Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the association between Helicobacter pylori infection with diabetes mellitus type one and the effect of infected Helicobacter pylori on glycemic control.
Methods
This case control study was conducted on children with and without type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Demographic data and gastrointestinal symptoms in both groups and glycemic control status and duration of diabetes were recorded in patients with T1DM. Stool test was done on all children to detect Helicobacter pylori antigen.
Results
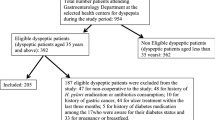
Sixty three children with T1DM with a mean of 10.88 ± 2.84 years and 105 control children with an average age 10.17 ± 2.55 years (P = 0/09) were involved in this study. The frequency of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with T1DM was 17/63 (27%) and 25/105 (23.8%) in control group, (P = 0/64). The frequency of bloating, epigastric pain and nausea was not significantly different between the two groups. The frequency of epigastric pain in children with diabetes with helicobacter infection was significantly higher than non-infected children with diabetes (29.4% vs. 2.2%) (P = 0.004).The mean duration of diabetes (P = 0.53), age diagnosis of diabetes (P = 0.09), fasting blood glucose (P = 0.18), glycosylated hemoglobin (P = 0.08) and the daily insulin dose (P = 0.18) in patients with T1DM with and without helicobacter pylori infection had not significantly different.
Conclusions
There was no significant association between Helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes in children 5–15 years old, and glycemic control status was not difference in patients with T1DM with and without Helicobacter pylori infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hjelm K, Mufunda E, Nambozi G, Kemp J. Preparing nurses to face the pandemic of diabetes mellitus: a literature review. JAN. 2003;41:424–34.
Maahs DM, West NA, Lawrence JM, Mayer-Davis EJ. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2010;39:481–97.
Arslan D, Kendirci M, Kurtoglu S, Kula M. Helicobacter pylori infection in children with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2000;13:553–6.
Giannakis M, Chen SL, Karam SM, Engstrand L, Gordon JI. Helicobacter pylori evolution during progression from chronic atrophic gastritis to gastric cancer and its impact on gastric stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:4358–63.
Kusters JG, van Vliet AH, Kuipers EJ. Pathogenesis of helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:449–90.
Kadhim G, Omar H, Ismail A. Risk factors associated with peptic ulcer disease. J Bioengineer Biomedical Sci. 2015;5:1.
Abu-Median HAK, Mirghani UA. Effect of H.pylori on iron deficiency anemia. Khartoum Med J. 2010;30(1):393–7.
Nouraie M, Latifi Navid S, Rezvan H, Radmard AR, Maghsudlu M, Zaer-Rezaii H, et al. Childhood hygienic practice and family education status determine the prevalence of helicobacter pylori infection in Iran. Helicobacter. 2009;14:40–6.
Chiu W, Chick W, Kwok K. A home-made rapid urease test in the diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection. Singap Med J. 1999;40:243–5.
Fayed SB, Dayem E, Abd SM, Khalil E, El Kader MA, El Halim EA. Helicobacter pylori infection in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Maced J Med Sci. 2014;7:114–8.
Papamichael KX, Papaioannou G, Karga H, Roussos A, Mantzaris GJ. Helicobacter pylori infection and endocrine disorders: is there a link. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:2701–7.
Marietti M, Gasbarrini A, Saracco G, Pellicano R. Helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes mellitus: the 2013 state of art. Panminerva Med. 2013;55:277–81.
Zhou X, Zhang C, Wu J, Zhang G. Association between helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;99:200–8.
Bazmamoun H, Rafeey M, Nikpouri M, Ghergherehchi R. Helicobacter pylori infection in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a case-control study. J Res Health Sci. 2016;16:68–71.
Begue RE, Gomez R, Compton T, Vargas A. Effect of helicobacter pylori eradication in the glycemia of children with type 1 diabetes: a preliminary study. South Med J. 2002;95:842–6.
Zekry OA, Elwahid HAA. The association between helicobacter pylori infection, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and autoimmune thyroiditis. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2013;88:143–7.
Gasbarrini A, Ojetti V, Pitocco D, De Luca A, Franceschi F, Candelli M, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection in patients affected by insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;10:469–72.
Woodward M, Morrison C, Mccoll K. An investigation into factors associated with helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53:175–81.
Xia HH, Talley NJ, Kam EP, Young LJ, Hammer J, Horowitz M. Helicobacter pylori infection is not associated with diabetes mellitus, nor with upper gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:1039–46.
El-Eshmawy MM, El-Hawary AK, Abdel Gawad SS, El-Baiomy AA. Helicobacter pylori infection might be responsible for the interconnection between type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroiditis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2011;3(1):28.
Valkonen KH, Ringner M, Ljungh Å, Wadström T. High-affinity binding of laminin by helicobacter pylori: evidence for a lectin-like interaction. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993;7:29–37.
Dai Y-N, Yu W-L, Zhu H-T, Ding J-X, Yu C-H, Li Y-M. Is helicobacter pylori infection associated with glycemic control in diabetics? World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:5407–16.
Chobot A, Bak-Drabik K, Skała-Zamorowska E, Krzywicka A, Kwiecien J, Polanska J. Helicobacter pylori infection in type 1 diabetes children and adolescents using 13C urea breath test. Pol J Microbiol. 2014;63:63–7.
Horikawa C, Kodama S, Fujihara K, Yachi Y, Tanaka S, Suzuki A, et al. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with glycemic control in patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res. 2014.
Okuda M, Lin Y, Kikuchi S. Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1149:107–20.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Clinical Research Development Unit of Amirkola Children’s Hospital and the Research Council and Non-Communicable Pediatric Diseases Research Center of Babol University of Medical Sciences for their contribution to this project.
Funding
This study is part of the doctoral dissertation of Dr. Negar Noushiravan and was supported by a research grant from the Non-Communicable Pediatric Diseases Research Center of Babol University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 9339615).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors have No conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaeili Dooki, M.R., Alijanpour Aghamaleki, M., Noushiravani, N. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and type 1 diabetes mellitus in children. J Diabetes Metab Disord 19, 243–247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00497-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00497-1