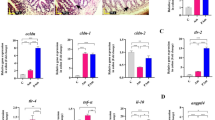
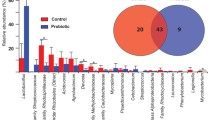
Abstract
Obesity, diabetes, and related metabolic and health conditions are significant concerns in societies worldwide, necessitating the development of effective treatment and prevention strategies. Gut microbiota, particularly Akkermansia muciniphila (A. muciniphila), have emerged as key players in the onset of obesity and diabetes due to their impact on metabolic pathways related to food absorption, low-grade inflammation, and insulin signaling. Using A. muciniphila have been identified as a promising approach in obesity and diabetes management. However, the complex culture conditions and animal-based culture medium limitations, restrict its therapeutic perspectives as a probiotic. Pasteurized A. muciniphila has been found to be safe and potentially more cost-effective compared to live strains. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) obese-diabetic models have been used in previous studies due to their functional conservation in lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis. These models offer a novel, easy-to-maintain platform for researchers studying obesity and diabetes. So, investigations are suggested to evaluate the effects of pasteurized A. muciniphila on gut microbiota composition, inflammation, and metabolic complications in an obese-diabetic zebrafish model. The findings can be translated into several potential implications and can lead to a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying the effects of A. muciniphila on obesity and diabetes in the host’s body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boles A, Kandimalla R, Reddy PH. Dynamics of diabetes and obesity: epidemiological perspective. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(5):1026–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.01.016.
Grant B, Sandelson M, Agyemang-Prempeh B, Zalin A. Managing obesity in people with type 2 diabetes. Clin Med (Lond). 2021;21(4):e327–231. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmed.2021-0370.
Baothman OA, Zamzami MA, Taher I, Abubaker J, Abu-Farha M. The role of gut microbiota in the development of obesity and diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2016;15(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-016-0278-4.
Ejtahed H-S, Angoorani P, Soroush A-R, Atlasi R, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Mortazavian AM, et al. Probiotics supplementation for the obesity management; a systematic review of animal studies and clinical trials. J Funct Foods. 2019;52:228–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.10.039.
Hasani A, Ebrahimzadeh S, Hemmati F, Khabbaz A, Hasani A, Gholizadeh P. The role of Akkermansia muciniphila in obesity, diabetes and atherosclerosis. J Med Microbiol. 2021;70(10). https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.001435.
Shahriary A, Hoseini-Tavassol Z, Soroush A-R, Ejtahed H-S, Larijani B. Comparing the effects of Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila on management of obesity and diabetes. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2021;30(193):71–83.
Ashrafian F, Keshavarz Azizi Raftar S, Shahryari A, Behrouzi A, Yaghoubfar R, Lari A, et al. Comparative effects of alive and pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila on normal diet-fed mice. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):17898. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95738-5.
Plovier H, Everard A, Druart C, Depommier C, Van Hul M, Geurts L, et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat Med. 2017;23(1):107–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4236.
Rodrigues VF, Elias-Oliveira J, Pereira ÍS, Pereira JA, Barbosa SC, Machado MSG, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and gut Immune System: a good friendship that attenuates inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Front Immunol. 2022;13:934695. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.934695.
Xu Y, Wang N, Tan H-Y, Li S, Feng Y. Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in obesity: interactions with lipid metabolism, immune response and gut systems. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:495670.
Cani PD, de Vos WM. Next-Generation Beneficial microbes: the case of Akkermansia muciniphila. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:1765. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01765.
Shirvani-Rad S, Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Mohseni S, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Soroush AR, Hoseini-Tavassol Z, et al. Probiotics as a complementary therapy for management of obesity: a systematic review. Evidence-based Complement Altern Medicine: eCAM. 2021;2021:6688450. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6688450.
Salehpour A, Rezaei M, Khoradmehr A, Tahamtani Y, Tamadon A. Which hyperglycemic model of zebrafish (Danio rerio) suites my type 2 diabetes mellitus research? A scoring system for available methods. Front Cell Dev Biology. 2021;9:438.
Zang L, Maddison LA, Chen W. Zebrafish as a model for obesity and diabetes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:91. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00091.
Mohammadi H, Manouchehri H, Changizi R, Bootorabi F, Khorramizadeh MR. Concurrent metformin and silibinin therapy in diabetes: assessments in zebrafish (Danio rerio) animal model. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020;19(2):1233–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00637-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hoseini Tavassol, Z., Ejtahed, HS. & Hasani-Ranjbar, S. Insights from the potential impact of pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila in zebrafish models of obesity and diabetes. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-024-01438-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-024-01438-y