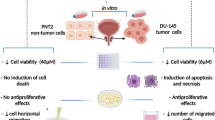
Abstract
Prostate cancer is the second most frequent and the fifth greatest cause of death in men. Although diet has been connected to the prevalence of cancer in addition to other factors, the relation between cancer and prevention is weak. Treatment options are at risk due to cell resistance. To identify new combinations, we tried plant-derived quercetin with bicalutamide on cell lines. To determine the cytotoxicity and apoptotic potential of plant-derived quercetin and its combination, MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] and dual stain assays were performed. In silico protein–ligand interaction was performed to support the in vitro findings. A thin layer, column, and high-performance chromatography were used to purify quercetin along with an authentic sample. In the cytotoxic study, quercetin was minimized by 80% similar to bicalutamide and a combination of quercetin and bicalutamide by 50% when compared to controls by 2%. Quercetin and bicalutamide showed a similar binding affinity for androgen receptors (9.7 and 9.8), hub genes (10.8 and 10.0), and a few other PCa-related genes (9.4 and 9.1). We propose to conclude that the combination of quercetin plus bicalutamide can be used for chemotherapy if additional in vivo studies are conducted. The intake of foods high in polyphenolic compounds can help to prevent prostate cancer. Examination of quercetin on several cell lines will provide a definite conclusion to combat cancers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Al-Oqail MM, Farshori NN (2021) Antioxidant and anticancer efficacies of Anethum graveolens against human breast carcinoma cells through oxidative stress and caspase dependency. Biomed Res Int 4(2021):5535570. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5535570
Anuradha KM, James SN (2013) The role of E-Cadherin-catenin complex in prostate cancer progression. In: Advances in prostate cancer. InTech https://doi.org/10.5772/52751
Boam T (2015) Anti-androgenic effects of flavonols in prostate cancer. Ecancermedicalscience 9:585
Carabet LA, Lallous N, Leblanc E et al (2018) Computer-aided drug discovery of Myc-Max inhibitors as potential therapeutics for prostate cancer. Eur J Med Chem 5(160):108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.023
Carmena M, Wheelock M, Funabiki H (2012) The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC): from easy rider to the godfather of mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(12):789–803. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3474
Chandrappa C, Govindappa M, Anil Kumar N et al (2014) Identification and separation of quercetin from ethanol extract of Carmona retusa by thin layer chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 3(6):2020–2029
Chen D, Oezguen N, Urvil P et al (2016) Regulation of protein-ligand binding affinity by hydrogen bond pairing. Sci Adv 25 2(3):e1501240. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1501240
Chen X, Shao Y, Li Y (2022) The cell cycle gene centromere protein K (CENPK) contributes to the malignant progression and prognosis of prostate cancer. Transl Cancer Res 11(5):1099–1111. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-21-2164
Choudhari AS, Mandave PC, Deshpande M et al (2020) Phytochemicals in cancer treatment: From preclinical studies to clinical practice. Front Pharmacol 10:1614
Cifuentes E, Mataraza JM, Yoshida BA (2004) Physical and functional interaction of androgen receptor with calmodulin in prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(2):464–469. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307161101
Clinton SK, Giovannucci EL, Hursting SD (2020) The World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research third expert report on diet, nutrition, physical activity, and cancer: impact and future directions. J Nutr 150(4):663–671
Copello VA, Burnstein KL et al (2022) The kinesin KIF20A promotes progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer through autocrine activation of the androgen receptor. Oncogene 41(20):2824–2832. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02307-9
Crawford ED, Moul JW (2015) ADT risks and side effects in advanced prostate cancer: cardiovascular and acute renal injury. Oncology 29(1):55–55
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7:42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
David AVA, Arulmoli R, Parasuraman S (2016) Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: a bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacogn Rev 10(20):84
Gallivan JP, Dougherty DA (1999) Cation-pi interactions in structural biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 17 96(17):9459–9464. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.17.9459
Gamba M, Asllanaj E, Raguindin PF et al (2021) Nutritional and phytochemical characterization of radish (Raphanus sativus): a systematic review. Trends Food Sci Technol 113:205–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.04.045
Gibellini L, Pinti M, Nasi M et al (2011) Quercetin and cancer chemoprevention. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/neq053
Hashemzaei M, Delarami Far A, Yari A et al (2017) Anticancer and apoptosis-inducing effects of quercetin in vitro and in vivo. Oncology 38(2):819–828. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5766
Hu L, Huang H, Hei M et al (2019) Structural analysis of fungal CENP-H/I/K homologs reveals a conserved assembly mechanism underlying proper chromosome alignment. Nucleic Acids Res 47(1):468–479. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1108
Jana S, Shekhawat GS (2010) Anethum graveolens: an Indian traditional medicinal herb and spice. Pharmacogn Rev 4(8):179–184
Kawabata R, Oie S, Takahashi M et al (2011) Up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 by 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) leads to the potent anti-proliferative effect of androgen deprivation therapy combined with 5-FU in human prostate cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol 38(6):1489–1500
Key TJ, Bradbury KE, Perez-Cornago A et al (2020) Diet, nutrition, and cancer risk: what do we know and what is the way forward? BMJ 368:m511
