Abstract
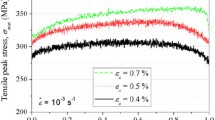
Low cycle fatigue behavior of a quenched and tempered high-strength steel (Q960E) was studied in the strain amplitude ranging from ± 0.5% to ± 1.2% at room temperature. As a result of fatigue loading, the dislocation structural evolution and fracture mechanism were examined and studied by transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that this Q960E steel showed cyclic softening at different strain amplitudes, and the softening tendency was more apparent at strain amplitude of ± (0.6–1.2)% than that at ± 0.5%. The reduction in dislocation density with increasing strain amplitude is responsible for the softening tendency of cyclic stress with the strain amplitude. The material illustrates near-Masing behavior at strain amplitude ranging from ± 0.6% to ± 1.2%. The near-Masing behavior of Q960E high-strength steel can be the result of stability of martensite lath at different strain amplitudes. Partial transformation from martensite laths to dislocation cells is responsible for the derivation from ideal Masing behavior. In the SEM examination of fracture surfaces, transgranular cracks initiate on the sample surface. Striations can be found during the crack propagation stage.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Branco, J.D. Costa, F.V. Antunes, Theor. Appl. Fract. Mec. 58(1), 28 (2012)
S. Glodež, M. Knez, N. Jezernik, J. Kramberger, Eng. Fail. Anal. 16(7), 2348 (2009)
P.C. Chakraborti, M.K. Mitra, Int. J. Fatigue 28(3), 194 (2006)
P. Verma, N.C.S. Srinivas, S.R. Singh, V. Singh, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 652, 30 (2016)
A. Chauhan, D. Litvinov, J. Aktaa, Int. J. Fatigue 93, Part 1,1 (2016)
R.K. Dutta, M. Amirthalingam, M.J.M. Hermans, I.M. Richardson, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 559, 86 (2013)
W.S. Chang, J. Mater. Sci. 37(10), 1973 (2002)
B. Jiang, M. Wu, M. Zhang, F. Zhao, Z. Zhao, Y. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 707, 306 (2017)
J.C. Zhang, H.S. Di, Y.G. Deng, S.C. Li, R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 645, 232 (2015)
M.C. Marinelli, I. Alvarez-Armas, U. Krupp, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 684, 254 (2017)
J. Kang, F.C. Zhang, X.Y. Long, B. Lv, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 666, 88 (2016)
Y.J. Li, D. Liu, W.N. Zhang, J. Kang, D. Chen, G. Yuan, G.D. Wang, Mater. Lett. 230, 36 (2018)
F. Peng, Y. Xu, X. Gu, Y. Wang, X. Liu, J. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 723, 247 (2018)
X.U. Zhenlin, J. Fang, Hot Working Technology 45(15), 4 (2017)
B. Fournier, M. Sauzay, A. Rarcelo, F. Barcelo, A. Pineau, J. Nucl. Mater. 71, 386–388 (2009)
H.W. Zhou, Y.Z. He, H. Zhang, Y.W. Cen, Int. J. Fatigue 47, 83 (2013)
B. Fournier, M. Sauzay, C. Caës, M. Noblecourt, M. Mottot, A. Bougault, V. Rabeau, A. Pineau, Int. J. Fatigue 30(4), 649 (2008)
S.L. Mannan, M. Valsan, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 48(2), 160 (2006)
H.W. Zhou, Y.Z. He, M. Cui, Y.W. Cen, J.Q. Jiang, Int. J. Fatigue 56, 1 (2013)
H.W. Zhou, Y.Z. He, Y.W. Cen, J.Q. Jiang, Adv. Mater. Res. 815, 875 (2013)
F. Ellyin, Fatigue damage, crack growth and life prediction (Springer, Netherlands, 1997), pp. 278–380
D. Lefebvre, F. Ellyin, Int. J. Fatigue 6(1), 9 (1984)
P.P. Sarkar, P.S. De, S.K. Dhua, P.C. Chakraborti, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 707, 125 (2017)
K. Guguloth, S. Sivaprasad, D. Chakrabarti, S. Tarafder, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 604, 196 (2014)
S. Goyal, S. Mandal, P. Parameswaran, R. Sandhya, C.N. Athreya, K. Laha, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 696, 407 (2017)
S. Sivaprasad, S.K. Paul, A. Das, N. Narasaiah, S. Tarafder, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527(26), 6858 (2010)
A. Plumtree, H.A. Abdel-Raouf, Int. J. Fatigue 23(9), 799 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the financial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51674079) and Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. KJ2018A0062, KJ2017A128 and KJ2017A066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, FM., Zhou, HW., Liu, XH. et al. Masing Behavior and Microstructural Change of Quenched and Tempered High-Strength Steel Under Low Cycle Fatigue. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 32, 1346–1354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-019-00893-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-019-00893-4