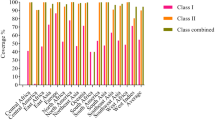
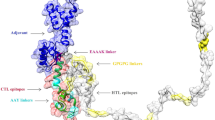
Abstract
Human toxoplasmosis is a global public health concern and a commercial vaccine is still lacking. The present in silico study was done to design a novel vaccine candidate using tachyzoite-specific SAG1-realted sequence (SRS) proteins. Overlapping B-cell and strictly-chosen human MHC-I binding epitopes were predicted and connected together using appropriate spacers. Moreover, a TLR4 agonist, human high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1), and His-tag were added to the N- and C-terminus of the vaccine sequence. The final vaccine had 442 residues and a molecular weight of 47.71 kDa. Physico-chemical evaluation showed a soluble, highly antigenic and non-allergen protein, with coils and helices as secondary structures. The vaccine 3D model was predicted by ITASSER server, subsequently refined and was shown to possess significant interactions with human TLR4. As well, potent stimulation of cellular and humoral immunity was demonstrated upon chimeric vaccine injection. Finally, the outputs showed that this vaccine model possesses top antigenicity, which could provoke significant cell-mediated immune profile including IFN-γ, and can be utilized towards prophylactic purposes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aasim SR, Patil CR, Kumar A, Sharma K (2022) Identification of vaccine candidate against Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 using immunoinformatic approaches. Silic Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-022-00128-y
Ahmadpour E et al (2022) Toxoplasma gondii Infection in marine animal species, as a potential source of food contamination: systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Parasitol 67:592–605
Almeria S, Dubey JP (2021) Foodborne transmission of Toxoplasma gondii infection in the last decade An overview. Res Vet Sci 135:371–385
Asghari A et al (2021a) Development of a chimeric vaccine candidate based on Toxoplasma gondii major surface antigen 1 and apicoplast proteins using comprehensive immunoinformatics approaches. Eur J Pharm Sci 162:105837
Asghari A, Majidiani H, Nemati T, Fatollahzadeh M, Shams M, Naserifar R, Kordi BJBri, (2021b) Toxoplasma gondii tyrosine-rich oocyst wall protein: a closer look through an in silico prism. BioMed Res Int 2021:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1315618
Austhof E et al (2021) Scoping review of toxoplasma postinfectious sequelae. Foodborne Pathog Dis 18:687–701
Brisse M, Vrba SM, Kirk N, Liang Y (2020) Emerging concepts and technologies in vaccine development. Front Immunol 11:2578
Cheng J, Randall AZ, Sweredoski MJ, PJnar B (2005) SCRATCH: a protein structure and structural feature prediction server. Nucl Acids Res 33:W72–W76
Chu KB, Quan FS (2021) Advances in Toxoplasma gondii vaccines: current strategies and challenges for vaccine development. Vaccines 9:413
Craig DB, Dombkowski AA (2013) Disulfide by Design 2.0: a web-based tool for disulfide engineering in proteins. BMC Bioinform 14:1–7
Deng H et al (2021) Mathematical modelling of Toxoplasma gondii transmission: A systematic review. Food Waterborne Parasitol 22:e00102
Dimitrov I, Bangov I, Flower DR, Doytchinova I (2014a) AllerTOP v. 2—a server for in silico prediction of allergens. J Mol Model 20:1–6
Dimitrov I, Naneva L, Doytchinova I, Bangov I (2014b) AllergenFP: allergenicity prediction by descriptor fingerprints. Bioinformatics 30:846–851
Doytchinova IA, Flower DR (2007) VaxiJen: a server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform 8:1–7
Dubey JP (2021) Outbreaks of clinical toxoplasmosis in humans: five decades of personal experience, perspectives and lessons learned. Parasit Vectors 14:1–12
Dunay IR, Gajurel K, Dhakal R, Liesenfeld O, Montoya, (2018) Treatment of toxoplasmosis: historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin Microbiol Rev 31:e00057-e117
Dupont CD, Christian DA, Hunter CA 2012 Immune response and immunopathology during toxoplasmosis. In: Seminars in immunopathology, Springer, pp 793–813
Foroutan M, Ghaffarifar F, Sharifi Z, Dalimi A (2020) Vaccination with a novel multi-epitope ROP8 DNA vaccine against acute Toxoplasma gondii infection induces strong B and T cell responses in mice Comparative Immunology. Microbiol Infect Dis 69:101413
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server The proteomics protocols handbook, pp. 571–607
Hammed-Akanmu M et al (2022) Designing a multi-epitope vaccine against toxoplasma gondii: an immunoinformatics approach. Vaccines 10:1389
Han SJC, Research (2015) Clinical vaccine development 4:46–53
Hebditch M, Carballo-Amador MA, Charonis S, Curtis R, Warwicker J (2017) Protein–Sol: a web tool for predicting protein solubility from sequence. Bioinformatics 33:3098–3100
Heo L, Park H, Seok C (2013) GalaxyRefine: Protein structure refinement driven by side-chain repacking. Nucl Acids Res 41:W384–W388
