Abstract
Objective
An increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity across the world can lead to serious health complications. The present narrative review highlighted the results of research on obesity management affiliated to the Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute (EMRI), Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Methods
All documents from the EMRI focused on obesity topics were searched using PubMed and Scopus databases up to December 2019.
Results
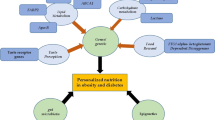
EMRI research projects conducted in obesity field cover several topics including childhood obesity, epidemiology of obesity, roles of genetic factors and gut microbiota in excess weight, as well as weight management by medicinal herbs and nutritional interventions. The increasing prevalence of excess-weight in children and adults indicates that conventional weight management strategies alone are not successful in obesity control and complementary therapies including herbal medicine could be helpful. Moreover, clarifying the role of the human genome and microbiome in different responses of individuals to dietary recommendations could be effective in achieving personalized nutrition.
Conclusion
Further population-based studies focusing on national and international collaborations are needed to progress more practical strategies to face with obesity challenge in different age ranges.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world-a growing challenge. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(3):213–5.
Jafari-Adli S, Jouyandeh Z, Qorbani M, Soroush A, Larijani B, Hasani-Ranjbar S. Prevalence of obesity and overweight in adults and children in Iran; a systematic review. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2014;13(1):121.
World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight: World Health Organization. 2006. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-andoverweight
Ahadi Z, Shafiee G, Qorbani M, Sajedinejad S, Kelishadi R, Arzaghi SM, et al. An overview on the successes, challenges and future perspective of a national school-based surveillance program: the CASPIAN study. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2014;13(1):120.
Angoorani P, Heshmat R, Ejtahed HS, Motlagh ME, Ziaodini H, Taheri M, et al. The association of parental obesity with physical activity and sedentary behaviors of their children: the CASPIAN-V study. J Pediatr (Versão em Português). 2018;94(4):410–8.
Ejtahed HS, Heshmat R, Motlagh ME, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Ziaodini H, Taheri M, et al. Association of parental obesity with cardiometabolic risk factors in their children: The CASPIAN-V study. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2018;13(4):e0193978.
Angoorani P, Heshmat R, Ejtahed H-S, Motlagh ME, Ziaodini H, Taheri M, et al. Validity of triglyceride–glucose index as an indicator for metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-V study. Eating and weight disorders-studies on anorexia. Bulimia Obes. 2018;23(6):877–83.
Angoorani P, Khademian M, Ejtahed H-S, Heshmat R, Motlagh ME, Vafaeenia M, et al. Are non-high–density lipoprotein fractions associated with pediatric metabolic syndrome? The CASPIAN-V study. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):257.
Ejtahed HS, Kelishadi R, Qorbani M, Motlagh ME, Hasani‐Ranjbar S, Angoorani P, Beshtar S, Ziaodini H, Taheri M, Heshmat R. Utility of waist circumference‐to‐height ratio as a screening tool for generalized and central obesity among Iranian children and adolescents: The CASPIAN‐V study. Pediat Diab. 2019;20(5):530–7.
Heshmat R, Heidari M, Ejtahed H-S, Motlagh ME, Mahdavi-Gorab A, Ziaodini H, et al. Validity of a continuous metabolic syndrome score as an index for modeling metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-V study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017;9(1):89.
Ejtahed H-S, Qorbani M, Motlagh ME, Angoorani P, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Ziaodini H, et al. Association of anthropometric indices with continuous metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-V study. Eating and weight disorders-studies on anorexia. Bulimia Obes. 2018;23(5):597–604.
Payab M, Kelishadi R, Qorbani M, Motlagh ME, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Ejtahed HS, Ardalan G, Arefirad T, Asayesh H, Heshmat R. Association of healthy foods intake with anthropometric measures and blood pressure in a national sample of Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-IV Study. Minerva Pediat. 2016;71(5):420–30.
