Abstract
Objectives
Emerging publications indicate that diabetes predisposes patients with COVID-19 to more severe complications, which is partly attributed to inflammatory condition. In the current review, we reviewed recent published literature to provide evidence on the role of insulin resistance (IR) in diabetes, the association between diabetes and COVID-19 severity and mortality, the impact of COVID-19 infection on incident new-onset diabetes, mechanisms responsible for IR in COVID-19 patients, and the predictive value of different surrogates of IR in COVID-19.
Method
The literature search performs to find out studies that have assessed the association between IR surrogates and morbidity and mortality in patients with COVID-19.
Results
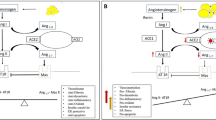
We showed that there is a bulk of evidence in support of the fact that diabetes is a potent risk factor for enhanced morbidity and mortality in COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 patients with diabetes are more prone to remarkable dysglycemia compared to those without diabetes, which is associated with an unfavourable prognosis. Furthermore, SARS-COV2 can make patients predispose to IR and diabetes via activating ISR, affecting RAAS signaling pathway, provoking inflammation, and changing the expression of PPARɣ and SREBP-1. Additionally, higher IR is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in COVID-19 patients and different surrogates of IR can be utilized as a prognostic biomarker for COVID-19 patients.
Conclusion
Different surrogates of IR can be utilized as predictors of COVID-19 complications and death.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi A, Jalilian M, Sarbarzeh PA, Vlaisavljevic Z. Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;166:108347.
Abu-Farha M, Thanaraj TA, Qaddoumi MG, Hashem A, Abubaker J, Al-Mulla F. The role of lipid metabolism in COVID-19 virus infection and as a drug target. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3544.
Accili D. Can COVID-19 cause diabetes? Nat Metab. 2021;3(2):123–5.
Affinati AH, Wallia A, Gianchandani RY. Severe hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a report of two cases. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;7(1):1–5.
Al-Goblan AS, Al-Alfi MA, Khan MZ. Mechanism linking diabetes mellitus and obesity. Diabetes, Metab Syndr Obes: Targets Ther. 2014;7:587–91. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S67400.
Al-Hakeim HK, Al-Rubaye HT, Jubran AS, Almulla AF, Moustafa SR, Maes M. Increased insulin resistance due to Long COVID is associated with depressive symptoms and partly predicted by the inflammatory response during acute infection. Braz J Psychiatry. 2023;45(3):205–15. https://doi.org/10.47626/1516-4446-2022-3002.
Al-Hakeim HK, Khairi Abed A, Rouf Moustafa S, Almulla AF, Maes M. Tryptophan catabolites, inflammation, and insulin resistance as determinants of chronic fatigue syndrome and affective symptoms in long COVID. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023;16:1194769. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2023.1194769.
Alcántara-Alonso E, Molinar-Ramos F, González-López JA, Alcántara-Alonso V, Muñoz-Pérez MA, Lozano-Nuevo JJ, Benítez-Maldonado DR, Mendoza-Portillo E. High triglyceride to HDL-cholesterol ratio as a biochemical marker of severe outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;44:437–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.04.020.
Alshammari S, AlMasoudi AS, AlBuhayri AH, AlAtwi HM, AlHwiti SS, Alaidi HM, Alshehri AM, Alanazi NA, Aljabri A, Al-Gayyar MM. Effect of COVID-19 on glycemic control, insulin resistance, and pH in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Cureus. 2023;15(2):e35390. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35390.
Alshawi A, Al-Shukry AF, Mohammed HA, Majeed TR, Abduljaleel AK, Mohammed MS. COVID-19 infection causes insulin-resistance between hospitalised patients in Najaf governorate. AIP Conf Proc. 2023;2776(1). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0135959.
Amaro ALP, Ventura JCR, Garcia LRB, Garcia EIP, Calderon JGV, Flandes RNH. Importance of insulin resistance in the COVID-19 era: a retrospective analysis of a single center in Mexico [Article]. Cureus J Med Sci. 2022;14(9):29542. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.29542.
Ashraf F, Mehmood M, Aurang Zeb M, Rehman Ju, Siddiqui FM. Evaluation of triglyceride-glucose index as a marker for severity in new onset diabetes in patients of COVID-19 pneumonia-a single center study. Access Microbiol. 2023;000548:v000543.
