Abstract
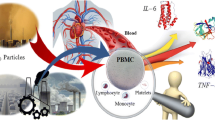
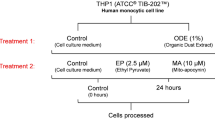
Long-term exposure to airborne particles of 10 µm and less in size (PM10) in dust can lead to increased risk of diseases such as respiratory, cardiovascular, lung cancer and atherosclerosis. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of water-soluble PM10 particles in the Middle East Dust (MED) storm in Ahvaz, Iran, on the production of TNF-α by human monocytes. In addition, we assessed the level of induction of apoptosis in isolated A549 human pulmonary epithelial cells. For this purpose, isolated human blood monocytes (250,000 to 300,000 cell/ ml) as well as isolated human pulmonary A549 epithelial cells (100,0000 cell/ ml) were exposed to various concentrations (62.5, 125, 250, 500 µg/ml) of water-soluble PM10 particles for different incubation periods (12, 24, 48 h). The results showed that exposure to PM10 particles increased the production of TNF-α in human monocytes and promoted apoptosis induction in A549 cells, in both concentration and incubation of period-dependent manner. In conclusion, airborne dust particles in Ahvaz city contain active compounds capable of increasing production of the pro-inflammatory cytokine, TNF-α, and inducing apoptosis of lung epithelial cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessandria L, Schilirò T, Degan R, Traversi D, Gilli G. Cytotoxic response in human lung epithelial cells and ion characteristics of urban-air particles from Torino, a northern Italian city. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2014;21(8):5554–64.
Alfaro-Moreno E, Martínez L, García-Cuellar C, Bonner JC, Murray JC, Rosas I,... Osornio-Vargas ÁR. Biologic effects induced in vitro by PM10 from three different zones of Mexico City. Environ Health Perspect. 2002;110(7):715–20.
Assessment NC, f. E. & NC. Air quality criteria for particulate matter (vol. 3): US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development.. . 1996.
Bølling AK, Totlandsdal AI, Sallsten G, Braun A, Westerholm R, Bergvall C,... Cassee F. Wood smoke particles from different combustion phases induce similar pro-inflammatory effects in a co-culture of monocyte and pneumocyte cell lines. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012;9(1):45.
Brook RD, Rajagopalan S, Pope CA III, Brook JR, Bhatnagar A, Diez-Roux AV,... Mittleman MA. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: an update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121(21):2331–78.
Brown D, Donaldson K, Stone V. Effects of PM 10 in human peripheral blood monocytes and J774 macrophages. Respir Res. 2004;5(1):29.
Cho H-Y, Morgan DL, Bauer AK, Kleeberger SR. Signal transduction pathways of tumor necrosis factor–mediated lung injury induced by ozone in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175(8):829–39.
Collart MA, Belin D, Vassalli J-D, De Kossodo S, Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986;164(6):2113–8.
Corsini E, Budello S, Marabini L, Galbiati V, Piazzalunga A, Barbieri P,... Galli CL. Comparison of wood smoke PM2. 5 obtained from the combustion of FIR and beech pellets on inflammation and DNA damage in A549 and THP-1 human cell lines. Arch Toxicol. 2013;87(12):2187–99.
Dagher Z, Garçon G, Billet S, Gosset P, Ledoux F, Courcot D,... Shirali P. Activation of different pathways of apoptosis by air pollution particulate matter (PM2. 5) in human epithelial lung cells (L132) in culture. Toxicology. 2006;225(1):12–24.
Dominici F, Peng RD, Ebisu K, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Bell ML. Does the affect of PM10 on mortality depend on PM nickel and vanadium content? A reanalysis of the NMMAPS data. Environ Health Perspect. 2007;115(12):1701–3.
Englert N. Fine particles and human health—a review of epidemiological studies. Toxicol Lett. 2004;149(1–3):235–42.
Essner R, Rhoades K, McBride WH, Morton D, Economou J. IL-4 down-regulates IL-1 and TNF gene expression in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989;142(11):3857–61.
Farsani MH, Shirmardi M, Alavi N, Maleki H, Sorooshian A, Babaei A, Asgharnia H, Marzouni MB, Goudarzi G. Evaluation of the relationship between PM10 concentrations and heavy metals during normal and dusty days in Ahvaz, Iran. Aeol Res. 2018;33:12–22.
Fuss IJ, Kanof ME, Smith PD, Zola H. Isolation of whole mononuclear cells from peripheral blood and cord blood. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2009;85(1):7.1. 1-7.1. 8.
Goudarzi G, Sorooshian A, Maleki H. Local and Long-Range Transport Dust Storms Over the City of Ahvaz: A Survey Based on Spatiotemporal and Geometrical Properties. Pure Appl Geophys. 2020;177(8):3979–3997
Hadaddezfuli R, Khodadadi A, Assarehzadegan M-A, Pipelzadeh MH, Saadi S. Hemiscorpius lepturus venom induces expression and production of interluckin-12 in human monocytes. Toxicon. 2015;100:27–31.