Payab M, Kelishadi R, Qorbani M, Motlagh ME, Ranjbar SH, Ardalan G, et al. Association of junk food consumption with high blood pressure and obesity in Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-IV Study. J Pediatr. 2015;91(2):196–205.
Zahedi H, Kelishadi R, Heshmat R, Hasani SR, Esmaeil MM, Ardalan G, et al. Association of adolescents’ weight status with life satisfaction: role of self, peers, family and school perception; the CASPIAN-IV Study. Minerva Pediatr. 2019;71(3):235–41.
Hasani-Ranjbar S, Shirzad N, Mashayekh Bakhshi F. A 3-year-old boy with severe obesity and pseudoacromegaly; short course treatment with Orlistat. Iran J Diabetes Lipid Disord. 2010;9:1–5.
Payab M, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Merati Y, Esteghamati A, Qorbani M, Hematabadi M, et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome and different obesity phenotype in Iranian male military personnel. Am J Men’s Health. 2017;11(2):404–13.
Ejtahed HS, Soroush MR, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Angoorani P, Mousavi B, Masumi M, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and health-related quality of life in war-related bilateral lower limb amputees. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2017;16:17.
Gholami M, Sharifi F, Shahriari S, Khoshnevisan K, Larijani B, Amoli MM. Association of interleukin-6 polymorphisms with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine. 2019;123:154769.
Hasani-Ranjbar S, Amoli MM, Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Rumi Y, Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J, Samimi H, et al. Effect of adiponectin gene polymorphisms on waist circumference in patients with diabetes. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2012;11(1):14.
Payab M, Amoli MM, Qorbani M, Hasani-Ranjbar S. Adiponectin gene variants and abdominal obesity in an Iranian population. Eati Weight Disord. 2017;22(1):85–90.
Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Amoli MM, Heshmat R, Sajadi M, Derakhshan R, et al. Gender-specific differences in the association of adiponectin gene polymorphisms with body mass index. Rev Diabet Stud. 2010;7(3):241.
Talaschian M, Amoli MM, Enayati S, Payab M, Hasani-Ranjbar S. Association between Trp48Arg polymorphism of the CD11c gene and risk for obesity among Iranian population. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2018;17(2):197–201.
Payab M, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Aletaha A, Ghasemi N, Qorbani M, Atlasi R, et al. Efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity: A protocol for systematic review. Medicine. 2018;97(1):e8825.
Hasani-Ranjbar S, Jouyandeh Z, Abdollahi M. A systematic review of anti-obesity medicinal plants-an update. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2013;12(1):28.
Hasani-Ranjbar S, Nayebi N, Larijani B, Abdollahi M. A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(25):3073.
Namazi N, Larijani B, Ayati MH, Abdollahi M. The effects of Nigella sativa L. on obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;219:173–81.
Kamali SH, Khalaj AR, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Esfehani MM, Kamalinejad M, Soheil O, et al. Efficacy of ‘Itrifal Saghir’, a combination of three medicinal plants in the treatment of obesity; A randomized controlled trial. Daru. 2012;20(1):33.
Mousavi S, Milajerdi A, Sheikhi A, Kord-Varkaneh H, Feinle‐Bisset C, Larijani B, et al. Resveratrol supplementation significantly influences obesity measures: a systematic review and dose–response meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2019;20(3):487–98.
Mousavi SM, Milajerdi A, Varkaneh HK, Gorjipour MM, Esmaillzadeh A. The effects of curcumin supplementation on body weight, body mass index and waist circumference: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutri. 2020;60(1):171–80.
Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Shadman Z, Ejtahed H-S, Atlasi R, Abdollahi M, Larijani B. Quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials of herbal medicines conducted in metabolic disorders in Middle East countries: A systematic review. Complement Ther Med. 2018;38:61–6.
Mansouri M, Nayebi N, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Taheri E, Larijani B. The effect of 12 weeks Anethum graveolens (dill) on metabolic markers in patients with metabolic syndrome; a randomized double blind controlled trial. DARU J Pharm Sci. 2012;20(1):47.