Atkinson MA, Powers AC. Distinguishing the real from the hyperglycaemia: does COVID-19 induce diabetes? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(6):328–9.
Ayres JS. A metabolic handbook for the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Metab. 2020;2(7):572–85.
Barron E, Bakhai C, Kar P, Weaver A, Bradley D, Ismail H, Knighton P, Holman N, Khunti K, Sattar N. Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(10):813–22.
Bellia A, Andreadi A, Giudice L, De Taddeo S, Maiorino A, D’Ippolito I, Giorgino FM, Ruotolo V, Romano M, Magrini A. Atherogenic dyslipidemia on admission is associated with poorer outcome in people with and without diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(9):2149–57.
Bellia C, Andreadi A, D’Ippolito I, Scola L, Barraco S, Meloni M, Lauro D, Bellia A. Prevalence and risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus after COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14.
Benigni A, Cassis P, Remuzzi G. Angiotensin II revisited: new roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. EMBO Mol Med. 2010;2(7):247–57.
Beydoun HA, Ng TK, Beydoun MA, Shadyab AH, Jung SY, Costanian C, Saquib N, Ikramuddin FS, Pan K, Zonderman AB. Biomarkers of glucose homeostasis as mediators of the relationship of body mass index and waist circumference with COVID-19 outcomes among postmenopausal women: The Women’s Health Initiative. Clin Nutr. 2023;42(9):1690–700.
Beydoun HA, Ng TKS, Beydoun MA, Shadyab AH, Jung SY, Costanian C, Saquib N, Ikramuddin FS, Pan K, Zonderman AB, Manson JE. Biomarkers of glucose homeostasis as mediators of the relationship of body mass index and waist circumference with COVID-19 outcomes among postmenopausal women: the women’s health initiative. Clin Nutr. 2023;42(9):1690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2023.07.004.
Biter Hİ, Kalyoncuoğlu M, Tosu AR, Çakal S, Apaydın Z, Gümüşdağ A, Çınar T, Eyüpkoca F, Belen E, Can MM. Prognostic value of the TyG index for in-hospital mortality in nondiabetic COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2022;68:1297–302.
Boles A, Kandimalla R, Reddy PH. Dynamics of diabetes and obesity: Epidemiological perspective. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(5):1026–36.
Borrayo G, Basurto L, González-Escudero E, Diaz A, Vázquez A, Sánchez L, Hernández- González GO, Barrera S, Degollado JA, Córdova N, Avelar F. TG/HDL-C ratio as cardio-metabolic biomarker even in normal weight women. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2018;14(2):261–7. https://doi.org/10.4183/aeb.2018.261.
Burke SD, Zsengellér ZK, Khankin EV, Lo AS, Rajakumar A, DuPont JJ, McCurley A, Moss ME, Zhang D, Clark CD. Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 promotes angiotensin II sensitivity in preeclampsia. J Clin Investig. 2016;126(7):2561–74.
Calcaterra V, Biganzoli G, Dilillo D, Mannarino S, Fiori L, Pelizzo G, Zoia E, Fabiano V, Carlucci P, Camporesi A, Corti C, Mercurio G, Izzo F, Biganzoli E, Zuccotti G. Non-thyroidal illness syndrome and SARS-CoV-2-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children [Article]. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022;45(1):199–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01647-9.
Cao X, Yang F, Shi T, Yuan M, Xin Z, Xie R, Li S, Li H, Yang J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1–7)/Mas axis activates Akt signaling to ameliorate hepatic steatosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21592.
Ceriello A, De Nigris V, Prattichizzo F. Why is hyperglycaemia worsening COVID-19 and its prognosis? Diabetes, Obes Metab. 2020;22(10):1951.
Chang Y, Jeon J, Song TJ, Kim J. Association of triglyceride-glucose index with prognosis of COVID-19: A population-based study. J Infect Public Health. 2022;15(8):837–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2022.06.014.
Chang Y, Jeon J, Song TJ, Kim J. Association of triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with severe complications of COVID-19. Heliyon. 2023;9(6):e17428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17428.
