Abstract
Background
The PI3K/AKT/FOXO signaling pathway plays an important role in the survival, proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells. The aim of the present study was to explore whether metformin could affect insulin-promoting cell growth by regulation of this pathway.
Material and methods
Anaplastic thyroid cancer cells were treated with 0–60 mM metformin for 24, 48 and 72 h. Cell viability, morphology, apoptosis and migration were investigated by MTT assay, microscopy observation, AnexinV-PI and the wound healing assay, respectively. Expression levels of PI3K, AKT and FOXO1 were detected by RT-qPCR, and proteins phosphorylated levels were determined by ELISA.
Results
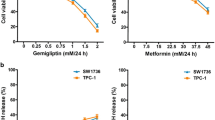
Metformin decreased cell viability and migration in a significant time-and dose-dependent manner, and induced apoptosis and morphological changes in the cells. RT-qPCR results showed that expression levels of PI3K, AKT and FOXO1 was inhibited by metformin (P < 0.05). However, there was no significant change in the expression level of AKT following metformin treatment for C643 cell line (P > 0.05). ELISA results showed that metformin treatment had no significant effects on the phosphorylated levels of PI3K, AKT and FOXO1 (P > 0.05).
Conclusuion
The downregulation of FOXO1 was intensified by metformin, but no increase in cell viability was observed following FOXO1 downregulation by metformin. However, the exact molecular mechanism of metformin on inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway and subsequent decrease in cell viability remains unclear and further studies are required for its clarification.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nozhat Z, Hedayati M. PI3K/AKT pathway and its mediators in thyroid carcinomas. Molecular diagnosis & therapy. 2016;20(1):13–26.
Nozhat Z, Hedayati M, Pourhassan H. Signaling pathways in medullary thyroid carcinoma: therapeutic implications. International Journal of Endocrine Oncology. 2016;3(4):299–312.
Cornett WR, Sharma AK, Day TA, Richardson MS, Hoda RS, van Heerden JA, et al. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: an overview. Curr Oncol Rep. 2007;9(2):152–8.
AIN KB. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: behavior, biology, and therapeutic approaches. Thyroid. 1998;8(8):715–26.
Chen G, Xu S, Renko K, Derwahl M. Metformin inhibits growth of thyroid carcinoma cells, suppresses self-renewal of derived cancer stem cells, and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2012;97(4):E510–E20.
Klubo-Gwiezdzinska J, Costello J Jr, Patel A, Bauer A, Jensen K, Mete M, et al. Treatment with metformin is associated with higher remission rate in diabetic patients with thyroid cancer. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2013;98(8):3269–79.
Sahra IB, Laurent K, Loubat A, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene. 2008;27(25):3576–86.
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M. Metformin is an AMP kinase–dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(21):10269–73.
Yung MMH, Chan DW, Liu VWS, Yao K-M, Ngan HY-S. Activation of AMPK inhibits cervical cancer cell growth through AKT/FOXO3a/FOXM1 signaling cascade. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(1):327.
Rattan R, Giri S, Hartmann LC, Shridhar V. Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an AMP-kinase dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(1):166–78.
Bikas A, Van Nostrand D, Jensen K, Desale S, Mete M, Patel A, et al. Metformin attenuates 131I-induced decrease in peripheral blood cells in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2016;26(2):280–6.
Chen G, Nicula D, Renko K, Derwahl M. Synergistic anti-proliferative effect of metformin and sorafenib on growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells and their stem cells. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(4):1994–2000.
Cho SW, Yi KH, Han SK, Sun HJ, Kim YA, Oh B-C, et al. Therapeutic potential of metformin in papillary thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;393(1):24–9.
Han B, Cui H, Kang L, Zhang X, Jin Z, Lu L, et al. Metformin inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth, migration, and EMT through the mTOR pathway. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(8):6295–304.
Bartolomé A, Guillén C, Benito M. Role of the TSC1-TSC2 complex in the integration of insulin and glucose signaling involved in pancreatic β-cell proliferation. Endocrinology. 2010;151(7):3084–94.
Paes JE, Ringel MD. Dysregulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in thyroid neoplasia. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2008;37(2):375–87.
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Jia K, Dong Y, Ma W. Metformin inhibits the proliferation of A431 cells by modulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Experimental and therapeutic medicine. 2015;9(4):1401–6.
Tzivion G, Dobson M, Ramakrishnan G. FoxO transcription factors; regulation by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-molecular. Cell Res. 2011;1813(11):1938–45.
Guttilla IK, White BA. Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(35):23204–16.
