Abstract
Purpose of Review
In this review, we highlight new advances in diagnostic and therapeutic modalities of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and progress in understanding of its pathophysiology which has led to these advances.
Recent Findings
The new pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatment options have also focused on improving adherence to the treatment. It has made it possible to treat some more resistant pediatric patients with EoE.
Summary
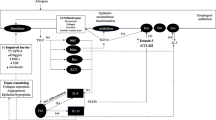
EoE is the result of esophageal dysfunction secondary to inflammatory/immune response of esophagus to certain antigens present in food or environment, which may be known or unknown. Treatment modalities are directed towards elimination of inciting antigen in the form of dietary eliminations, medications with anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory effects. Recent research data has supported some new dietary approaches and medication for better response to treatment and improved treatment outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3.
Furuta GT. Eosinophils in the esophagus: acid is not the only cause. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998;26:468.
Ahmad M, Soetikno RM, Ahmed A. The differential diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;30:242.
Winter HS, Madara JL, Stafford RJ, et al. Intraepithelial eosinophils: a new diagnostic criterion for reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1982;83:818.
Shiflett DW, Gilliam JH, Wu WC, et al. Multiple esophageal webs. Gastroenterology. 1979;77:556.
Hurrell JM, Genta RM, Dellon ES. Prevalence of esophageal eosinophilia varies by climate zone in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:698.
Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:940.
Vazquez-Elizondo G, Ngamruengphong S, Khrisna M, et al. The outcome of patients with oesophageal eosinophilic infiltration after an eight-week trial of a proton pump inhibitor. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38:1312.
Franciosi JP, Tam V, Liacouras CA, Spergel JM. A case-control study of sociodemographic and geographic characteristics of 335 children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:415.
Brusilovsky M, Bao R, Rochman M, et al. Host-microbiota interactions in the esophagus during homeostasis and allergic inflammation. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:521.
Witmer CP, Susi A, Min SB, Nylund CM. Early infant risk factors for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67:610.
Spergel JM, Book WM, Mays E, et al. Variation in prevalence, diagnostic criteria, and initial management options for eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the United States. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52:300.
Shah SC, Tepler A, Peek RM Jr, et al. Association between helicobacter pylori exposure and decreased odds of eosinophilic esophagitis- a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:2185.
Bischoff S, Crowe SE. Gastrointestinal food allergy: new insights into pathophysiology and clinical perspectives. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1089.
Straumann A, Bauer M, Fischer B, et al. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with a T(H)2-type allergic inflammatory response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:954.
Zhang S, Shoda T, Aceves SS, et al. Mast cell-pain connection in eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy. 2022;77:1895.
Saffari H, Hoffman LH, Peterson KA, et al. Electron microscopy elucidates eosinophil degranulation patterns in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1728.
Sherrill JD, Rothenberg ME. Genetic and epigenetic underpinnings of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2014;43:269.
Litosh VA, Rochman M, Rymer JK, et al. Calpain-14 and its association with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:1762.
Zhu X, Wang M, Mavi P, et al. Interleukin-15 expression is increased in human eosinophilic esophagitis and mediates pathogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:182.
Hirano I, Dellon ES, Hamilton JD, et al. Efficacy of dupilumab in a phase 2 randomized trial of adults with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:111. Dupilumab is effective in the treatment of allergic, atopic, and type 2 inflammatory diseases, and was also found to be effective and safe in the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis.
Mishra A, Wang M, Pemmaraju VR, et al. Esophageal remodeling develops as a consequence of tissue specific IL-5-induced eosinophilia. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:204.
Woodruff SA, Masterson JC, Fillon S, et al. Role of eosinophils in inflammatory bowel and gastrointestinal diseases. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52:650.
Fox VL, Nurko S, Furuta GT. Eosinophilic esophagitis: it’s not just kid’s stuff. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:260.
Wen T, Aronow BJ, Rochman Y, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies inflammatory tissue T cells in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:2014.
Almansa C, Krishna M, Buchner AM, et al. Seasonal distribution in newly diagnosed cases of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:828.
Antico A, Fante R. Esophageal hypereosinophilia induced by grass sublingual immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1482.
Lucendo AJ, Arias A, Tenias JM. Relation between eosinophilic esophagitis and oral immunotherapy for food allergy: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014;113:624.
Alexander ES, Martin LJ, Collins MH, et al. Twin and family studies reveal strong environmental and weaker genetic cues explaining heritability of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:1084.
Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:11.
Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn TF, Beausoleil JL, et al. 14 years of eosinophilic esophagitis: clinical features and prognosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;48:30.
Hill DA, Dudley JW, Spergel JM. The prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in pediatric patients with IgE-mediated food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5:369.
Remedios M, Campbell C, Jones DM, Kerlin P. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: clinical, endoscopic, histologic findings, and response to treatment with fluticasone propionate. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:3.
Munoz-Osores E, Maldonado-Campos I, Olivares-Labbe MT, et al. Corticosteroids for eosinophilic esophagitis in children: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2020;146
Limketkai BN, Shah SC, Hirano I, et al. Epidemiology and implications of concurrent diagnosis of eosinophilic oesophagitis and IBD based on a prospective population-based analysis. Gut. 2019;68:2152.