Chen M, Zhu B, Chen D, Hu X, Xu X, Shen W-J, Hu C, Li J, Qu S. COVID-19 may increase the risk of insulin resistance in adult patients without diabetes: a 6-month prospective study. Endocr Pract. 2021;27(8):834–41.
Chen MC, Zhu B, Chen D, Hu XZ, Xu XQ, Shen WJ, Hu CC, Li J, Qu S. COVID-19 may increase the risk of insulin resistance in adult patients without diabetes: a 6-month prospective study [Article]. Endocr Pract. 2021;27(8):834–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eprac.2021.04.004.
Chidambaram V, Tun NL, Haque WZ, Majella MG, Sivakumar RK, Kumar A, Hsu AT-W, Ishak IA, Nur AA, Ayeh SK. Factors associated with disease severity and mortality among patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0241541.
Cohen P. The twentieth century struggle to decipher insulin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(11):867–73.
Corona G, Pizzocaro A, Vena W, Rastrelli G, Semeraro F, Isidori AM, Pivonello R, Salonia A, Sforza A, Maggi M. Diabetes is most important cause for mortality in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021;22:275–96.
Cromer SJ, Colling C, Schatoff D, Leary M, Stamou MI, Selen DJ, Putman MS, Wexler DJ. Newly diagnosed diabetes vs. pre-existing diabetes upon admission for COVID-19: Associated factors, short-term outcomes, and long-term glycemic phenotypes. J Diabetes Complicat. 2022;36(4):108145.
da Silva A, Caldas APS, Rocha DMUP, Bressan J. Triglyceride-glucose index predicts independently type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Prim Care Diabetes. 2020;14(6):584–93.
DeBose-Boyd RA, Ye J. SREBPs in lipid metabolism, insulin signaling, and beyond. Trends Biochem Sci. 2018;43(5):358–68.
Desterke C, Turhan AG, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Griscelli F. PPARγ cistrome repression during activation of lung monocyte-macrophages in severe COVID-19. Iscience. 2020;23(10):101611.
Dhakal BP, Sweitzer NK, Indik JH, Acharya D, William P. SARS-CoV-2 infection and cardiovascular disease: COVID-19 heart. Heart Lung Circ. 2020;29(7):973–87.
Donnelly N, Gorman AM, Gupta S, Samali A. The eIF2α kinases: their structures and functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70:3493–511.
Dupont V, Kanagaratnam L, Goury A, Poitevin G, Bard M, Julien G, Bonnivard M, Champenois V, Noel V, Mourvillier B. Excess soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 correlates with endothelial dysfunction and organ failure in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72(10):1834–7.
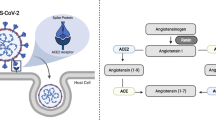
Elshafei A, Khidr EG, El-Husseiny AA, Gomaa MH. RAAS, ACE2 and COVID-19; a mechanistic review. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(11):6465–70.
Fabre B, Machulsky NF, Olano C, Jacobsen D, Gomez ME, Perazzi B, Zago V, Zopatti D, Ferrero A, Schreier L, Berg G. Remnant cholesterol levels are associated with severity and death in COVID-19 patients. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):17584. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21177-5.
Fahed M, Abou Jaoudeh MG, Merhi S, Mosleh JMB, Ghadieh R, Al Hayek S, El Hayek Fares JE. Evaluation of risk factors for insulin resistance: a cross sectional study among employees at a private university in Lebanon. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020;20:1–14.
Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(4):e21.
Finucane FM, Davenport C. Coronavirus and obesity: could insulin resistance mediate the severity of Covid-19 infection? Front Public Health. 2020;8:184.
Gangadharan C, Ahluwalia R, Sigamani A. Diabetes and COVID-19: Role of insulin resistance as a risk factor for COVID-19 severity. World J Diabetes. 2021;12(9):1550.
Garcia-Carretero R, Vazquez-Gomez O, Lopez-Lomba M, Gil-Prieto R, Gil-de-Miguel A. Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome as risk factors for hospitalization in patients with COVID-19: pilot study on the use of machine learning. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2023.0083.
Gojda J, Koudelková K, Ouřadová A, Lang A, Krbcová M, Gvozdeva A, Šebo V, Slagmolen L, Potočková J, Tůma P, Rossmeislová L, Anděl M, Karpe F, Schlesinger S. Severe COVID-19 associated hyperglycemia is caused by beta cell dysfunction: a prospective cohort study. Nutr Diabetes. 2023;13(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-023-00241-7.