Harbizadeh A, Mirzaee SA, Khosravi AD, Shoushtari FS, Goodarzi H, Alavi N, Ankali KA, Rad HD, Maleki H, Goudarzi G. Indoor and outdoor airborne bacterial air quality in day-care centers (DCCs) in greater Ahvaz, Iran. Atmos Environ. 2019;216:116927.
Hensel G, Männel DN, Pfizenmaier K, Krönke M. Autocrine stimulation of TNF-alpha mRNA expression in HL-60 cells. Lymphokine Res. 1987;6(2):119–25.
Jansky L, Reymanova P, Kopecky J.J.P.r. Dynamics of cytokine production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated by LPS, or infected by Borrelia. Physiol Res. 2003;52(5):593–598.
Levy JI, Hammitt JK, Spengler JD. Estimating the mortality impacts of particulate matter: what can be learned from between-study variability? Environ Health Perspect. 2000;108(2):109–17.
Munker R, Gasson J, Ogawa M, Koeffler HP. Recombinant human TNF induces production of granulocyte–monocyte colony-stimulating factor. Nature. 1986;323(6083):79–81.
Naimabadi A, Ghadiri A, Idani E, Babaei AA, Alavi N, Shirmardi M,... Rouhizadeh A. Chemical composition of PM10 and it's in vitro toxicological impacts on lung cells during the Middle Eastern Dust (MED) storms in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ Pollut. 2016;211:316–24.
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. 2006;311(5761):622–7.
Nuñez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y, Inohara N. Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene. 1998;17(25):3237–45.
Park E-J, Yi J, Chung K-H, Ryu D-Y, Choi J, Park K. Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett. 2008;180(3):222–9.
Pope III, Dockery DW. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: lines that connect. J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 2006;56(6):709–42.
Rad HD, Assarehzadegan MA, Goudarzi G, Sorooshian A, Birgani YT, Maleki H, Jahantab S, Idani E, Babaei AA, Neisi A. Do Conocarpus erectus airborne pollen grains exacerbate autumnal thunderstorm asthma attacks in Ahvaz, Iran? Atmos Environ. 2019; 213:311–325.
Radmanesh E, Maleki H, Goudarzi G, Zahedi A, Kalkhajeh SG, Hopke P, Mard SA, Olad S. Cerebral ischemic attack, epilepsy and hospital admitted patients with types of headaches attributed to PM10 mass concentration in Abadan, Iran. Aeolian Res. 2019;41:100541.
Sahu D, Kannan G, Vijayaraghavan R. Carbon black particle exhibits size dependent toxicity in human monocytes. Int J Inflamm. 2014;2014:827019.
Samadi MT, Khorsandi H, Bahrami Asl F, Poorolajal J, Tayebinia H. The affect of long-term exposures to hypersaline particles originated from drying Urmia hypersaline Lake on the increased cardiovascular risks in the villagers around the Lake. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J. 2020;26(2):335–48.
Schwarze P, Øvrevik J, Låg M, Refsnes M, Nafstad P, Hetland R, Dybing E. Particulate matter properties and health effects: consistency of epidemiological and toxicological studies. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2006;25(10):559–79.
Soto K, Garza K, Murr L. Cytotoxic effects of aggregated nanomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2007;3(3):351–8.
Stein A, Draxler RR, Rolph GD, Stunder BJ, Cohen M, Ngan, F J. B. o. t. A. M. S. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull Am Meteorol Soc. 2015;96(12):2059–2077.
Sydlik U, Bierhals K, Soufi M, Abel J, Schins RP, Unfried K. Ultrafine carbon particles induce apoptosis and proliferation in rat lung epithelial cells via specific signaling pathways both using EGF-R. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;291(4):L725-33.
Upadhyay D, Panduri V, Ghio A, Kamp DW. Particulate matter induces alveolar epithelial cell DNA damage and apoptosis: role of free radicals and the mitochondria. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29(2):180–7.
van Eeden SF, Hogg JC. Systemic inflammatory response induced by particulate matter air pollution: the importance of bone-marrow stimulation. J Toxic Environ Health A. 2002;65(20):1597–613.
van Eeden SF, Tan WC, Suwa T, Mukae H, Terashima T, Fujii T,... Hogg JC. Cytokines involved in the systemic inflammatory response induced by exposure to particulate matter air pollutants (PM10). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(5):826–30.
Vogel CFA, Sciullo E, Wong P, Kuzmicky P, Kado N, Matsumura F. Induction of proinflammatory cytokines and C-reactive protein in human macrophage cell line U937 exposed to air pollution particulates. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113(11):1536–41.
Wahl LM, Smith PD. (1995). Isolation of monocyte/macrophage populations. Curr Protoc Immunol. 1995;16(1):7.6. 1-7.6. 8.
Wanidworanun C, Strober W. Predominant role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human monocyte IL-10 synthesis. J Immunol. 1993;151(12):6853–61.
Acknowledgements
The financial support for this research was done by Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (CMRC-9410). We also appreciate the department of Environmental Health Engineering, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences for preparing the samples of water-soluble dust particles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi Dehcheshmeh, M., Ghadiri, A., Rashno, M. et al. Effect of water-soluble PM10 on the production of TNF-α by human monocytes and induction of apoptosis in A549 human lung epithelial cells. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 19, 143–150 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00588-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00588-4