Abstract
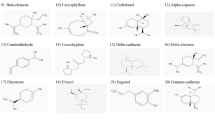
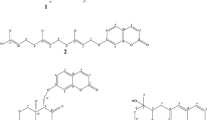
Cannabis sativa L. Cannabaceae, used for psychoactive rituals in Mesopotamia. Here, we investigated in vitro inhibitory activity of methyl alcohol extract derived from leaves and resin of cannabis against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE). Moreover, the binding affinity (BA; kcal/mol) of selected phytochemicals of cannabis to AChE and BChE has been predicted in silico. Phytochemicals of cannabis had acceptable BA towards AChE ranging from – 6.4 (beta-pinene) to – 11.4 (campesterol) and BChE ranging from – 5.5 (alpha-pinene) to – 9.8 (cannabioxepane). All cannabinoids, flavonoids (apigenin), terpenes, and phytosterols of cannabis were double inhibitors due they utilized hydrogen bonds and hydrophobically interacted with both catalytic triad and peripheral anionic site (PAS) of AChE and BChE. Campesterol is phytosterol docked with AChE and BChE via hydrogen bond and it will be a lead-like molecule for further drug design. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid has been docked with AChE and BChE and it can be a candidate molecule for further drug design. To sum up, this study not only approved cholinesterase inhibitory effects of cannabis but also suggested an array of phytocompounds as hit small molecules for discovery or design of ecofriendly botanical antiinsectants or phytonootropic drugs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali M, Muhammad S, Shah MR, Khan A, Rashid U, Farooq U, Ullah F, Sadiq A, Ayaz M, Ali M, Latif A, Ahmad M (2017) Neurologically potent molecules from Crataegus oxyacantha; isolation, anticholinesterase inhibition, and molecular docking. Front Pharmacol 8:327
Bajda M, Więckowska A, Hebda M, Guzior N, Sotriffer CA, Malawska B (2013) Structure-based search for new inhibitors of cholinesterases. Int J Mol Sci 14(3):5608–5632
Balkis A, Tran K, Lee YZ, Ng K (2015) Screening flavonoids for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase identified baicalein as the most potent inhibitor. J Agric Sci 7(9):26
Beard CM, Kokmen E, O’brien PC, Kurland LT (1995) The prevalence of dementia is changing over time in Rochester, Minnesota. Neurology 45(1):75–79
Berman HM, Battistuz T, Bhat TN, Bluhm WF, Bourne PE, Burkhardt K, Fagan P (2002) The protein data bank. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:899–907
Carod-Artal FJ (2013) Psychoactive plants in ancient Greece. Neurosci History 1(1):28–38
Cheng F, Li W, Zhou Y, Shen J, Wu Z, Liu G, Lee PW, Tang Y (2012) Admetsar: a comprehensive source and free tool for assessment of chemical admet properties. J Chem Inf Model 52:3099–3105
Dallakyan S, Olson AJ (2015) Small–molecule library screening by docking with PyRx. Methods Mol Biol 1263:243–450
Darvesh S, Hopkins DA, Geula C (2003) Neurobiology of butyrylcholinesterase. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(2):131
Ding X, Ouyang MA, Liu X, Wang RZ (2013) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of flavonoids from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba against brown planthopper. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/645086
Dohi S, Terasaki M, Makino M (2009) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and chemical composition of commercial essential oils. J Agric Food Chem 57(10):4313–4318
Eichler JERRY, Anselment A, Sussman JL, Massoulié JEAN, Silman ISRAEL (1994) Differential effects of" peripheral" site ligands on Torpedo and chicken acetylcholinesterase. Mol Pharmacol 45(2):335–340
Ellman GL, Courtney DK, Andreas V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Elufioye TO, Obuotor EM, Agbedahunsi JM, Adesanya SA (2017) Anticholinesterase constituents from the leaves of Spondias mombin L. (Anacardiaceae). Biol Targets Therapy 11:107
Fischedick JT, Hazekamp A, Erkelens T, Choi YH, Verpoorte R (2010) Metabolic fingerprinting of Cannabis sativa L. cannabinoids and terpenoids for chemotaxonomic and drug standardization purposes. Phytochemistry. 71(17–18):2058–2073
Flores-Sanchez IJ, Verpoorte R (2008) Secondary metabolism in cannabis. Phytochem Rev 7(3):615–639
Gitau WJ (2015) Evaluation of the composition, physico-chemical characteristics, surfactant and anti-microbial potential of Commiphora abyssinica gum resin (doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi)
Greig NH, Lahiri DK, Sambamurti K (2002) Butyrylcholinesterase: an important new target in Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Int Psychogeriatr 14(S1):77–91
Grotenhermen F, Russo EB (2006) Handbook of Cannabis Therapeutics: From Bench to Bedside; [a Compilation of Selected Articles from the Journal of Cannabis Therapeutics... from 2001 to 2004]. Haworth Press
Gulluni N, Re T, Loiacono I, Lanzo G, Gori L, Macchi C, Epifani F, Bragazzi N, Firenzuoli F (2018) Cannabis essential oil: a preliminary study for the evaluation of the brain effects. eCAM. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1709182
Hartsel, J. A., Eades, J., Hickory, B., Makriyannis, A. 2016. Cannabis sativa and Hemp. In Nutraceuticals (pp. 735–754).
