Abstract
Background
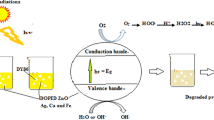
Azo dyes represent the most commonly used group of dyes in the textile industry. These organic dyes are mainly resistant to biodegradation and may exhibit toxic and carcinogenic properties. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of doping zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) with transition metals (silver, manganese, and copper) on the photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO NPs in the removal of Direct Blue 15 dye from aqueous environments under ultraviolet (UV) radiation and visible light irradiation.
Methods
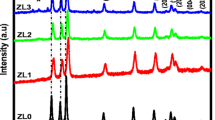
One or two metals were used for doping the NPs. In total, seven types of undoped and transition metal-doped NPs were synthesized using the thermal solvent method with ZnO precursors and transition metal salts. The characteristics of the synthesized NPs were determined based on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and zeta potential measurements.
Results
The produced ZnO NPs did not exhibit any particular photocatalytic activities under UV radiation and visible light irradiation. The highest removal efficiency under UV radiation was about 74% in the presence of silver-doped ZnO NPs, while the maximum efficiency under visible light was 70% in the presence of copper-doped ZnO NPs. The lowest removal efficiency was related to pure ZnO, which was 18.4% and 14.6% under UV and visible light irradiation, respectively. Although the efficiency of dye removal under visible light was not high compared to UV radiation, this efficiency was noteworthy in terms of both practical and economic aspects since it was achieved without the presence of ultraviolet radiation.
Conclusions
The synthesis of transition metal-doped ZnO nanophotocatalysts (with one or two metals) under UV radiation or visible light irradiation could be used as an efficient and promising technology for the photocatalytic removal of Direct Blue 15 dye from aqueous environments.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the necessary data have been given in the paper. If other investigators need our data for their works, they can contact corresponding authors through the email.
Abbreviations
- AFM:
-
Atomic Force Microscopy
- AOP:
-
Advanced Oxidation Processes
- CAS:
-
Chemical Abstracts Service
- CB:
-
Conduction Band
- DLS:
-
Dynamic Light Scattering
- EC:
-
European Community
- EDX:
-
Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
- ELS:
-
Electrophoretic Light Scattering
- FTIR:
-
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- PALS:
-
Phase Analysis Light Scattering
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- VB:
-
Valence Band
- XRD:
-
X-ray Diffraction
References
Boumaza S, Kaouah F, Hamane D, Trari M, Omeiri S, Bendjama Z. Visible light assisted decolorization of azo dyes: Direct Red 16 and Direct Blue 71 in aqueous solution on the p-CuFeO2/n-ZnO system. J Mol Catal A Chem. 2014;393:156–65.
Alvarez LH, Meza-Escalante ER, Gortáres-Moroyoqui P, Morales L, Rosas K, García-Reyes B, et al. Influence of redox mediators and salinity level on the (bio) transformation of Direct Blue 71: kinetics aspects. J Environ Manag. 2016;183:84–9.
Ertugay N, Acar FN. Removal of COD and color from Direct Blue 71 azo dye wastewater by Fenton’s oxidation: kinetic study. Arab J Chem. 2013;10:1158–63.
Saien J, Soleymani A. Degradation and mineralization of Direct Blue 71 in a circulating upflow reactor by UV/TiO2 process and employing a new method in kinetic study. J Hazard Mater. 2007;144:506–12.
Zandsalimi Y, Taimori P, Soltani RDC, Rezaee R, Abdullahi N, Safari M. Photocatalytic removal of acid red 88 dye using zinc oxide nanoparticles fixed on glass plates. J Adv Environ Health Res. 2015;3:102–10.
Shirmardi M, Mahvi AH, Mesdaghinia A, Nasseri S, Nabizadeh R. Adsorption of acid red18 dye from aqueous solution using single-wall carbon nanotubes: kinetic and equilibrium. Desalin Water Treat. 2013;51(34–36):6507–16.
Nadafi K, Vosoughi M, Asadi A, Borna MO, Shirmardi M. Reactive Red 120 dye removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on nano-alumina. J Water Chem Technol. 2014;36(3):125–33.
Shirmardi M, Mesdaghinia A, Mahvi AH, Nasseri S, Nabizadeh R. Kinetics and equilibrium studies on adsorption of acid red 18 (Azo-Dye) using multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) from aqueous solution. J Chem. 2012;9(4):2371–83.
Konicki W, Sibera D, Mijowska E, Lendzion-Bieluń Z, Narkiewicz U. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on acid dye Acid Red 88 adsorption by magnetic ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;398:152–60.
Shahmoradi B, Negahdary M, Maleki A. Hydrothermal synthesis of surface-modified, manganese-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for photodegradation of methylene blue. Environ Eng Sci. 2012;29(11):1032–7.