Abonia JP, Wen T, Stucke EM, et al. High prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:378.
Zimmermann D, Criblez DH, Dellon ES, et al. Acute herpes simplex viral esophagitis occurring in 5 immunocompetent individuals with eosinophilic esophagitis. ACG Case Rep J. 2016;3:165.
Nurko S, Teitelbaum JE, Husain K, et al. Association of Schatzki ring with eosinophilic esophagitis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;38:436.
Furuta GT, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1640.
García-Compeán D, González González JA, Marrufo García CA, et al. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: a prospective study. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;43:204.
Mackenzie SH, Go M, Chadwick B, et al. Eosinophilic oesophagitis in patients presenting with dysphagia--a prospective analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:1140.
Kidambi T, Toto E, Ho N, et al. Temporal trends in the relative prevalence of dysphagia etiologies from 1999-2009. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:4335.
Bohm M, Richter JE, Kelsen S, Thomas R. Esophageal dilation: simple and effective treatment for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis and esophageal rings and narrowing. Dis Esophagus. 2010;23:377.
Gisa M, Laserra G, Marabotto E, et al. Achalasia and obstructive motor disorders are not uncommon in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:1554.
Fox VL, Nurko S, Teitelbaum JE, et al. High-resolution EUS in children with eosinophilic “allergic” esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:30.
Roman S, Hirano I, Kwiatek MA, Gonsalves N, Chen J, Kahrilas PJ, Pandolfino JE. Manometric features of eosinophilic esophagitis in esophageal pressure topography. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;23(208–214):e111.
Sá CC, Kishi HS, Silva-Werneck AL, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with typical gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms refractory to proton pump inhibitor. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011;66:557.
Safroneeva E, Straumann A, Coslovsky M, et al. Symptoms have modest accuracy in detecting endoscopic and histologic remission in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:581.
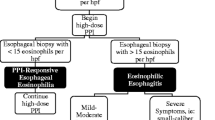
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, et al. Updated international consensus diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:1022.
Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, et al. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679.
Collins MH. Histopathologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2008;18:59.
Lee S, de Boer WB, Naran A, et al. More than just counting eosinophils: proximal oesophageal involvement and subepithelial sclerosis are major diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic oesophagitis. J Clin Pathol. 2010;63:644.
Vicario M, Blanchard C, Stringer KF, et al. Local B cells and IgE production in the oesophageal mucosa in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut. 2010;59:12.
Nelson MJ, Miller FH, Moy N, et al. Comparison of endoscopy and radiographic imaging for detection of esophageal inflammation and remodeling in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:962.
Erwin EA, James HR, Gutekunst HM, et al. Serum IgE measurement and detection of food allergy in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;104:496.
Dellon ES, Gibbs WB, Fritchie KJ, et al. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic findings distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:1305.
Dellon ES, Aderoju A, Woosley JT, et al. Variability in diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2300.
Shoda T, Wen T, Aceves SS, et al. Eosinophilic oesophagitis endotype classification by molecular, clinical, and histopathological analyses: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:477.
Carlson DA. Editorial: Widening the use of the functional lumen imaging probe to kids with eosinophilic esophagitis: esophageal narrowing is not just an adult problem. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1474.
Dalby K, Nielsen RG, Kruse-Andersen S, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and eosinophilic esophagitis in infants and children. A study of esophageal pH, multiple intraluminal impedance and endoscopic ultrasound. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:1029.
Nicodème F, Hirano I, Chen J, et al. Esophageal distensibility as a measure of disease severity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1101.
Patel DA, Higginbotham T, Slaughter JC, et al. Development and validation of a mucosal impedance contour analysis system to distinguish esophageal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1617.
Moawad FJ, Maydonovitch CL, Veerappan GR, et al. Esophageal motor disorders in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:1427.
Januszewicz W, Tan WK, Lehovsky K, et al. Safety and acceptability of esophageal cytosponge cell collection device in a pooled analysis of data from individual patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17:647.
Boyce JA, Assa'a A, Burks AW, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States: summary of the NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel Report. Nutrition. 2011;27:253.
Dellon ES, Guo R, McGee SJ, et al. A novel allergen-specific immune signature-directed approach to dietary elimination in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019;10:e00099.
Alsalamah M, Makhajia M, Somers G, et al. Anaphylaxis to milk after elimination diet for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:752.
van Rhijn BD, Vlieg-Boerstra BJ, Versteeg SA, et al. Evaluation of allergen-microarray-guided dietary intervention as treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1095.
Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn TF, Cianferoni A, et al. Identification of causative foods in children with eosinophilic esophagitis treated with an elimination diet. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:461.
Spergel JM, Andrews T, Brown-Whitehorn TF, et al. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with specific food elimination diet directed by a combination of skin prick and patch tests. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;95:336.
Ram G, Lee J, Ott M, et al. Seasonal exacerbation of esophageal eosinophilia in children with eosinophilic esophagitis and allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;115:224.
Katzka DA. Eosinophilic esophagitis and proton pump-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: what is in a name? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:2023.