Houghton PJ, Ren Y, Howes MJ (2006) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from plants and fungi. Natural Prod Rep 23(2):181–199
Kendall D, Alexander S (2017) Cannabinoid Pharmacology (Vol. 80). Academic Press
Klocke JA, Darlington MV, Balandrin MF (1987) 1, 8-Cineole (Eucalyptol), a mosquito feeding and ovipositional repellent from volatile oil of Hemizonia fitchii (Asteraceae). J Chem Ecol 13(12):2131–2141
Kua J, Zhang Y, Eslami AC, Butler JR, McCammon JA (2003) Studying the roles of W86, E202, and Y337 in binding of acetylcholine to acetylcholinesterase using a combined molecular dynamics and multiple docking approach. Protein Sci 12(12):2675–2684
Lee DC, Ahn YJ (2013) Laboratory and simulated field bioassays to evaluate larvicidal activity of Pinus densiflora hydrodistillate, its constituents and structurally related compounds against Aedes albopictus, Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens pallens in relation to their inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase activity. Insects 4:217–229
Li HY, Liu XC, Chen XB, Liu QZ, Liu ZL (2015) Chemical composition and insecticidal activities of the essential oil of Clinopodium chinense (Benth) Kuntze aerial parts against Liposcelis bostrychophila badonnel. J Food Prot 78(10):1870–1874
Loizzo MR, Tundis R, Menichini F, Menichini F (2008) Natural products and their derivatives as cholinesterase inhibitors in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: an update. Curr Med Chem 15(12):1209–1228
Lomarat P, Sripha K, Phanthong P, Kitphati W, Thirapanmethee K, Bunyapraphatsara N (2015) In vitro biological activities of black pepper essential oil and its major components relevant to the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Thai J Pharm Sci 39(3)
McPartland JM (1997) Cannabis as repellent and pesticide. J Int Hemp Assoc 4(2):89–94
Miyazawa M, Yamafuji C (2006) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity by tea tree oil and constituent terpenoids. Flavour Fragrance J 21(2):198–201
Mogana R, Adhikari A, Debnath S, Hazra S, Hazra B, Teng-Jin K, Wiart C (2014) 2014. The antiacetylcholinesterase and antileishmanial activities of Canarium patentinervium Miq, Biomed Research International
Montserrat-de la Paz S, Marín-Aguilar F, García-Gimenez MD, Fernández-Arche MA (2014) Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil: analytical and phytochemical characterization of the unsaponifiable fraction. J Agric Food Chem 62(5):1105–1110
Murugesan S, Rajeshkannan C, Suresh Babu D, Sumathi R, Manivachakam P (2012) Identification insecticidal properties in common weed-Lantana camara Linn. by gas chromatography and mass spectrum (GC-MS-MS). Adv Appl Sci Res 3(5):2754–2759
Omri AE, Han J, Kawada K, Abdrabbah MB, Isoda H (2012) Luteolin enhances cholinergic activities in PC12 cells through ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Brain Res 1437:16–25
Onyenekwe PC, Stahl M, Adejo G (2012) Post-irradiation changes of the volatile oil constituents of Monodora myristica (Gaertn) Dunal. Nat Prod Res 26(21):2030–2034
Ordentlich A, Barak D, Kronman C, Ariel N, Segall Y, Velan B, Shafferman A (1998) Functional characteristics of the oxyanion hole in human acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem 273(31):19509–19517
Owokotomo IA, Ekundayo O, Abayomi TG, Chukwuka AV (2015) In-vitro anti-cholinesterase activity of essential oil from four tropical medicinal plants. Toxicol Rep 2:850–857
Pagani A, Scala F, Chianese G, Grassi G, Appendino G, Taglialatela-Scafati O (2011) Cannabioxepane, a novel tetracyclic cannabinoid from hemp, Cannabis sativa L. Tetrahedron 67(19):3369–3373
Radic Z, Gibney G, Kawamoto S, MacPhee-Quigley K, Bongiorno C, Taylor P (1992) Expression of recombinant acetylcholinesterase in a baculovirus system: kinetic properties of glutamate 199 mutants. Biochemistry 31(40):9760–9767
