Abstract
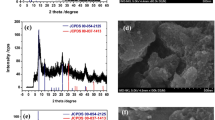
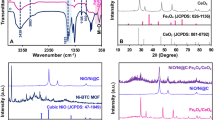
Ionic liquid (IL)-assisted Co3O4 nanostructures were synthesized by a simple, facile and novel low-temperature aqueous chemical growth method and used for the modification of glassy carbon electrode (GCE) for the selective determination of ascorbic acid (AA). Different volumes of IL were used in the preparation of nanostructures to examine the effect of IL on the morphology and electrochemical performance of the synthesized material. The functionalities of the prepared material were investigated by FTIR, while the crystalline nature and phase purity of the material were confirmed by XRD results. FESEM analysis were carried out to expose the surface characteristics of the prepared nanostructures and the results demonstrated that the cobalt oxide nanostructures possess nanorods like morphology. The EDX results verified the maximum elemental percent composition for the cobalt and oxygen in the synthesized material. The electrochemical performance of Co3O4 nanostructures modified GCE was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The electrochemical results demonstrated that the modified electrode shown outstanding performance in the determination of AA with a very low limit of detection (1 µM) along with higher stability and repeatability features. The novel AA sensor manifested exceptional sensitivity and selectivity over a wide linear range of concentration from 0.05 to 3 mM with the coefficient of determination R2 = 0.998. The applicability of the developed sensor was examined in the pharmaceutical samples that contain AA and the sensor selectively detected the AA from multiple ingredients that were present in their formulation with acceptable recovery.
Graphic abstract
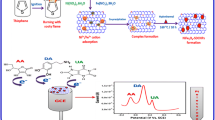
It describes the synthesis of [BMIM][PF6] IL functionalized cobalt oxide nanostructures through low-temperature aqueous chemical growth method and the synthesized material was utilized to fabricate an electrochemical sensor (Co3O4/GCE) for the selective determination of Ascorbic acid.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, X., Zhang, X., Guo, X., Kang, Q., Shen, D., Zou, G.: Sensitive and selective determining ascorbic acid and activity of alkaline phosphatase based on electrochemiluminescence of dual-stabilizers-capped CdSe quantum dots in carbon nanotube-nafion composite. Talanta 154, 175–182 (2016)
Intarakamhang, S., Leson, C., Schuhmann, W., Schulte, A.: A novel automated electrochemical ascorbic acid assay in the 24-well microtiter plate format. Anal. Chim. Acta 687(1), 1–6 (2011)
Shahamirifard, S.A., Ghaedi, M.: A new electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of arbutin and vitamin C based on hydroxyapatite-ZnO-Pd nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111474 (2019)
Buledi, J.A., Ameen, S., Khand, N.H., Solangi, A.R., Taqvi, I.H., Agheem, M.H., Wajdan, Z.: CuO nanostructures based electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and ascorbic acid. Electroanalysis (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202000083
Zhang, X., Cao, Y., Yu, S., Yang, F., Xi, P.: An electrochemical biosensor for ascorbic acid based on carbon-supported PdNinanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 44, 183–190 (2013)
Weng, Y.-C., Lee, Y.-G., Hsiao, Y.-L., Lin, C.-Y.: A highly sensitive ascorbic acid sensor using a Ni–Pt electrode. Electrochim. Acta 56(27), 9937–9945 (2011)
Choi, H.K., Gao, X., Curhan, G.: Vitamin C intake and the risk of gout in men: a prospective study. Arch. Intern. Med. 169(5), 502–507 (2009)
Hu, B., Liu, Y., Wang, Z.-W., Song, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, Z., Liu, C.-S.: Bimetallic-organic framework derived porous Co3O4/Fe3O4/C-loaded g-C3N4nanocomposites as non-enzymic electrocatalysis oxidization toward ascorbic acid, dopamine acid and uric acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 441, 694–707 (2018)
