., Nano Today, 2009, 4, 494
Wang W. S., Zhen L., Xu C. Y., Li Y., Shao W. Z., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 19390
Lou X. W., Yuan C., Rhoades E., Zhang Q., Archer A., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2006, 16, 1679
Guan Y., Wang C., Wang B., Ma J., Xu X. M., Sun Y. F., Liu F. M., Liang X. S., Gao Y., Lu G. Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(5), 837
Li J., Zeng H. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 15839
Yu H. G., Yu J. G., Liu S.W., Mann S., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19, 4327
Yin Y. D., Erdonmez C. K., Cabot A., Hughes S., Alivisatos A. P., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2006, 16, 1389
Chen X. Y., Qiao M. H., Xie S. H., Fan K., Zhou W. Z., He H. Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 13305
Xu H. L., Wang W. Z., Zhou L., Cryst. Growth Des., 2008, 8, 3486
Ye T. N., Dong Z. H., Zhao Y. N., Yu J. G., Wang F. Q., Guo S. K., Zou Y. C., Langmuir, 2011, 27, 8878
Ye T. N., Dong Z. H., Zhao Y. N., Yu J. G., Wang F. Q., Guo S. K., Zou Y. C., Cryt. Eng. Comm., 2011, 13, 3842
Ye T. N., Dong Z. H., Zhao Y. N., Yu J. G., Wang F. Q., Zhang L. L., Zou Y. C., Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 2601
Dong Z. H., Ye T. N., Zhao Y. N., Yu J. G., Wang F. Q., Zhang L. L., Wang X. B., Guo S. K., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 5978
Li Y. L., Zhao J. Z., Zhao Y., Hao X. L., Hou Z. Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(6), 1040
Wang H. K., Rogach A. L., Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 123
Wang Z. Y., Wang Z. C., Madhavi S., Lou X. W., Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18, 7561
Chen J. S., Lou X. W., Small, 2013, 9, 1877
Baes C. F., Mesmer R. E., The Hydrolysis of Cations, Wiley-VCH, New York, 1976
Brinker C. J., Scherer G. W., Sol-Gel Science: the Physics and Chemistry of Sol-gel Processing, Academic Press, San Diego, 1990
Liu M. X., Ma X. M., Gan L. H., Xu Z. J., Zhu D. Z., Chen L. W., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 17107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Nos.21271138, 21371070, 21071060), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, China(No.10JCZDJC21500) and the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry of Jilin University, China(No.2015-02).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Guo, J., Wang, X. et al. Rational fabrication of size tunable SnO2 hollow microspheres. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 31, 719–723 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-015-4452-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-015-4452-4