Govender N, Khaliq OP, Moodley J, Naicker T. Insulin resistance in COVID-19 and diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021;15(4):629–34.
Goyal A, Gupta Y, Kalaivani M, Bhatla N, Tandon N. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 on progression of glycemic and cardiometabolic variables and changes in insulin indices: a longitudinal study. Diabetes Ther. 2021;12(11):3011–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-021-01158-z.
Grygiel-Górniak B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: nutritional and clinical implications-a review. Nutr J. 2014;13:1–10.
Gutch M, Kumar S, Razi SM, Gupta KK, Gupta A. Assessment of insulin sensitivity/resistance. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;19(1):160–4. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.146874.
Hartmann-Boyce J, Rees K, Perring JC, Kerneis SA, Morris EM, Goyder C, Otunla AA, James OE, Syam NR, Seidu S. Risks of and from SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 in people with diabetes: a systematic review of reviews. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(12):2790–811.
He X, Liu C, Peng J, Li Z, Li F, Wang J, Hu A, Peng M, Huang K, Fan D. COVID-19 induces new-onset insulin resistance and lipid metabolic dysregulation via regulation of secreted metabolic factors. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):427.
Hirata AE, Alvarez-Rojas F, Carvalheira JBC, de Oliveira Carvalho CR, Dolnikoff MS, Saad MJA. Modulation of IR/PTP1B interaction and downstream signaling in insulin sensitive tissues of MSG-rats. Life Sci. 2003;73(11):1369–81.
Hou Y, Moreau F, Chadee K. PPARγ is an E3 ligase that induces the degradation of NFκB/p65. Nat Commun. 2012;3(1):1300.
Ide T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Matsuzaka T, Nakakuki M, Yamamoto T, Nakagawa Y, Takahashi A, Suzuki H, Sone H. SREBPs suppress IRS-2-mediated insulin signalling in the liver. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(4):351–7.
Kai H, Kai M. Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors—lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19. Hypertens Res. 2020;43(7):648–54.
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G, Quon MJ. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(7):2402–10. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.85.7.6661.
Khatami F, Saatchi M, Zadeh SST, Aghamir ZS, Shabestari AN, Reis LO, Aghamir SMK. A meta-analysis of accuracy and sensitivity of chest CT and RT-PCR in COVID-19 diagnosis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):22402.
Khunti K, Del Prato S, Mathieu C, Kahn SE, Gabbay RA, Buse JB. COVID-19, hyperglycemia, and new-onset diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(12):2645–55.
Klip A, McGraw TE, James DE. Thirty sweet years of GLUT4. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(30):11369–81.
Konigshoff M, Wilhelm A, Jahn A, Sedding D, Amarie OV, Eul B, Seeger W, Fink L, Gunther A, Eickelberg O. The angiotensin II receptor 2 is expressed and mediates angiotensin II signaling in lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;37(6):640–50.
Lauterbach MA, Wunderlich FT. Macrophage function in obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Pflügers Archiv-Eur J Physiol. 2017;469:385–96.
Lee W, Ahn JH, Park HH, Kim HN, Kim H, Yoo Y, Shin H, Hong KS, Jang JG, Park CG. COVID-19-activated SREBP2 disturbs cholesterol biosynthesis and leads to cytokine storm. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):186.
Leiria LO, Arantes-Costa FM, Calixto MC, Alexandre EC, Moura RF, Folli F, Prado CM, Prado MA, Prado VF, Velloso LA. Increased airway reactivity and hyperinsulinemia in obese mice are linked by ERK signaling in brain stem cholinergic neurons. Cell Rep. 2015;11(6):934–43.
Lemieux I, Lamarche B, Couillard C, Pascot A, Cantin B, Bergeron J, Dagenais GR, Després JP. Total cholesterol/HDL cholesterol ratio vs LDL cholesterol/HDL cholesterol ratio as indices of ischemic heart disease risk in men: the Quebec Cardiovascular Study. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(22):2685–92. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.161.22.2685.
Li G, Chen Z, Lv Z, Li H, Chang D, Lu J. Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: associations and possible mechanisms. Int J Endocrinol. 2021;2021:1.
