Abstract
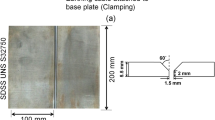
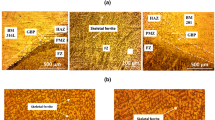
This work focuses on studying the effect of welding heat input within the range from 1 to 5 kJ/mm on the microstructure and the corresponding mechanical and corrosion properties of dissimilar joint between superaustenitic stainless steel (UNS S31254) and Incoloy 28 (UNS N08028). The two materials were butt-welded with ER NiCrMo3. The metallurgical changes associated with welding of SASS and Incoloy 28 were studied using optical microscope, SEM, and EDX. The mechanical and corrosion properties were investigated using tensile test, Vickers hardness test, and pitting and crevice corrosion tests. The weld metal microstructure showed precipitates with needle-like shape at 3 and 5 kJ/mm. Also, the microstructure showed unmixed zone (UMZ) at the fusion line of both SASS and Incoloy 28 sides at all the investigated heat inputs. The Mo microsegregation within UMZ at Incoloy 28 side increased as the heat input increased from 1 to 5 kJ/mm but that in SASS increased with increasing heat input from 1 to 3 kJ/mm and then decreased with increasing from 3 to 5 kJ/mm. The ultimate tensile strengths for all specimens at all the investigated heat inputs are acceptable. The average hardness noticeably changed in weld metal as the heat input increased from 1 to 5 kJ/mm. Other zones such as HAZ or UMZ did not demonstrate marked changes in the average hardness. The pitting and crevice corrosion rates of the weld joint were found significant at 1 and 3 kJ/mm but insignificant at 5 kJ/mm according to ASTM G48.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Liljas, Weld. World 36, 55 (1995)
J.C.M. Farrar, The Alloy Tree, 1st edn. (CRC Press, New York, 2004), pp. 79–115
J. Anburaj, S.S.M. Nazirudeen, R. Narayanan, B. Anandavel, A. Chandrasekar, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 535, 99 (2012)
A. Hoseini Asli, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, J Mater. Sci. Technol. 25, 603 (2009)
American Society for Testing and Materials, B668 (American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, 1997)
B.A. Soares, M.M. Schvartzman, W.R. Campos, Characterization of the dissimilar welding-austenitic stainless steel with filler metal of the nickel alloy. Paper presented at the International Nuclear Atlantic Conference, Santos, Brazil, 30 September 2007
J.S. Ogborn, D.L. Olson, M.J. Cieslak, Mater. Sci. Eng. 203, 134 (1995)
J.A. Brooks, J.C. Lippold, Welding, brazing, and soldering, in ASM Handbook, vol. 6, ed. by D.L. Olson, T.A. Siewert, S. Liu, G.R. Edwards (ASM International, Materials Park, 1993), p. 1170
J.R. Kearns, S.W. Borenstein, Microbiologically influenced corrosion testing of welded stainless alloys for nuclear power plant service water systems. Paper presented at the NACE Annual Conference and Corrosion Show, Cincinnati, 11–15 March 1991
Y. Cui, C.L. Xu, Q. Han, Scr. Mater. 55, 975 (2006)
S. Kou, Welding Metallurgy, 2nd edn. (Wiley, Hoboken, 2003), pp. 37–64
G.F. Vander Voort, G.M. Lucas, E.P. Manilova, Metallography and microstructures, in ASM Handbook, vol. 9, ed. by G.F. Vander Voort (ASM International, Materials Park, 2004), p. 1582
American Society for Testing and Materials, A370 (American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, 1997)
American Society for Testing and Materials, G48 (American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, 1997)
M.J. Clieslak, T.J. Headley, T. Kollie, A.D. Romig, Metall. Trans. A 19, 2319 (1988)
J.N. DuPont, W. Banovic, A.R. Marder, Weld. J., 125 (2003)
S.W. Banovic, J.N. DuPont, A.R. Marder, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 7, 374 (2002)
J.R. Davis (ed.), Corrosion of Weldments (ASM International, Materials Park, 2006)
American Society for Mechanical Engineers, IX (ASME International, New York, 2010)
American Society for Testing and Materials, A312 (American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, 1995)
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciatively acknowledge the members of the Mechanical Testing and Welding Laboratory at the Department of Metallurgy for their aid in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Rahman, M.S., Abdel Raheem, N.A. & El Koussy, M.R. Effect of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Properties of Dissimilar Weld Joint Between Incoloy 28 and Superaustenitic Stainless Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 27, 259–266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-014-0058-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-014-0058-y