Du, J., Tao, Y., Zhang, J., Xiong, Z., Xie, A., Luo, S., Li, X., Yao, C.: Co3O4-CuNi/reduced graphene composite for non-enzymatic detection of ascorbic acid. Mater. Technol. 34, 1–9 (2019)
Jiang, J., Du, X.: Sensitive electrochemical sensors for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid based on Au@ Pd-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. Nanoscale 6(19), 11303–11309 (2014)
Grotzkyj Giorgi, M., Howland, K., Martin, C., Bonner, A.B.: A novel HPLC method for the concurrent analysis and quantitation of seven water-soluble vitamins in biological fluids (plasma and urine): a validation study and application. Sci. World J. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/359721
Wang, X., Han, Q., Cai, S., Wang, T., Qi, C., Yang, R., Wang, C.: Excellent peroxidase mimicking property of CuO/Pt nanocomposites and their application as an ascorbic acid sensor. Analyst 142(13), 2500–2506 (2017)
Wang, J., Zhou, M., Dong, R., Cong, X., Zhang, R., Wang, X.: Simultaneous determination of peroxide hydrogen and ascorbic acid by capillary electrophoresis with platinum nanoparticles modified micro-disk electrode. Electroanalysis 29(11), 2483–2490 (2017)
Chen, H., Wang, Q., Shen, Q., Liu, X., Li, W., Nie, Z., Yao, S.: Nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots based long-persistent chemiluminescence system for ascorbic acid imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 91, 878–884 (2017)
Özyürek, M., Güçlü, K., Bektaşoğlu, B., Apak, R.: Spectrophotometric determination of ascorbic acid by the modified CUPRAC method with extractive separation of flavonoids–La (III) complexes. Anal. Chim. Acta 588(1), 88–95 (2007)
Zhu, S., Lei, C., Gao, Y., Sun, J., Peng, H., Gao, H., Zhang, R., Wang, R., Zhao, X.-E., Wang, H.: Simple and label-free fluorescence detection of ascorbic acid in rat brain microdialysates in the presence of catecholamines. New J. Chem. 42(5), 3851–3856 (2018)
Na, W., Li, N., Xingguang, S.: Enzymatic growth of single-layer MnO2nanosheets in situ: Application to detect alkaline phosphatase and ascorbic acid in the presence of sulfanilic acid functionalized graphene quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B 274, 172–179 (2018)
Peng, J., Ling, J., Zhang, X.-Q., Zhang, L.-Y., Cao, Q.-E., Ding, Z.-T.: A rapid, sensitive and selective colorimetric method for detection of ascorbic acid. Sens. Actuators B 221, 708–716 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Liu, P., Xie, S., Chen, M., Zhang, M., Cai, Z., Liang, R., Zhang, Y., Cheng, F.: A novel electrochemical ascorbic acid sensor based on branch-trunk Ag hierarchical nanostructures. J. Electroanal. Chem. 818, 250–256 (2018)
Abellán-Llobregat, A., Vidal, L., Rodríguez-Amaro, R., Canals, A., Morallon, E.: Evaluation of herringbone carbon nanotubes-modified electrodes for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 285, 284–291 (2018)
Jo, A., Kang, M., Cha, A., Jang, H.S., Shim, J.H., Lee, N.-S., Kim, M.H., Lee, Y., Lee, C.: Nonenzymatic amperometric sensor for ascorbic acid based on hollow gold/ruthenium nanoshells. Anal. Chim. Acta 819, 94–101 (2014)
Sha, R., Badhulika, S.: Facile green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/tin oxide composite for highly selective and ultra-sensitive detection of ascorbic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 816, 30–37 (2018)
Zaidi, S.A., Shahzad, F., Batool, S.: Progress in cancer biomarkers monitoring strategies using graphene modified support materials. Talanta 210, 120669 (2020)
Kucukkolbasi, S., Erdogan, Z., Baslak, C., Sogut, D., Kus, M.: A highly sensitive ascorbic acid sensor based on graphene oxide/CdTe quantum dots-modified glassy carbon electrode. Russ. J. Electrochem. 55(2), 107–114 (2019)
Wu, G.-H., Wu, Y.-F., Liu, X.-W., Rong, M.-C., Chen, X.-M., Chen, X.: An electrochemical ascorbic acid sensor based on palladium nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide. Anal. Chim. Acta 745, 33–37 (2012)