Li S, Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Bifurcation of insulin signaling pathway in rat liver: mTORC1 required for stimulation of lipogenesis, but not inhibition of gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107(8):3441-3446.
Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J Pharm Anal. 2020;10(2):102–8.
Liontos A, Biros D, Kavakli A, Matzaras R, Tsiakas I, Athanasiou L, Samanidou V, Konstantopoulou R, Vagias I, Panteli A. Glycemic dysregulation, inflammation and disease outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: beyond diabetes and obesity. Viruses. 2023;15(7):1468.
Liontos A, Biros D, Kavakli A, Matzaras R, Tsiakas I, Athanasiou L, Samanidou V, Konstantopoulou R, Vagias I, Panteli A, Pappa C, Kolios NG, Nasiou M, Pargana E, Milionis H, Christaki E. Glycemic dysregulation, inflammation and disease outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: beyond diabetes and obesity. Viruses. 2023;15(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071468
Liu H, Liu J, Liu J, Xin S, Lyu Z, Fu X. Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, a simple but effective indicator in predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:828581. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.828581.
Liu X, Tan Z, Huang Y, Zhao H, Liu M, Yu P, Ma J, Zhao Y, Zhu W, Wang J. Relationship between the triglyceride-glucose index and risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21(1):1–17.
Lu PD, Harding HP, Ron D. Translation reinitiation at alternative open reading frames regulates gene expression in an integrated stress response. J Cell Biol. 2004;167(1):27–33.
Mahmudpour M, Vahdat K, Keshavarz M, Nabipour I. The COVID-19-diabetes mellitus molecular tetrahedron. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(5):4013–24.
Mehraeen E, Dadras O, Afsahi AM, Karimi A, Pour MM, Mirzapour P, Barzegary A, Behnezhad F, Habibi P, Salehi MA. Vaccines for COVID-19: a systematic review of feasibility and effectiveness. Infect Disord-Drug Targets (Formerly Curr Drug Targets-Infect Disord). 2022;22(2):65–78.
Minh HV, Tien HA, Sinh CT, Thang DC, Chen CH, Tay JC, Siddique S, Wang TD, Sogunuru GP, Chia YC. Assessment of preferred methods to measure insulin resistance in Asian patients with hypertension. J Clin Hypertens. 2021;23(3):529–37.
Minh HV, Tien HA, Sinh CT, Thang DC, Chen CH, Tay JC, Siddique S, Wang TD, Sogunuru GP, Chia YC, Kario K. Assessment of preferred methods to measure insulin resistance in Asian patients with hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2021;23(3):529–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.14155.
Montefusco L, Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Loretelli C, Rossi A, Pastore I, Daniele G, Abdelsalam A, Maestroni A, Dell’Acqua M, Ippolito E, Assi E, Usuelli V, Seelam AJ, Fiorina RM, Chebat E, Morpurgo P, Lunati ME, Bolla AM, Finzi G, Abdi R, Bonventre JV, Rusconi S, Riva A, Corradi D, Santus P, Nebuloni M, Folli F, Zuccotti GV, Galli M, Fiorina P. Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Metab. 2021;3(6):774–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00407-6.
Montefusco L, Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Loretelli C, Rossi A, Pastore I, Daniele G, Abdelsalam A, Maestroni A, Dell’Acqua M. Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Metab. 2021;3(6):774–85.
Pal R, Bhansali A. COVID-19, diabetes mellitus and ACE2: the conundrum. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162.
Park G-M, Cho Y-R, Won K-B, Yang YJ, Park S, Ann SH, Kim Y-G, Park EJ, Kim S-J, Lee S-G. Triglyceride glucose index is a useful marker for predicting subclinical coronary artery disease in the absence of traditional risk factors. Lipids Health Dis. 2020;19:1–7.
Peric S, Stulnig TM. Diabetes and COVID-19: disease—management—people. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2020;132:356–61.
Phillips MI, Kagiyama S. Angiotensin II as a pro-inflammatory mediator. Curr Opin Investig Drugs (London, England: 2000). 2002;3(4):569–77.
Rahimzadeh H, Tamehri Zadeh SS, Khajavi A, Saatchi M, Reis LO, Guitynavard F, Dehghani S, Soleimani V, Aghamir SMK. The tsunami of COVID-19 infection among kidney transplant recipients: a single-center study from Iran. J Epidemiol Global Health. 2021;11(4):389–96.
