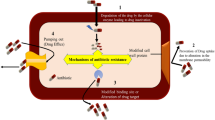
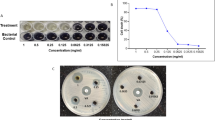
Abstract
Neisseria gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease from gonorrhea that lacks treatment; despite the urgency, the absence of adequate drugs, lack of human correlates of protection, and inadequate animal models of infection have delayed progress toward the prevention of gonococcal infection. Lactobacillus crispatus is a lactic acid bacterium typically found in the human vaginal microbiota. Peptides from L. crispatus have shown a potential therapeutic option for targetting N. gonorrhea. Bioinformatics analysis is important for speeding up drug target acquisition, screening refinement, and evaluating adverse effects and drug resistance prediction. Therefore, this study identified an antimicrobial peptide from the bacteriocin immunity protein (BIP) of L. crispatus using the bioinformatics tool and Collection of Antimicrobial Peptide (CAMPR3). Based on the AMP score and highest ADMET properties, the peptide SM20 was chosen for docking analysis. SM20 was docked against multiple proteins from the genome of the AMR bacterium N. gonorrhea using an online tool; protein-peptide interactions were established and visualized using the PyMol visualizing tool. Molecular docking was carried out using the CABSdock tool, and multiple conformations were obtained against the membrane proteins of N. gonorrhoea. The peptide SM20 exhibited higher docking scores and ADMET properties. Therefore, SM20 could be further encapsulated with cellulose; it can be applied topically to the genital tract to target N. gonorrhea infection. The controlled release of the antimicrobial peptide from the gel can provide sustained delivery of the treatment, increasing its efficacy and reducing the risk of resistance development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Amabebe E, Anumba DOC (2018) The vaginal microenvironment: the physiologic role of Lactobacilli. Front Med 5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00181
Arvidson CG, Kirkpatrick R, Witkamp MT, Larson JA, Schipper CA, Waldbeser LS, O’Gaora P, Cooper M, So M (1999) Neisseria gonorrhoeae mutants altered in toxicity to human fallopian tubes and molecular characterization of the genetic locus involved. Infect Immun 67:643–652. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.67.2.643-652.1999
Brook G (2015) The performance of non-NAAT point-of-care (POC) tests and rapid NAAT tests for chlamydia and gonorrhoea infections. An assessment of currently available assays. Sex Transm Infect 91:539–544. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2014-051997
Cao Y, Li L (2014) Improved protein-ligand binding affinity prediction by using a curvature-dependent surface-area model. Bioinformatics 30:1674–1680. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu104
Casadei E, Bird S, Wadsworth S, González Vecino JL, Secombes CJ (2015) The longevity of the antimicrobial response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed a peptidoglycan (PG) supplemented diet. Fish Shellfish Immunol 44:316–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.02.039
Chitsaz M, Booth L, Blyth MT, O’mara ML, Brown MH (2019) Multi-drug resistance in neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification of functionally important residues in the mtrd efflux protein. MBio 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02277-19
Chow EPF, Walker S, Hocking JS, Bradshaw CS, Chen MY, Tabrizi SN, Howden BP, Law MG, Maddaford K, Read TRH, Lewis DA, Whiley DM, Zhang L, Grulich AE, Kaldor JM, Cornelisse VJ, Phillips S, Donovan B, McNulty AM, Templeton DJ, Roth N, Moore R, Fairley CK (2017) A multicentre double-blind randomised controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of daily use of antibacterial mouthwash against oropharyngeal gonorrhoea among men who have sex with men: the OMEGA (Oral Mouthwash use to Eradicate GonorrhoeA) study protocol. BMC Infect Dis 17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2541-3
Cornelissen CN, Hollander A (2011) TonB-dependent transporters expressed by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Front Microbiol 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2011.00117
Golparian D, Shafer WM, Ohnishi M, Unemo M (2014) Importance of multi-drug efflux pumps in the antimicrobial resistance property of clinical multidrug-resistant isolates of neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:3556–3559. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00038-14
Gupta S, Kapoor P, Chaudhary K, Gautam A, Kumar R, Raghava GPS (2013) In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 8:e73957. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073957
Gupta S, Kapoor P, Chaudhary K, Gautam A, Kumar R, Raghava GPS (2015) Peptide toxicity prediction. In: Zhou P, Huang J (eds) Computational peptidology. Springer, New York, pp 143–157
Jenssen H, Hamill P, Hancock REW (2006) Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:491–511. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00056-05
Kirkcaldy RD, Weston E, Segurado AC, Hughes G (2019) Epidemiology of gonorrhoea: a global perspective. Sex Health 16:401. https://doi.org/10.1071/SH19061
Lahsoune M, Boutayeb H, Zerouali K, Belabbes H, El Mdaghri N (2007) Prévalence et état de sensibilité aux antibiotiques d’Acinetobacter baumannii dans un CHU marocain. Med Mal Infect 37:828–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medmal.2007.05.006
Leuzzi R, Nesta B, Monaci E, Cartocci E, Serino L, Soriani M, Rappuoli R, Pizza M (2013) Neisseria gonorrhoeae PIII has a role on NG1873 outer membrane localization and is involved in bacterial adhesion to human cervical and urethral epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol 13:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-251
Li C, Deng X, Xie X, Liu Y, Angeli JPF, Lai L (2018) Activation of glutathione peroxidase 4 as a novel anti-inflammatory strategy. Front Pharmacol 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01120
Mikelsaar M, Zilmer M (2009) Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3—an antimicrobial and antioxidative probiotic. Microb Ecol Health Dis 21:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/08910600902815561
Mitchell C, Fredricks D, Agnew K, Hitti J (2015) Hydrogen peroxide-producing lactobacilli are associated with lower levels of vaginal interleukin-1β, independent of bacterial vaginosis. Sex Transm Dis 42:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000298