Hill D, Dubey JJCm, infection, (2002) Toxoplasma gondii: transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin Microbiol Infect 8:634–640
Jespersen MC, Peters B, Nielsen M, Pjnar M (2017) BepiPred-2.0: improving sequence-based B-cell epitope prediction using conformational epitopes. Nucl Acids Res 45:W24–W29
Khodadadi M, Ghaffarifar F, Dalimi A, Ahmadpour E (2021) Immunogenicity of in-silico designed multi-epitope DNA vaccine encoding SAG1, SAG3 and SAG5 of Toxoplasma gondii adjuvanted with CpG-ODN against acute toxoplasmosis in BALB/c mice. Acta Trop 216:105836
Klausen MS et al (2019) NetSurfP-2.0: Improved prediction of protein structural features by integrated deep learning proteins: structure function. Bioinformatics 87:520–527
Kozakov D et al (2017) The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nat Protoc 12:255–278
Laskowski R, MacArthur M, Thornton J (2006) PROCHECK: validation of protein-structure coordinates
Livingston B, Crimi C, Newman M, Higashimoto Y, Appella E, Sidney J, Sette A (2002) A rational strategy to design multiepitope immunogens based on multiple Th lymphocyte epitopes. J Immunol 168:5499–5506
Mahdevar E et al (2021) Exploring the cancer-testis antigen BORIS to design a novel multi-epitope vaccine against breast cancer based on immunoinformatics approaches. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(14):6363–6380
Mévélec M-N, Lakhrif Z, Dimier-Poisson I (2020) Key limitations and new insights into the Toxoplasma gondii parasite stage switching for future vaccine development in human, livestock, and cats. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.607198
Meza B, Ascencio F, Sierra-Beltrán AP, Torres J, Angulo CJI (2017) A novel design of a multi-antigenic, multistage and multi-epitope vaccine against Helicobacter pylori: an in silico approach. Infect Genet Evol 49:309–317
Parvizpour S, Pourseif MM, Razmara J, Rafi MA, Omidi Y (2020) Epitope-based vaccine design: a comprehensive overview of bioinformatics approaches. Drug Discover Today 25:1034–1042
Ponomarenko J, Bui HH, Li W, Fusseder N, Bourne PE, Sette A, Peters B (2008) ElliPro: a new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform 9:1–8
Rapin N, Lund O, Castiglione F (2011) Immune system simulation online. Bioinformatics 27:2013–2014
Ras-Carmona A, Pelaez-Prestel HF, Lafuente EM, Reche PAJC (2021) BCEPS: A web server to predict linear B cell epitopes with enhanced immunogenicity and cross-reactivity. Cells 10:2744
Reed SG, Orr MT, Fox CB (2013) Key roles of adjuvants in modern vaccines. Nat Med 19:1597–1608
Rezaei F, Sarvi S, Sharif M, Hejazi SH, Sattar Pagheh A, Aghayan SA, Daryani A (2019) A systematic review of Toxoplasma gondii antigens to find the best vaccine candidates for immunization. Microial Pathog 126:172–184
Saha S, Raghava GP (2007) Prediction methods for B-cell epitopes. In: Flower DR (ed) Immunoinformatics. Humana Press, Springer, pp 387–394
Soria-Guerra RE, Nieto-Gomez R, Govea-Alonso DO, Rosales-Mendoza SJJobi, (2015) An overview of bioinformatics tools for epitope prediction: implications on vaccine development. J Biomed Inform 53:405–414
Talebi S, Bolhassani A, Sadat SM, Vahabpour R, Agi E, Shahbazi SJB (2017) Hp91 immunoadjuvant: An HMGB1-derived peptide for development of therapeutic HPV vaccines. Biomed Pharamcotherapy 85:148–154
Theisen TC, Boothroyd JCJb, (2021) Transcriptional signatures of clonally derived Toxoplasma tachyzoites reveal novel insights into the expression of a family of surface proteins. PLoS ONE 17:e0262374
UniProt Consortium (2019) UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucl Acids Res 47:D506–D515
Wasmuth JD et al (2012) Integrated bioinformatic and targeted deletion analyses of the SRS gene superfamily identify SRS29C as a negative regulator of Toxoplasma virulence. Mbbio 3:e00321-e1312
Yang J, Zhang Y (2015) I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucl Acids Res 43:W174–W181
Yao B, Zheng D, Liang S, Zhang C (2020) SVMTriP: a method to predict B-cell linear antigenic epitopes. Immunoinformatics 299–307
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the staff of zoonotic diseases research center Ilam University of Medical Sciences, Ilam, Iran for their kind assistance in preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and NN conceived the study idea and protocol; HH, MCB and EG performed bioinformatics analyses, vaccine construction and subsequent validations; BNG and HM drafted the manuscript; HI performed docking analysis; MS and NN critically revised the work. All authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare none.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shams, M., Heydaryan, S., Bashi, M.C. et al. In silico design of a novel peptide-based vaccine against the ubiquitous apicomplexan Toxoplasma gondii using surface antigens. In Silico Pharmacol. 11, 5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-023-00140-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-023-00140-w