Rahmati M, Keshvari M, Mirnasuri S, Yon DK, Lee SW, Il Shin J, Smith L. The global impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the incidence of pediatric new-onset type 1 diabetes and ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2022;94(11):5112–27.
Rajpal A, Rahimi L, Ismail-Beigi F. Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes. 2020;12(12):895–908.
Ramezankhani A, Habibi-Moeini AS, Zadeh SST, Azizi F, Hadaegh F. Effect of family history of diabetes and obesity status on lifetime risk of type 2 diabetes in the Iranian population. J Global Health. 2022;12.
Reiterer M, Rajan M, Gómez-Banoy N, Lau JD, Gomez-Escobar LG, Gilani A, Alvarez-Mulett S, Sholle ET, Chandar V, Bram Y, Hoffman K, Rubio-Navarro A, Uhl S, Shukla AP, Goyal P, tenOever BR, Alonso LC, Schwartz RE, Schenck EJ, Safford MM, Lo JC. Hyperglycemia in acute COVID-19 is characterized by adipose tissue dysfunction and insulin resistance. medRxiv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.21.21254072.
Reiterer M, Rajan M, Gómez-Banoy N, Lau JD, Gomez-Escobar LG, Ma L, Gilani A, Alvarez- Mulett S, Sholle ET, Chandar V. Hyperglycemia in acute COVID-19 is characterized by insulin resistance and adipose tissue infectivity by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Metab. 2021;33(11):2174–88 (e2175).
Ren H, Yang Y, Wang F, Yan Y, Shi X, Dong K, Yu X, Zhang S. Association of the insulin resistance marker TyG index with the severity and mortality of COVID-19. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):1–8.
Ren HH, Yang Y, Wang F, Yan YL, Shi XL, Dong K, Yu XF, Zhang SJ. Association of the insulin resistance marker TyG index with the severity and mortality of COVID-19 [Article]. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-020-01035-2.
Roca-Ho H, Riera M, Palau V, Pascual J, Soler MJ. Characterization of ACE and ACE2 expression within different organs of the NOD mouse. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):563.
Roden M, Price TB, Perseghin G, Petersen KF, Rothman DL, Cline GW, Shulman GI. Mechanism of free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in humans. J Clin Investig. 1996;97(12):2859–65.
Rodriguez-Calvo T, Sabouri S, Anquetil F, von Herrath MG. The viral paradigm in type 1 diabetes: Who are the main suspects? Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15(10):964–9.
Rohani-Rasaf M, Mirjalili K, Vatannejad A, Teimouri M. Are lipid ratios and triglyceride- glucose index associated with critical care outcomes in COVID-19 patients? PLoS One. 2022;17(8):e0272000. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0272000.
Romaní-Pérez M, Outeiriño-Iglesias V, Moya CM, Santisteban P, González-Matías LC, Vigo E, Mallo F. Activation of the GLP-1 receptor by liraglutide increases ACE2 expression, reversing right ventricle hypertrophy, and improving the production of SP-A and SP-B in the lungs of type 1 diabetes rats. Endocrinology. 2015;156(10):3559–69.
Rubino F, Amiel SA, Zimmet P, Alberti G, Bornstein S, Eckel RH, Mingrone G, Boehm B, Cooper ME, Chai Z. New-onset diabetes in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(8):789–90.
Saiepour D, Sehlin J, Oldenborg P-A. Hyperglycemia-induced protein kinase C activation inhibits phagocytosis of c3b-and immunoglobulin g–opsonized yeast particles in normal human neutrophils. J Diabetes Res. 2003;4:125–32.
Santos A, Magro DO, Evangelista-Poderoso R, Saad MJA. Diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance in COVID-19: molecular interrelationship and therapeutic implications. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021;13:1–14.
Scheen A. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Acta Clin Belg. 2003;58(6):335–41.
Seggelke SA, Ingram CC, Crawley S, Low Wang CC. Insulin resistance in a hospitalized COVID-19 patient: a case review. Clin Diabetes. 2021;39(2):228–32.