Baksh, H., Buledi, J.A., Khand, N.H., Solangi, A.R., Mallah, A., Sherazi, S.T., Abro, M.I.: Ultra-selective determination of carbofuran by electrochemical sensor based on nickel oxide nanoparticles stabilized by ionic liquid. Monatsheftefür Chem. Chem. Mon. 151, 1689–1696 (2020)
Saksena, K., Shrivastava, A., Kant, R.: Chiral analysis of ascorbic acid in bovine serum using ultrathin molecular imprinted polyaniline/graphite electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 795, 103–109 (2017)
Wu, X., Xing, Y., Pierce, D., Zhao, J.X.: One-pot synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/metal (oxide) composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(43), 37962–37971 (2017)
Hussain, M.M., Asiri, A.M.: Rahman MM (2020) Non-enzymatic simultaneous detection of acetylcholine and ascorbic acid using ZnO. CuO nanoleaves: Real sample analysis. Microchem. J. 159, 105534 (2020)
Bukkitgar, S.D., Kumar, S., Singh, S., Singh, V., Reddy, K.R., Sadhu, V., Bagihalli, G.B., Shetti, N.P., Reddy, C.V., Ravindranadh, K.: Functional nanostructured metal oxides and its hybrid electrodes. Recent advancements in electrochemical biosensing applications. Microchem. J. 159, 105522 (2020)
Hei, Y., Li, X., Zhou, X., Liu, J., Hassan, M., Zhang, S., Yang, Y., Bo, X., Wang, H.-L., Zhou, M.: Cost-effective synthesis of three-dimensional nitrogen-doped nanostructured carbons with hierarchical architectures from the biomass of sea-tangle for the amperometric determination of ascorbic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 1029, 15–23 (2018)
Hussain, S., Zaidi, S.A., Vikraman, D., Kim, H.-S., Jung, J.: Facile preparation of tungsten carbide nanoparticles for an efficient oxalic acid sensor via imprinting. Microchem. J. 159, 105404 (2020)
Ganjali, M.R., Salimi, H., Tajik, S., Beitollahi, H., Rezapour, M., Larijani, B.: Application of Fe3O4@ SiO2/MWCNT film on glassy carbon electrode for the sensitive electroanalysis of levodopa. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 12(6), 5243–5253 (2017)
Ganjali, M.R., Beitollahi, H., Zaimbashi, R., Tajik, S., Rezapour, M., Larijani, B.: Voltammetric determination of dopamine using glassy carbon electrode modified with ZnO/Al2O3nanocomposite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 2519–2529 (2018)
He, B.-S., Zhang, J.-X.: Rapid detection of ascorbic acid based on a dual-electrode sensor system using a powder microelectrode embedded with carboxyl multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sensors 17(7), 1549 (2017)
Shetti, N.P., Bukkitgar, S.D., Reddy, K.R., Reddy, C.V., Aminabhavi, T.M.: ZnO-based nanostructured electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors in biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111417 (2019)
Dakshayini, B., Reddy, K.R., Mishra, A., Shetti, N.P., Malode, S.J., Basu, S., Naveen, S., Raghu, A.V.: Role of conducting polymer and metal oxide-based hybrids for applications in ampereometric sensors and biosensors. Microchem. J. 147, 7–24 (2019)
Kumar, S., Bukkitgar, S.D., Singh, S., Singh, V., Reddy, K.R., Shetti, N.P., Venkata Reddy, C., Sadhu, V., Naveen, S.: Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on graphene functionalized with metal oxide nanostructures for healthcare applications. ChemistrySelect 4(18), 5322–5337 (2019)
Shetti, N.P., Bukkitgar, S.D., Reddy, K.R., Reddy, C.V., Aminabhavi, T.M.: Nanostructured titanium oxide hybrids-based electrochemical biosensors for healthcare applications. Colloids Surf. B 178, 385–394 (2019)
Bao, L., Li, T., Chen, S., Peng, C., Li, L., Xu, Q., Chen, Y., Ou, E., Xu, W.: 3D graphene frameworks/Co3O4 composites electrode for high-performance supercapacitor and enzymeless glucose detection. Small 13(5), 1602077 (2017)
Memon, S.A., Hassan, D., Buledi, J.A., Solangi, A.R., Memon, S.Q., Palabiyik, I.M.: Plant material protected cobalt oxide nanoparticles: Sensitive electro-catalyst for tramadol detection. Microchem. J. 159, 105480 (2020)
