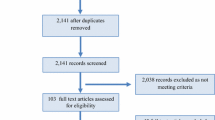
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used for post-exercise recovery and reduction of muscle soreness and pain. While many studies have contradictory results on whether NSAIDs hinder the post-exercise recovery process, this study sought to identify more clearly the effects of NSAIDs on the exercise-induced inflammatory response, muscle protein synthesis, and overall post-exercise muscle recovery.
Recent Findings
NSAID ingestion is common for the reduction of delayed onset muscle soreness after exercise or to decrease pain and inflammation during the rehabilitation of a muscle injury. However, there is evidence that while NSAIDs reduce the activity of cyclooxygenase (Cox-2) which generates prostaglandins that mediate inflammation and pain, they may also play a role in the reduction of protein synthesis and slow the restoration of functional recovery by disrupting the natural anti-inflammatory response during muscle recovery.
Summary
While most of the ten articles selected for this review had low-participant numbers, they provided evidence that large doses of NSAIDs used after high-intensity interval training can reduce muscle protein synthesis and hypertrophy while lower doses have little to no effect on these factors. Thus, taking large doses of NSAIDs can be detrimental to muscle recovery and hypertrophy after exercise training. Further research is required to determine the varying effects of different NSAIDs and dosages.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Rouzer CA, Marnett LJ. Cyclooxygenases: structural and functional insights. J Lipid Res. 2009;50(Suppl):S29-34. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R800042-JLR200.
Allaj V, Guo C, Nie D. Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and cancer. Ceii Biosci. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-3-8.
Lilja M, Mandić M, Apró W, Melin M, Olsson K, Rosenborg S, Gustafsson T, Lundberg TR. High doses of anti-inflammatory drugs compromise muscle strength and hypertrophic adaptations to resistance training in young adults. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12748.This study involving 31 healthy young adults demonstrated that the maximal recommended dosage of ibuprofen can attenuate the strength and hypertrophy of muscles following resistance training.
Ho AM, Bedair H, Fu FH, Huard J. The role of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) after acute exercise-induced muscle injuries: review article. Int SportMed J. 2004;5:209–27.
Hertel J. The role of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of acute soft tissue injuries. J Athl Train. 1997;32(4):350–8.
Markworth JF, Vella L, Lingard BS, Tull DL, Rupasinghe TW, Sinclair AJ, Maddipati KR, Cameron-Smith D. Human inflammatory and resolving lipid mediator responses to resistance exercise and ibuprofen treatment. Am J Physiol-Regulatory, Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;305(11):R1281–96. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00128.2013. This study demonstrated that ibuprofen can block the normal inflammation response following exercise.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Bourton I, Hoffman TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systemic reviews. BJM. 2021;372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n7.
Verhagen AP, de Vet HC, de Bie RA, Kessels AG, Boers M, Bouter LM, et al. The Delphi list: a criteria list for quality assessment of randomized control trials for conducting systematic reviews developed by Delphi consensus. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998;51:1235–41.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice, 3rd ed. Philadelphia (PA): F. A. Davis Company. 2015b;pp. 368–369.
Fraga GS, Aidar FJ, Matos DG, Marçal AC, Santos JL, Souza RF, Carneiro AL, Vasconcelos AB, Da Silva-Grigoletto ME, van den Tillaar R, Cabral BT, Reis VM. Effects of ibuprofen intake in muscle damage, body temperature, and muscle power in paralympic powerlifting athletes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(14):5157.
Nieman DC. Ibuprofen use, endotoxemia, inflammation, and plasma cytokines during ultramarathon competition. Yearbook Sports Med. 2006;2006:199–200.
Donnelly AE, McCormick K, Maughan RJ, Whiting PH, Clarkson PM. Effects of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug on delayed onset muscle soreness and indices of damage. Br J Sports Med. 1988;22(1):35–8.
Donnelly AE, Maughan RJ, Whiting PH. Effects of ibuprofen on exercise-induced muscle soreness and indices of muscle damage. Br J Sports Med. 1990;24:191–5.
Gulick DT, Kimura IF, Sitler M, Paolone A, Kelly JD. Various treatment techniques on signs and symptoms of delayed onset muscle soreness. J Athl Train. 1996;31(2):145–52.
Krentz JR, Quest B, Farthing JP, Quest DW, Chilibeck PD. The effects of ibuprofen on muscle hypertrophy, strength, and soreness during resistance training. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2008;33(3):470–5.
Hasson SM, Daniels JC, Divine JG, Niebuhr BR, Richmond S, Stein PG, Williams J. Effect of ibuprofen use on muscle soreness, damage, and performance: a preliminary investigation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993;25:9–17.
Trappe TA, White F, Lambert CP, Cesar D, Hellerstein M, Evans WJ. Effect of ibuprofen and acetaminophen on postexercise muscle protein synthesis. Am J Physiology-Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282(3):E551–6.
Mackey AL, Kjaer M, Dandanell S, Mikkelsen KH, Holm L, Døssing S, Kadi F, Koskinen SO, Jensen CH, Schrøder HD, Langberg H. The influence of anti-inflammatory medication on exercise-induced myogenic precursor cell responses in humans. J Appl Physiol. 2007;103(2):425–31.
Lundberg TR, Howatson G. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs in sports: implications for exercise performance and training adaptations. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(11):2252–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13275. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/sms.13275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bateman, L.S., McSwain, R.T., Lott, T. et al. Effects of Ibuprofen on Muscle Hypertrophy and Inflammation: a Review of Literature. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 11, 43–50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-023-00381-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-023-00381-y