Passari AK, Yadav MK, Singh BP (2018) In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial activities and antibiotic susceptibility profiling of culturable actinobacteria from fresh water streams. Indian J Exp Biol 56:665–673
Pires DEV, Blundell TL, Ascher DB (2015) pkCSM: Predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J Med Chem 58:4066–4072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00104
Prabhu BN, Kanchamreddy SH, Sharma AR, Bhat SK, Bhat PV, Kabekkodu SP, Satyamoorthy K, Rai PS (2021) Conceptualization of functional single nucleotide polymorphisms of polycystic ovarian syndrome genes: an in silico approach. J Endocrinol Invest 44:1783–1793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01498-4
Raju SV, Sarkar P, Pasupuleti M, Saraswathi NT, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Esmail GA, Arshad A, Arockiaraj J (2021) Pharmacological importance of TG12 from tachykinin and its toxicological behavior against multidrug-resistant bacteria Klebsiella pneumonia. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 245:108974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.108974
Reddy KVR, Yedery RD, Aranha C (2004) Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24:536–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.09.005
Remmele CW, Xian Y, Albrecht M, Faulstich M, Fraunholz M, Heinrichs E, Dittrich MT, Tobias M, Reinhardt R, Rudel T (2014) Transcriptional landscape and essential genes of neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nucleic Acid Res 42:10579–10595. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku762
Riley MA, Wertz JE (2002) Bacteriocins: evolution, ecology, and application. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:117–137. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.161024
Salminen S, Collado MC, Endo A, Hill C, Lebeer S, Quigley EMM, Sanders ME, Shamir R, Swann JR, Szajewska H, Vinderola G (2021) The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:649–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
Sathyamoorthi A, Bhatt P, Ravichandran G, Kumaresan V, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Arockiaraj J (2017) Gene expression and in silico analysis of snakehead murrel interleukin 8 and antimicrobial activity of C-terminal derived peptide WS12. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 190:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2017.06.008
Sathyamoorthi A, Kumaresan V, Palanisamy R, Pasupuleti M, Arasu MV, Al-Dhabi NA, Marimuthu K, Amin SMN, Arshad A, Yusoff FM, Arockiaraj J (2019) Therapeutic cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAP) derived from fish aspartic proteinase cathepsin D and its antimicrobial mechanism. Int J Pept Res Ther 25:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9652-y
Sudhakaran G, Prathap P, Guru A, Haridevamuthu B, Murugan R, Almutairi BO, Almutairi MH, Juliet A, Gopinath P, Arockiaraj J (2022a) Reverse pharmacology of Nimbin-N2 attenuates alcoholic liver injury and promotes the hepatoprotective dual role of improving lipid metabolism and downregulating the levels of inflammatory cytokines in zebrafish larval model. Mol Cell Biochem 477:2387–2401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04448-7
Sudhakaran G, Rajesh R, Murugan R, Velayutham M, Guru A, Boopathi S, Muthupandian S, Gopinath P, Arockiaraj J (2022b) Nimbin analog N2 alleviates high testosterone induced oxidative stress in CHO cells and alters the expression of Tox3 and Dennd1a signal transduction pathway involved in the PCOS zebrafish. Phyther Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7685
Velayutham M, Sarkar P, Sudhakaran G, Al-Ghanim KA, Maboob S, Juliet A, Guru A, Muthupandian S, Arockiaraj J (2022a) Anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities of a short molecule, PS14 derived from the virulent cellulose binding domain of Aphanomyces invadans, on human laryngeal epithelial cells and an in vivo zebrafish embryo model. Molecules 27:7333. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217333
Velayutham M, Sarkar P, Rajakrishnan R, Kuppusamy P, Juliet A, Arockiaraj J (2022b) Antiproliferation of MP12 derived from a fungus, Aphanomyces invadans virulence factor, cysteine-rich trypsin inhibitor on human laryngeal epithelial cells, and in vivo zebrafish embryo model. Toxicon 210:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.02.019
Wang HC, Ko TP, Wu ML, Ku SC, Wu HJ, Wang AHJ (2012) Neisseria conserved protein DMP19 is a DNA mimic protein that prevents DNA binding to a hypothetical nitrogen-response transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res 40:5718–5730. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks177
Wang C, Tu M, Wu D, Chen H, Chen C, Wang Z, Jiang L (2018) Identification of an ACE-inhibitory peptide from walnut protein and its evaluation of the inhibitory mechanism. Int J Mol Sci 19:1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041156
Winther-Larsen HC, Hegge FT, Wolfgang M, Hayes SF, Van Putten JPM, Koomey M (2001) Neisseria gonorrhoeae PilV, a type IV pilus-associated protein essential to human epithelial cell adherence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:15276–15281. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.261574998
Yeaman MR, Yount NY (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev 55:27–55. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.55.1.2
Zielke RA, Wierzbicki IH, Weber JV, Gafken PR, Sikora AE (2014) Quantitative proteomics of the neisseria gonorrhoeae cell envelope and membrane vesicles for the discovery of potential therapeutic targets. Mol Cell Proteomics 13:1299–1317. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M113.029538
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.S, D.K, M.S: performed the experiments. A.A, A.G, J.A: wrote the manuscript and supervised this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this work.
Ethics statements
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sudhakaran, G., Kesavan, D., Selvam, M. et al. Gonorrhea caused due to antimicrobial-resistant bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae treated using probiotic peptide. In Silico Pharmacol. 12, 17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-023-00185-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-023-00185-x