Myatt SS, Wang J, Monteiro LJ, Christian M, Ho K-K, Fusi L, et al. Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70(1):367–77.
Xie L, Ushmorov A, Leithäuser F, Guan H, Steidl C, Färbinger J, et al. FOXO1 is a tumor suppressor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2012;119(15):3503–11.
Haflidadóttir BS, Larne O, Martin M, Persson M, Edsjö A, Bjartell A, et al. Upregulation of miR-96 enhances cellular proliferation of prostate cancer cells through FOXO1. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72400.
Zaballos MA, Santisteban P. FOXO1 controls thyroid cell proliferation in response to TSH and IGF-I and is involved in thyroid tumorigenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 2013;27(1):50–62.
Zhang X, Tang N, Hadden TJ, Rishi AK. Akt, FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-molecular. Cell Res. 2011;1813(11):1978–86.
Song H-m, Song J-l, Li D-f, Hua K-y, Zhao B-k, Fang L. Inhibition of FOXO1 by small interfering RNA enhances proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via Akt/FOXO1/Bim pathway. OncoTargets and therapy. 2015;8:3565.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Pezzino V, Squatrito S, Belfiore A, et al. The role of insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in cancer and other diseases. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2008;114(1):23–37.
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Tanaka K, Fukamizu A. Insulin-induced phosphorylation of FKHR (Foxo1) targets to proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2003;100(20):11285–90.
Zhang B, Gui L, Zhao X, Zhu L, Li Q. FOXO1 is a tumor suppressor in cervical cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(2):6605–16.
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Investig. 2001;108(8):1167–74.
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krähenbühl S, Jick SS, Meier CR. Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1304–8.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(7):489–501.
Karnevi E, Said K, Andersson R, Rosendahl AH. Metformin-mediated growth inhibition involves suppression of the IGF-I receptor signalling pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(1):235.
Sarfstein R, Friedman Y, Attias-Geva Z, Fishman A, Bruchim I, Werner H. Metformin downregulates the insulin/IGF-I signaling pathway and inhibits different uterine serous carcinoma (USC) cells proliferation and migration in p53-dependent or-independent manners. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61537.
Song J, Ren P, Zhang L, Wang XL, Chen L, Shen YH. Metformin reduces lipid accumulation in macrophages by inhibiting FOXO1-mediated transcription of fatty acid-binding protein 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393(1):89–94.
Li X, Kover KL, Heruth DP, Watkins DJ, Moore WV, Jackson K, et al. New insight into metformin action: regulation of ChREBP and FoXO1 activities in endothelial cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2015;29(8):1184–94.
Zatara G, Hertz R, Shaked M, Mayorek N, Morad E, Grad E, et al. Suppression of FoxO1 activity by long-chain fatty acyl analogs. Diabetes. 2011;60(7):1872–81.
Barbato DL, Tatulli G, Aquilano K, Ciriolo M. FoxO1 controls lysosomal acid lipase in adipocytes: implication of lipophagy during nutrient restriction and metformin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(10):e861.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Research Institute for Endocrine Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences Tehran, Iran for their excellent technical and financial supports. This manuscript was extracted from PhD thesis of Zahra Nozhat (grant No: 852). The authors wish to acknowledge Ms. Niloofar Shiva for editing of English grammar and syntax of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Key Points
• Metformin decreased cell viability of ATC-derived cells in a dose-and time-dependent manner
• Decrease of cell viability by metformin significantly was associated with the downregulation of PI3K and AKT mRNA levels of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
• Metformin increased the downregulation of FOXO1but an increase in cell viability following FOXO1 downregulation was not observed
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 829 kb)
ESM 2
(PDF 449 kb)
ESM 3
(PDF 449 kb)
ESM 4
(PDF 449 kb)
ESM 5
(RAR 84288 kb)
ESM 6
(PNG 25 kb)
ESM 7
(PNG 29 kb)
ESM 8
(PNG 27 kb)
ESM 9
(PPTX 42002 kb)
ESM 10
(PNG 13 kb)
ESM 11
(PNG 13 kb)
ESM 12
(PNG 13 kb)
ESM 13
(PPTX 156 kb)
ESM 14
(PNG 8 kb)
ESM 15
(PNG 17 kb)
ESM 16
(PNG 15 kb)
ESM 17
(PNG 17 kb)
ESM 18
(PNG 14 kb)
ESM 19
(PNG 13 kb)
ESM 20
(PNG 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nozhat, Z., Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S., Azizi, F. et al. Effects of metformin on the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway in anaplastic thyroid Cancer cell lines. DARU J Pharm Sci 26, 93–103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-018-0208-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-018-0208-2