Mozia S, Tomaszewska M, Morawski AW. Photocatalytic degradation of azo-dye acid red 18. Desalination. 2005;185(1–3):449–56.
Sathishkumar P, Pugazhenthiran N, Mangalaraja RV, Asiri AM, Anandan S. ZnO supported CoFe2O4 nanophotocatalysts for the mineralization of Direct Blue 71 in aqueous environments. J Hazard Mater. 2013;252:171–9.
Ajmal A, Majeed I, Malik R, Iqbal M, Nadeem MA, Hussain I, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes on Cu2O-CuO/TiO2 anatase powders. J Environ Chem Eng. 2016;4(2):2138–46.
Ghaneian MT, Morovati P, Ehrampoush MH, Tabatabaee M. Humic acid degradation by the synthesized flower-like Ag/ZnO nanostructure as an efficient photocatalyst. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2014;12:138.
Zhou K, Hu X-Y, Chen B-Y, Hsueh C-C, Zhang Q, Wang J, et al. Synthesized TiO2/ZSM-5 composites used for the photocatalytic degradation of azo dye: intermediates, reaction pathway, mechanism and bio-toxicity. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;383:300–9.
Mittal M, Sharma M, Pandey OP. UV–visible light induced photocatalytic studies of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation method. Sol Energy. 2014;110:386–97.
Karimi L, Zohoori S, Yazdanshenas ME. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solutions under UV irradiation using nano-strontium titanate as the nanophotocatalyst. J Saudi Chem Soc. 2014;18(5):581–8.
Hadi M, McKay G, Samarghandi MR, Maleki A, Solaimany Aminabad M. Prediction of optimum adsorption isotherm: comparison of chi-square and log-likelihood statistics. Desalin Water Treat. 2012;49(1–3):81–94.
Senthilraja A, Subash B, Krishnakumar B, Rajamanickam D, Swaminathan M, Shanthi M. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of co-doped Ag–Au–ZnO for MB dye degradation under UV-A light. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2014;22:83–91.
Muhd Julkapli N, Bagheri S, Bee Abd Hamid S. Recent advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic decolorization of synthetic dyes. Sci World J. 2014;692307:1–25.
Samadi M, Zirak M, Naseri A, Khorashadizade E, Moshfegh AZ. Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films. 2016;605:2–19.
Elias M, Amin MK, Firoz SH, Hossain MA, Akter S, Hossain MA, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of Ce-doped ZnO/CNT composite with enhanced photo-catalytic activity. Ceram Int. 2017;43:84–91.
Xu C, Cao L, Su G, Liu W, Qu X, Yu Y. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of Co-doped ZnO powders. J Alloys Compd. 2010;497(1–2):373–6.
Subash B, Krishnakumar B, Swaminathan M, Shanthi M. Synthesis and characterization of cerium–silver co-doped zinc oxide as a novel sunlight-driven photocatalyst for effective degradation of reactive Red 120 dye. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2013;16(4):1070–8.
Soltani RDC, Jorfi S, Ramezani H, Purfadakari S. Ultrasonically induced ZnO–biosilica nanocomposite for degradation of a textile dye in aqueous phase. Ultrason Sonochem. 2016;28:69–78.
Mekasuwandumrong O, Pawinrat P, Praserthdam P, Panpranot J. Effects of synthesis conditions and annealing post-treatment on the photocatalytic activities of ZnO nanoparticles in the degradation of methylene blue dye. Chem Eng J. 2010;164(1):77–84.
Maleki A, Shahmoradi B. Solar degradation of Direct Blue 71 using surface modified iron doped ZnO hybrid nanomaterials. Water Sci Technol. 2012;65(11):1923–8.
Palmisano L, Augugliaro V, Sclafani A, Schiavello M. Activity of chromium-ion-doped titania for the dinitrogen photoreduction to ammonia and for the phenol photodegradation. J Phys Chem. 1988;92(23):6710–3.
Kumar R, Umar A, Kumar G, Akhtar MS, Wang Y, Kim SH. Ce-doped ZnO nanoparticles for efficient photocatalytic degradation of direct red-23 dye. Ceram Int. 2015;41(6):7773–82.
Chang CJ, Lin CY, Hsu MH. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ce-doped ZnO nanorods under UV and visible light. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2014;45(4):1954–63.
Subash B, Krishnakumar B, Velmurugan R, Swaminathan M, Shanthi M. Synthesis of Ce co-doped Ag–ZnO photocatalyst with excellent performance for NBB dye degradation under natural sunlight illumination. Cat Sci Technol. 2012;2(11):2319–26.
Sowa H, Ahsbahs H. High-pressure X-ray investigation of zincite ZnO single crystals using diamond anvils with an improved shape. J Appl Crystallogr. 2006;39(2):169–75.