Rothschild M, Bergström G, Wängberg SÅ (2005) Cannabis sativa: volatile compounds from pollen and entire male and female plants of two variants, Northern Lights and Hawaian Indica. Bot J Linn Soc 147(4):387–397
Russo EB (2007) History of cannabis and its preparations in saga, science, and sobriquet. Chem Biodivers 4(8):1614–1648
Ryz NR, Remillard DJ, Russo EB (2017) Cannabis roots: a traditional therapy with future potential for treating inflammation and pain. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 2(1):210–216
Schuster D, Spetea M, Music M, Rief S, Fink M, Kirchmair J, Schütz J, Wolber G, Langer T, Stuppner H, Rollinger JM, Schmidhammer H (2010) Morphinans and isoquinolines: acetylcholinesterase inhibition, pharmacophore modeling, and interaction with opioid receptors. Bioorg Med Chem 18(14):5071–5080
Sfara V, Zerba EN, Alzogaray RA (2009) Fumigant insecticidal activity and repellent effect of five essential oils and seven monoterpenes on first-instar nymphs of Rhodnius prolixus. J Med Entomol 46(3):511–515
Shanmuganathan B, Malar DS, Sathya S, Devi KP (2015) Antiaggregation potential of Padina gymnospora against the toxic Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide 25–35 and cholinesterase inhibitory property of its bioactive compounds. PLoS ONE 10(11):e0141708
Shoaib M, Shah I, Ali N, Shah SWA (2015) In vitro acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory potentials of essential oil of Artemisia macrocephala. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 10:87–91
Soreq H, Zakut H (1993) Human Cholinesterases and Anticholinesterases. Academic Press, New York
Sriraksa N, Wattanathorn J, Muchimapura S, Tiamkao S, Brown K, Chaisiwamongkol K (2012) Cognitive-enhancing effect of quercetin in a rat model of Parkinson's disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine. Evidence Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Suárez D, Field MJ (2005) Molecular dynamics simulations of human butyrylcholinesterase. Proteins Struct Func Bioinform 59(1):104–117
Sussman JL, Harel M, Frolow F, Oefner C, Goldman A, Toker L, Silman I (1991) Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science 253(5022):872–879
Taylor P, Radic Z (1994) The cholinesterases: from genes to proteins. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 34(1):281–320
Teall EK (2014) Medicine and doctoring in ancient Mesopotamia. Grand Valley J History 3(1):2
Thomsen R, Christensen MH (2006) Mol Dock: a new technique for high–accuracy molecular docking. J Med Chem 49:3315–3321
Turner CE, Elsohly MA, Boeren EG (1980) Constituents of Cannabis sativa L XVII A review of the natural constituents. J Nat Prod 43(2):169–234
Vellom DC, Radic Z, Li Y, Pickering NA, Camp S, Taylor P (1993) Amino acid residues controlling acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase specificity. Biochemistry 32(1):12–17
Wang ZT (2013) Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of β-carboline and quinoline alkaloids derivatives from the plants of genus Peganum. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/717232
Acknowledgement
IK and NY conceptualized the idea of this paper and BAH and IK conceived experimental and computational works and wrote the initial draft, and IK and NY critically revised and prepared the final manuscript. This paper originated from MSc thesis of third author submitted to Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Razi University 67149-67346, Kermanshah, Iran. This study was supported by intramural fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi, I., Yousofvand, N. & Hussein, B.A. In vitro cholinesterase inhibitory action of Cannabis sativa L. Cannabaceae and in silico study of its selected phytocompounds. In Silico Pharmacol. 9, 13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-021-00075-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40203-021-00075-0