Kotolloshi R, Mirzakhani K, Ahlburg J et al (2020) Thyroid hormone induces cellular senescence in prostate cancer cells through induction of DEC1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 201:105689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105689
Liu Y, Yang X, Gan J et al (2022) CB-Dock2: improved protein–ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Res 50(W1):W159–W164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac394
Lotfi N, Yousefi Z, Golabi M et al (2023) The potential anti-cancer effects of quercetin on blood, prostate and lung cancers: An update. Front Immunol 28(14):1077531. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1077531
Manivannan A, Kim JH, Kim DS et al (2019) Deciphering the nutraceutical potential of Raphanus sativus—a comprehensive overview. Nutrients 11(2):402
Nozawa M, Sugimoto K, Nagai Y et al (2016) Degarelix/bicalutamide combination versus degarelix alone as initial androgen-deprivation therapy. J Clin Oncol 34(2):183
Omar MN, Fahd AN, Ali SA et al (2021) Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia. Open Chem 19(1):408–416. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2021-0042
Penson DF, Armstrong AJ, Concepcion R et al (2016) Enzalutamide Versus Bicalutamide in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: The STRIVE Trial. J Clinical Oncol 34(18):2098–2106. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.64.9285
Rahman MA, Akhtar J (2017) Evaluation of anticancer activity of Cordia dichotoma leaves against a human prostate carcinoma cell line, PC3. J Tradit Complement Med 7(3):315–321
Rather RA, Bhagat M (2020) Quercetin as an innovative therapeutic tool for cancer chemoprevention: molecular mechanisms and implications in human health. Cancer Med 9(24):9181–9192. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1411
Rice MA, Malhotra SV, Stoyanova T (2019) Second-generation antiandrogens: from discovery to standard of care in castration resistant prostate cancer. Front Oncol 9:801
Sahu V, Khan A, Singh R (2008) Hydrophobic, polar and hydrogen bonding based drug-receptor interaction of tetrahydroimidazobenzodiazepinones. Am J Immunol 4(3):33–42. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajisp.2008.33.4210.3844/ajisp.2008.33.42
Sari Y, Isworo A, Upoyo AS et al (2021) The differences in health-related quality of life between younger and older adults and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Indonesia. Health Quality Life Outcomes 19(1):1–10
Senapati S, Mahanta AK, Kumar S, Maiti P (2018) Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct Target Ther 3(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-017-0004-3
Sharma S, Cwiklinski K, Mahajan SD et al (2023) Combination modality using quercetin to enhance the efficacy of docetaxel in prostate cancer cells. Cancers (basel) 15(3):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030902
Singh AN, Baruah MM, Sharma N (2017) Structure Based docking studies towards exploring potential anti-androgen activity of selected phytochemicals against Prostate Cancer. Sci Rep 7(1):1955. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02023-5
Su F, Daquinag AC, Ahn S et al (2021) Progression of prostate carcinoma is promoted by adipose stromal cell-secreted CXCL12 signaling in prostate epithelium. Npj Precision Oncology 5:26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-021-00160-9
Sung H, Ferlay J, Rebecca L et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Tam JZ, Palumbo T, Miwa JM et al (2022) Analysis of protein-protein interactions for intermolecular bond prediction. Molecules 27(19):6178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196178
Tyagi S, Gupta P, Saini AS (2011) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: a family of nuclear receptors role in various diseases. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2(4):236–240. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-4040.90879
Valença I, Ferreira AR, Correia M (2020) Prostate cancer proliferation is affected by the subcellular localization of MCT2 and accompanied by significant peroxisomal alterations. Cancers 12:3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113152
Ward AB, Mir H, Kapur N et al (2018) Quercetin inhibits prostate cancer by attenuating cell survival and inhibiting anti-apoptotic pathways. World J Surg Oncol 16(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1400-z
Yashaswee S, Trigun SK (2020) Cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis in melanoma (MDA-MB-435S) cells by Emodin. J Sci Res 64(2):1–9
Yu C, Cao H, He X et al (2017) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 (CDKN3) plays a critical role in prostate cancer via regulating cell cycle and DNA replication signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 96:1109–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.112
Zhang HW, Hu JJ, Fu RQ et al (2018) Flavonoids inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis and autophagy through down regulation of PI3Kγ mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K/ULK signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Sci Rep 8(1):1–13
Zhang R, Guo WH, Yang LH et al (2023) Identification of hub genes in prostate cancer by bioinformatics analysis. Open Access Library Journal 10:e9747. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1109747
Zhu H, Lin Q, Gao X et al (2023) Identification of the hub genes associated with prostate cancer tumorigenesis. Front Oncol 13:1168772. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1168772
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Kiranmayee P.: The concept, result analysis, manuscript writing, editing. Dr. Mary Shobharani I.: Performed the experiments, written and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Inala, M.S.R., Pamidimukkala, K. In vitro combination effects of plant-derived quercetin with synthetic bicalutamide on prostate cancer and normal cell lines: in silico comparison. In Silico Pharmacol. 12, 22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-024-00192-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-024-00192-6