Kathirvel P, Manoharan D, Mohan SM, Kumar S. Spectral investigations of chemical bath deposited zinc oxide thin films–ammonia gas sensor. J Optoelectron Biomed Mater. 2009;1:25–33.
Shirmardi M, Alavi N, Lima EC, Takdastan A, Mahvi AH, Babaei AA. Removal of atrazine as an organic micro-pollutant from aqueous solutions: a comparative study. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2016;103:23–35.
Kwon YJ, Kim KH, Lim CS. Characterization of ZnO nanopwders synthesized by the polymerized complex method via an organochemical route. J Ceram Process Res. 2002;3(3):146–9.
Mote VD, Huse VR, Dole BN. Synthesis and characterization of Cr doped ZnO nanocrystals. World J Condens Matter Phys. 2012;2(2):208–11.
Joshi K, Rawat M, Gautam SK, Singh RG, Ramola RC, Singh F. Band gap widening and narrowing in Cu-doped ZnO thin films. J Alloys Compd. 2016;680:252–8.
Wang R, Xin JH, Yang Y, Liu H, Xu L, Hu J. The characteristics and photocatalytic activities of silver doped ZnO nanocrystallites. Appl Surf Sci. 2004;227(1–4):312–7.
Shyni LS, Jagadish K, Srikantaswamy S, Abhilash M. Photocatalytic degradation and removal of heavy metals in pharmaceutical waste by selenium doped ZnO nano composite semiconductor. J For Res. 2016;2(5):47–54.
Suganthi KS, Rajan KS. Temperature induced changes in ZnO–water nanofluid: zeta potential, size distribution and viscosity profiles. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55(25–26):7969–80.
Mohammadzadeh S, Olya ME, Arabi AM, Shariati A, Nikou MK. Synthesis, characterization and application of ZnO-Ag as a nanophotocatalyst for organic compounds degradation, mechanism and economic study. J Environ Sci. 2015;35:194–207.
Dhatshanamurthi P, Shanthi M. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of azo dye in aqueous solutions using Ba@ Ag@ ZnO nanocomposite for self-sensitized under sunshine irradiation. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2017;42(8):5523–36.
Bordbar M, Khodadadi B, Mollatayefe N, Yeganeh FA. Influence of metal (Ag, Cd, Cu)-doping on the optical properties of ZnO nanopowder: variation of band gap. J Appl Chem. 2013;8(27):43–8.
Gallegos MV, Peluso MA, Thomas H, Damonte LC, Sambeth JE. Structural and optical properties of ZnO and manganese-doped ZnO. J Alloys Compd. 2016;689:416–24.
Li W, Wang G, Chen C, Liao J, Li Z. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanowires doped with Mn2+ and Co2+ ions. Nanomaterials. 2017;7(1):1–11.
Ullah R, Dutta J. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with manganese-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater. 2008;156(1–3):194–200.
Polat İ, Yılmaz S, Altın İ, Bacaksız E, Sökmen M. The influence of Cu-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanorods. Mater Chem Phys. 2014;148(3):528–32.
Mohan R, Krishnamoorthy K, Kim SJ. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods. Solid State Commun. 2012;152(5):375–80.
Sriram S, Lalithambika KC, Thayumanavan A. Experimental and theoretical investigations of photocatalytic activity of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. Optik. 2017;139:299–308.
Wang YY, Xie H, Zhang W, Tang YB, Chen FY. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of Fe-Ce-N tri-doped TiO2 catalysts. Adv Mater Res. 2013;750–752:1276–82.
Acknowledgments
The authors offer their thanks to the sponsors of the project.
Funding
This manuscript is extracted from the project approved by the Environmental Health Research Center and funded by the Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences (IR.MUK.REC.1396/89).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Designed the study, coordinated all the experiments, participated in manuscript preparation and final approval of the manuscript: AM, KY. Helped in manuscript preparation, data analysis and final approval of the manuscript: RE, BS. Performed laboratory tests, contributed to manuscript preparation and final approval of the manuscript: KH, HD, Contributed to data analysis and interpretation: RG, MS, and RR. Statistical analysis, critical revision: AJ, SHP. All authors reviewed and approved of the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Transition metal-doped ZnO NPs was used for photocatalytic removal of Direct Blue 15 dye.
• Photocatalytic activity of ZnO NPs was improved after doping with Ag, Mn, and Cu.
• SEM, XRD, FTIR, and AFM corroborated the synthesis of transition metal-doped NPs.
• Photocatalysis using Ag-doped ZnO NPs could degrade 74% of dye under UV radiation.
• About 70% of dye could be removed using Cu-doped ZnO NPs under visible light.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, R., Hossienzadeh, K., Maleki, A. et al. Effects of doping zinc oxide nanoparticles with transition metals (Ag, Cu, Mn) on photocatalytic degradation of Direct Blue 15 dye under UV and visible light irradiation. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 17, 479–492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00366-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00366-x