Ejtahed HS, Soroush AR, Angoorani P, Larijani B, Hasani-Ranjbar S. Gut microbiota as a target in the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders: a new approach to novel therapeutic agents. Horm Metab Res. 2016;48(6):349-58.
Ejtahed HS, Angoorani P, Soroush AR, Siadat SD, Shirzad N, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Larijani B. Our little friends with big roles: alterations of the gut microbiota in thyroid disorders. Endocrine Metabolic & Immune Disorders-Drug Targets. 2020;20(3):344-50.
Aazami H, DehghanBanadaki H, Ejtahed HS, Fahimfar N, Razi F, Soroush AR, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Pasalar P, Badi SA, Siadat SD, Larijani B. The landscape of microbiota research in Iran; a bibliometric and network analysis. J Diab Metab Disord. 2020;1–5.
Ejtahed HS, Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Soroush AR, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Siadat SD, Raes J, et al. Worldwide trends in scientific publications on association of gut microbiota with obesity. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22(1):65–71.
Ejtahed HS, Hasani-Ranjbar S. Neuromodulatory effect of microbiome on gut-brain axis; new target for obesity drugs. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2019;18(1):263–5.
Ejtahed HS, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Larijani B. Human microbiome as an approach to personalized medicine. Altern Ther Health Med. 2017;23(6):8–9.
Ejtahed H-S, Angoorani P, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Siadat S-D, Ghasemi N, Larijani B, et al. Adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgeries in morbidly obese patients: a systematic review. Microb Pathog. 2018;116:13–21.
Tabasi M, Ashrafian F, Khezerloo JK, Eshghjoo S, Behrouzi A, Javadinia SA, et al. Changes in gut microbiota and hormones after bariatric surgery: a bench-to-bedside review. Obes Surg. 2019;29(5):1663–74.
Ejtahed H-S, Soroush A-R, Siadat S-D, Hoseini-Tavassol Z, Larijani B, Hasani-Ranjbar S. Targeting obesity management through gut microbiota modulation by herbal products: A systematic review. Complement Ther Med. 2019;42:184–204.
Homayouni-Rad A, Soroush AR, Khalili L, Norouzi-Panahi L, Kasaie Z, Ejtahed HS. Diabetes management by probiotics: current Knowledge and Future Pespective. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. (Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutrition). 2016;86(3-4):215–27.
Ejtahed HS, Angoorani P, Soroush AR, Atlasi R, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Mortazavian AM, et al. Probiotics supplementation for the obesity management; A systematic review of animal studies and clinical trials. J Funct Foods. 2019;52:228–42.
Rad AH, Abbasalizadeh S, Vazifekhah S, Abbasalizadeh F, Hassanalilou T, Bastani P, et al. The future of diabetes management by healthy probiotic microorganisms. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(6):582–9.
Ejtahed HS, Tito RY, Siadat SD, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Hoseini-Tavassol Z, Rymenans L, Verbeke K, Soroush AR, Raes J, Larijani B. Metformin induces weight loss associated with gut microbiota alteration in non-diabetic obese women: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Eur J Endocrinol. 2019;180(3):165–76.
Mansouri M, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Yaghubi H, Rahmani J, Tabrizi YM, Keshtkar A, Varmaghani M, Sharifi F, Sadeghi O. Breakfast consumption pattern and its association with overweight and obesity among university students: a population-based study. Eating Weight Disord-Stud Anorexia Bulimia Obes. 2020;25(2):379–87.
Namazi N, Irandoost P, Larijani B, Azadbakht L. The effects of supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on anthropometric indices and body composition in overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(17):2720–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HSE, SHR and BL designed the study and drafted the manuscript. ARS helped in data extraction and interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ejtahed, HS., Hasani-Ranjbar, S., Soroush, AR. et al. Multidimensional perspective of obesity; prevention to treatment. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00705-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00705-y