Zhang X, Cheng E, Huo X, et al. Omeprazole blocks STAT6 binding to the eotaxin-3 promoter in eosinophilic esophagitis cells. PLoS One. 2012;7:e50037.
Protheroe C, Woodruff SA, de Petris G, et al. A novel histologic scoring system to evaluate mucosal biopsies from patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:749.
Sayej WN, Patel R, Baker RD, et al. Treatment with high-dose proton pump inhibitors helps distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from noneosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;49:393.
Aceves SS, Newbury RO, Dohil R, et al. Distinguishing eosinophilic esophagitis in pediatric patients: clinical, endoscopic, and histologic features of an emerging disorder. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;41:252.
Steiner SJ, Kernek KM, Fitzgerald JF. Severity of basal cell hyperplasia differs in reflux versus eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006;42:506.
Dellon ES, Chen X, Miller CR, et al. Tryptase staining of mast cells may differentiate eosinophilic esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:264.
Sridhara S, Ravi K, Smyrk TC, et al. Increased numbers of eosinophils, rather than only etiology, predict histologic changes in patients with esophageal eosinophilia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:735.
Lieberman JA, Morotti RA, Konstantinou GN, et al. Dietary therapy can reverse esophageal subepithelial fibrosis in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: a historical cohort. Allergy. 2012;67:1299.
Reed CC, Safta AM, Qasem S, et al. Combined and alternating topical steroids and food elimination diet for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:2381.
Abu-Sultaneh SM, Durst P, Maynard V, Elitsur Y. Fluticasone and food allergen elimination reverse sub-epithelial fibrosis in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:97.
Wolf WA, Jerath MR, Sperry SL, et al. Dietary elimination therapy is an effective option for adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1272.
Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, Alcedo J, et al. Step-up empiric elimination diet for pediatric and adult eosinophilic esophagitis: The 2-4-6 study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1365.
Hoofien A, Dias JA, Malamisura M, Rea F, Chong S, Oudshoorn J, Nijenhuis-Hendriks D, Otte S, Papadopoulou A, Romano C, Gottrand F, Miravet VV, Orel R, Oliva S, Junquera CG, Załęski A, Urbonas V, Garcia-Puig R, Gomez MJM, et al. Pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis: results of the European Retrospective Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis Registry (RetroPEER). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;68(4):552–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000002215.
Rank MA, Sharaf RN, Furuta GT, et al. Technical review on the management of eosinophilic esophagitis: a report from the AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1789.
Kliewer KL, Gonsalves N, Dellon ES, et al. One-food versus six-food elimination diet therapy for the treatment of eosinophilic oesophagitis: a multicentre, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;8:408. This knowledge can improve adherence and better treatment outcome in patients where multiple foods restriction are not needed and comparable results can be obtained with single food restriction.
Klinnert MD. Psychological impact of eosinophilic esophagitis on children and families. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009;29:99.
Arnim UV, Biedermann L, Aceves SS, et al. Monitoring patients with eosinophilic esophagitis in routine clinical practice - international expert recommendations. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;
Laserna-Mendieta EJ, Casabona S, Guagnozzi D, et al. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor therapy for eosinophilic oesophagitis in 630 patients: results from the EoE connect registry. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52:798.
Wolf WA, Cotton CC, Green DJ, et al. Predictors of response to steroid therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis and treatment of steroid-refractory patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:452.
Dohil R, Newbury R, Fox L, et al. Oral viscous budesonide is effective in children with eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:418.
Hirano I, Collins MH, Katzka DA, et al. Budesonide oral suspension improves outcomes in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: results from a phase 3 trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:525.
Dellon ES, Woosley JT, Arrington A, et al. Efficacy of budesonide vs fluticasone for initial treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:65.
Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Collins MH, et al. Clinical and immunopathologic effects of swallowed fluticasone for eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:568.
Lindberg GM, Van Eldik R, Saboorian MH. A case of herpes esophagitis after fluticasone propionate for eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;5:527.
Dellon ES, Woosley JT, Arrington A, et al. Rapid recurrence of eosinophilic esophagitis activity after successful treatment in the observation phase of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:1483.
Dupilumab. US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) approved product information. US Food & Drug Administration. Revised May 2022. Dupilumab is useful in non-responders, and in EoE patients with other atopic conditions like asthma/eczema.
Bridgewood C, Wittmann M, Macleod T, et al. T Helper 2 IL-4/IL-13 Dual blockade with dupilumab is linked to some emergent T helper 17–type diseases, including seronegative arthritis and enthesitis/enthesopathy, but not to humoral autoimmune diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2022;142:2660.
Jung KW, Gundersen N, Kopacova J, et al. Occurrence of and risk factors for complications after endoscopic dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:15.
Richter JE. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;29:815.
Stewart MJ, Shaffer E, Urbanski SJ, et al. The association between celiac disease and eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013;13:96.
Abonia JP, Blanchard C, Butz BB, et al. Involvement of mast cells in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:140.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, R. Eosinophilic Esophagitis, Then and Now: A Review. Curr Pediatr Rep 11, 233–244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40124-023-00309-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40124-023-00309-z