SeyedAlinaghi S, Karimi A, Barzegary A, Pashaei Z, Afsahi AM, Alilou S, Janfaza N, Shojaei A, Afroughi F, Mohammadi P. Mucormycosis infection in patients with COVID‐19: A systematic review. Health Sci Rep 2022;5(2).
Shimobayashi M, Albert V, Woelnerhanssen B, Frei IC, Weissenberger D, Meyer-Gerspach AC, Clement N, Moes S, Colombi M, Meier JA. Insulin resistance causes inflammation in adipose tissue. J Clin Investig. 2018;128(4):1538–50.
Shinoda H, Taguchi Y, Nakagawa R, Makino A, Okazaki S, Nakano M, Muramoto Y, Takahashi C, Takahashi I, Ando J. Amplification-free RNA detection with CRISPR–Cas13. Commun Biol. 2021;4(1):476.
Shulman R, Cohen E, Stukel TA, Diong C, Guttmann A. Examination of trends in diabetes incidence among children during the COVID-19 pandemic in Ontario, Canada, from March 2020 to September 2021. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(7):e2223394–e2223394.
Simental-Mendía LE, Rodríguez-Morán M, Guerrero-Romero F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2008;6(4):299–304.
Sjaarda LG, Bacha F, Lee S, Tfayli H, Andreatta E, Arslanian S. Oral disposition index in obese youth from normal to prediabetes to diabetes: relationship to clamp disposition index. J Pediatr. 2012;161(1):51–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.12.050.
Somasundaram NP, Ranathunga I, Ratnasamy V, Wijewickrama PSA, Dissanayake HA, Yogendranathan N, Gamage KKK, de Silva NL, Sumanatilleke M, Katulanda P. The impact of SARS-Cov-2 virus infection on the endocrine system. J Endocr Soc. 2020;4(8):bvaa082.
Soto ME, Guarner-Lans V, Díaz-Díaz E, Manzano-Pech L, Palacios-Chavarría A, Valdez-Vázquez RR, Aisa-Álvarez A, Saucedo-Orozco H, Pérez-Torres I. Hyperglycemia and loss of redox homeostasis in COVID-19 patients. Cells. 2022;11(6):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11060932.
Stager LM, Morgan CH, Watson CS, Morriss S, Gower BA, Fobian AD. The effects of COVID-19 virtual learning on body fat and insulin resistance in adolescents with overweight or obesity. Children. 2023;10(8):1398. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9067/10/8/1398.
Subir R. Use of pioglitazone in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Boon or bane? Diabetes Metab Syndr: Clin Res Rev. 2020;14(5):829–31.
Suganuma Y, Takahashi H, Sano H, Hayashi Y, Nishimura R. Changes in insulin resistance, body mass index and degree of obesity among junior high school students: A comparison before and after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. Pediatr Obes. 2023;18(10):e13065. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.13065.
Szczerbiński Ł, Okruszko MA, Szabłowski M, Sołomacha S, Sowa P, Kiszkiel Ł, Gościk J, Krętowski AJ, Moniuszko-Malinowska A, Kamiński K. Long-term effects of COVID-19 on the endocrine system – a pilot case-control study [Original Research]. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1192174.
Takeda M, Yamamoto K, Takemura Y, Takeshita H, Hongyo K, Kawai T, Hanasaki-Yamamoto H, Oguro R, Takami Y, Tatara Y. Loss of ACE2 exaggerates high-calorie diet–induced insulin resistance by reduction of GLUT4 in mice. Diabetes. 2013;62(1):223–33.
Tam CS, Xie W, Johnson WD, Cefalu WT, Redman LM, Ravussin E. Defining insulin resistance from hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(7):1605–10.
Tan WSD, Liao W, Zhou S, Mei D, Wong W-SF. Targeting the renin–angiotensin system as novel therapeutic strategy for pulmonary diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;40:9–17.
Triplitt C, Solis-Herrera C, Cersosimo E, Abdul-Ghani M, Defronzo RA. Empagliflozin and linagliptin combination therapy for treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(18):2819–33.
Tudoran C, Bende R, Bende F, Giurgi-Oncu C, Enache A, Dumache R, Tudoran M. Connections between diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome and the outcome of cardiac dysfunctions diagnosed during the recovery from COVID-19 in patients without a previous history of cardiovascular diseases. Biology. 2023;12(3):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030370.
