Abstract
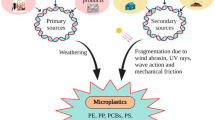
In this work, the amount and physical and chemical characteristics of airborne microplastics (MPs) pollution in dust samples in Sistan, located in the eastern part of Iran, is reported. Sampling stations were selected according to the wind direction and population density. MPs were collected by a static dust sampler and analyzed by optical microscopy and FT-IR spectroscopy. Results showed that the distribution frequency of MPs in residential and non-residential areas was 6 to 11 pieces per 100 g (pcs/100 g) with an average abundance of 9.8 pcs/100 g. Fragmented MPs were approximately consisted 64% of total MPs and their sizes were in the range of 0.9–3.8 mm. Polyethylene (49%), polystyrene (21%) and polyester (18%) were the main MPs presented in the dust samples. It was observed that population density and wind direction were the most important parameters affecting MPs pollution in dust.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Kitahara K-I, Nakata H. Sci Total Environ. 2020;736:139694.
Lindeque PK, Cole M, Coppock RL, Lewis CN, Miller RZ, Watts AJ, Wilson-McNeal A, Wright SL, Galloway TS. Environ Pollut. 2020;265:114721.
Rillig MC, Lehmann A. Science 2020;368(6498):1430–1431.
Haave M, Lorenz C, Primpke S, Gerdts G. Mar Pollut Bull. 2019;141:501–13.
Alam FC, Sembiring E, Muntalif BS, Suendo V. Chemosphere. 2019;224:637–45.
Xue B, Zhang L, Li R, Wang Y, Guo J, Yu K, Wang S. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(4):2210–7.
Dewar-Fowler VH. 2017. Uptake and Biological Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Sea Squirts, Master’s Thesis, University of Exeter.
Szymańska M, Obolewski K. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol. 2020;20(3):333–45.
Gola D, Tyagi PK, Arya A, Chauhan N, Agarwal M, Singh S, Gola S. Environ Nanatechnol Monit Manage. 2021;16:100552.
Brahney J, Mahowald N, Prank M, Cornwell G, Klimont Z, Matsui H, Prather KA. Proceed Nat Acad Sci. 2021, 118 (16), e2020719118.
Bergmann M, Lutz B, Tekman MB, Gutow L. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125 (1–2), 535–540.
Wang F, Lai Z, Peng G, Luo L, Liu K, Huang X, Xu Y, Shen Q, Li D. Sci Total Environ. 2021;800:149529.
Du J, Zhou Q, Li H, Xu S, Wang C, Fu L, Tang J. J Appl Toxicol 2021, 41 (1), 52–64.
Rashki A, Eriksson PG, Rautenbach CdW, Kaskaoutis DG, Grote W, Dykstra J. Chemosphere. 2013;90(2):227–36.
Ahmadi S, Ezeliora C, Sharki S, Osagie C, Ghosh S, Igwegbe C, Khan N. Int J Environ Sci Technol 2021, 1–14.
Behrooz RD, Esmaili-Sari A, Bahramifar N, Kaskaoutis D, Saeb K, Rajaei F. Aeolian Res 2017, 25, 87–105.
Behrooz RD, Kaskaoutis D, Grivas G, Mihalopoulos N. Chemosphere. 2021;262:127835.
Peng G, Zhu B, Yang D, Su L, Shi H, Li D. Environ Pollut. 2017;225:283–90.
Liu K, Wu T, Wang X, Song Z, Zong C, Wei N, Li D. Environ Sci Technol. 2019;53(18):10612–9.
Obbard RW. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health. 2018;1:24–9.
Abbasi S, Turner A, Hoseini M, Amiri H. Environ Sci Technol. 2021;55(9):5993–6000.
Abidli S, Toumi H, Lahbib Y, Trigui El Menif, N. Water, Air, & Soil Pollut 2017, 228 (7), 1–10.
Chen G, Feng Q, Wang J. Sci Total Environ. 2020;703:135504.
Liu K, Wang X, Fang T, Xu P, Zhu L, Li D. Sci Total Environ. 2019;675:462–71.
Dehghani S, Moore F, Akhbarizadeh R. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2017;24 (25):20360–20371.
Perez L, Tobías A, Querol X, Pey J, Alastuey A, Díaz J, Sunyer J. Environ Int. 2012;48:150–5.
Klein M, Fischer EK. Sci Total Environ. 2019;685:96–103.
Mbachu O, Jenkins G, Pratt C, Kaparaju P. Water, Air & Soil Pollution 2020;231(2):1–27.
Prata JC. Environmental Pollution 2018, 234, 115–126.
Abbasi S, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Turner A, Kelly FJ, Dominguez AO, Jaafarzadeh N. Environ Pollut. 2019;244:153–64.
Vianello A, Jensen RL, Liu L, Vollertsen J. Scientific Reports 2019;9(1):1–11.
Begum SA, Rane AV, Kanny K, Applications of compatibilized polymer blends in automobile industry. In Compatibilization of Polymer Blends, Elsevier: 2020; pp 563–593.
Dris R, Gasperi J, Mirande C, Mandin C, Guerrouache M, Langlois V, Tassin B. Environ pollut 2017; 221:453–458.
Purwiyanto AIS, Prartono T, Riani E, Naulita Y, Cordova MR, Koropitan AF. Mar Pollut Bull. 2022;174:113195.
Liu J, Zhu X, Teng J, Zhao J, Li C, Shan E, Zhang C, Wang Q. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021;107:693–9.
Funding
This study was funded by Zabol University of Medical Sciences and the University of Sistan and Baluchestan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MRRK planned the study, performed the practical work and wrote the manuscript. MS co-wrote the manuscript and interpret the data. JP performed data modeling. AS performed the practical work. MK planned the revised study and co-wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahraki, M., Rezaei Kahkha, M., Piri, J. et al. Microplastics in atmospheric dust samples of Sistan: sources and distribution. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 20, 931–936 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-022-00833-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-022-00833-y