Valencia I, Peiro C, Lorenzo O, Sanchez-Ferrer CF, Eckel J, Romacho T. DPP4 and ACE2 in diabetes and COVID-19: therapeutic targets for cardiovascular complications? Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1161.
Vikram A, Tripathi DN, Kumar A, Singh S. Oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic complications, vol. 2014. Hindawi; 2014.
Wang Y, Yang W, Jiang X. Association between triglyceride-glucose index and hypertension: a meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:644035.
Warpechowski J, Leszczyńska P, Juchnicka D, Olichwier A, Szczerbiński Ł, Krętowski AJ. Assessment of the Immune response in patients with insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetes to COVID-19 vaccination. Vaccines. 2023;11(7):1203.
Wek R, Jiang H-Y, Anthony T. Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34(1):7–11.
Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, Curtis HJ, Mehrkar A, Evans D, Inglesby P. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020;584(7821):430–6.
Wu Y. Compensation of ACE2 function for possible clinical management of 2019-nCoV- induced acute lung injury. Virol Sin. 2020;35(3):256–8.
Wu Y, Zhang Z, Li Y, Li Y. The regulation of integrated stress response signaling pathway on viral infection and viral antagonism. Front Microbiol. 2022;12:814635.
Wu Z, Xie Y, Morrison RF, Bucher N, Farmer SR. PPARgamma induces the insulin- dependent glucose transporter GLUT4 in the absence of C/EBPalpha during the conversion of 3T3 fibroblasts into adipocytes. J Clin Investig. 1998;101(1):22–32.
Wysocki J, Ye M, Soler MJ, Gurley SB, Xiao HD, Bernstein KE, Coffman TM, Chen S, Batlle D. ACE and ACE2 activity in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2006;55(7):2132–9.
Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(5):311–21.
Yang J-K, Lin S-S, Ji X-J, Guo L-M. Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2010;47:193–9.
Yazdanpanah MH, Mardani M, Osati S, Ehrampoush E, Davoodi SH, Homayounfar R. COVID-19 induces body composition and metabolic alterations. Cureus. 2023;15(1):e34196. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.34196.
Yuan S, Chu H, Chan JF-W, Ye Z-W, Wen L, Yan B, Lai P-M, Tee K-M, Huang J, Chen D. SREBP-dependent lipidomic reprogramming as a broad-spectrum antiviral target. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):120.
Zanotto TM, Quaresma PG, Guadagnini D, Weissmann L, Santos AC, Vecina JF, Calisto K, Santos A, Prada PO, Saad MJ. Blocking iNOS and endoplasmic reticulum stress synergistically improves insulin resistance in mice. Mol Metab. 2017;6(2):206–18.
Zhang BP, Dong C, Li SZ, Song XQ, Wei W, Liu L. Triglyceride to High-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is an important determinant of cardiovascular risk and poor prognosis in coronavirus disease-19: a retrospective case series study [Article]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes-Targets Therapy. 2020;13:3925–36. https://doi.org/10.2147/dmso.S268992.
Zhao S, Yu S, Chi C, Fan X, Tang J, Ji H, Teliewubai J, Zhang Y, Xu Y. Association between macro-and microvascular damage and the triglyceride glucose index in community- dwelling elderly individuals: the Northern Shanghai Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):1–8.
Zheng YF, Wang J, Ding XH, Chen SY, Li J, Shen B. The correlation between triglyceride-glucose index and SARS-CoV-2 RNA re-positive in discharged COVID-19 patients [Article]. Infect Drug Resist. 2022;15:14. https://doi.org/10.2147/idr.S368568.
Zhou CC, Ahmad S, Mi T, Xia L, Abbasi S, Hewett PW, Sun C, Ahmed A, Kellems RE, Xia Y. Angiotensin II induces soluble fms-Like tyrosine kinase-1 release via calcineurin signaling pathway in pregnancy. Circ Res. 2007;100(1):88–95.
Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, Xiang J, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–62.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SSTZ; data curation: SSTZ, EM, FA, AZ; writing—original draft preparation: SSTZ, FA; review and editing: MB, EM, SASA; preparing figures: AZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mehraeen, E., Abbaspour, F., Banach, M. et al. The prognostic significance of insulin resistance in COVID-19: a review. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-024-01385-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-024-01385-8