Elhag, S., Ibupoto, Z., Nour, O., Willander, M.: Synthesis of Co3O4 cotton-like nanostructures for cholesterol biosensor. Materials 8(1), 149–161 (2015)
Numan, A., Shahid, M.M., Omar, F.S., Ramesh, K., Ramesh, S.: Facile fabrication of cobalt oxide nanograin-decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as ultrasensitive platform for dopamine detection. Sens. Actuators B 238, 1043–1051 (2017)
Song, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Zhang, S., Liu, G., Chen, H., Qiu, J.: Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical performance of Co3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanosheet composites for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 112, 120–126 (2013)
Wang, G., Zhu, F., Xia, J., Wang, L., Meng, Y., Zhang, Y.: Preparation of Co3O4/carbon derived from ionic liquid and its application in lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 257, 138–145 (2017)
Sheldon, R.: Catalytic reactions in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 23, 2399–2407 (2001)
Fuller, J., Carlin, R.T., Osteryoung, R.A.: The room temperature ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate: electrochemical couples and physical properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144(11), 3881–3886 (1997)
Antonietti, M., Kuang, D., Smarsly, B., Zhou, Y.: Ionic liquids for the convenient synthesis of functional nanoparticles and other inorganic nanostructures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43(38), 4988–4992 (2004)
Zheng, W., Liu, X., Yan, Z., Zhu, L.: Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of large-scale TiO2 nanoparticles with controllable phase by hydrolysis of TiCl4. ACS Nano 3(1), 115–122 (2008)
Wasserscheid, P., Welton, T.: Ionic Liquids in Synthesis. John Wiley and Sons, Amsterdam (2008)
Shen, J., Shi, M., Yan, B., Ma, H., Li, N., Ye, M.: Ionic liquid-assisted one-step hydrothermal synthesis of TiO 2-reduced graphene oxide composites. Nano Res. 4(8), 795 (2011)
Al-Qirby, L.M., Radiman, S., Siong, C.W., Ali, A.M.: Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of Co3O4 nanocrystals in the presence of the ionic liquid [EMIM][BF4]. Ultrason. Sonochem. 38, 640–651 (2017)
Chang, A.S., Memon, N.N., Amin, S., Chang, F., Aftab, U., Abro, M.I., dad Chandio, A., Shah, A.A., Ibupoto, M.H., Ansari, M.A.: Facile non-enzymatic lactic acid sensor based on cobalt oxide nanostructures. Electroanalysis 31(7), 1296–1303 (2019)
Vinothkumar, V., Sangili, A., Chen, S.M., Veerakumar, P., Lin, K.-C.: Sr-doped NiO3 nanorods synthesized by simple sonochemical method as excellent materials for voltammetric determination of quercetin. New J. Chem. 44, 2821–2832 (2020)
Zhao, P., Ni, M., Xu, Y., Wang, C., Chen, C., Zhang, X., Li, C., Xie, Y., Fei, J.: A novel ultrasensitive electrochemical quercetin sensor based on MoS2-carbon nanotube@ graphene oxide nanoribbons/HS-cyclodextrin/graphene quantum dots composite film. Sens. Actuators B 299, 126997 (2019)
Du, J., Tao, Y., Zhang, J., Xiong, Z., Xie, A., Luo, S., Li, X., Yao, C.: Co3O4-CuNi/reduced graphene composite for non-enzymatic detection of ascorbic acid. Mater. Technol. 34(11), 665–673 (2019)
Li, L., Zhang, P., Li, Z., Li, D., Han, B., Tu, L., Li, B., Wang, Y., Ren, L., Yang, P.: CuS/Prussian blue core–shell nanohybrid as an electrochemical sensor for ascorbic acid detection. Nanotechnology 30(32), 325501 (2019)
Karaboduk, K.: Electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid based on AgNPs/PVP-modified glassy carbon electrode. ChemistrySelect 4(20), 6361–6369 (2019)
Du, J., Yue, R., Ren, F., Yao, Z., Jiang, F., Yang, P., Du, Y.: Novel graphene flowers modified carbon fibers for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 53, 220–224 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Ji, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, S., Zhang, T.: Electrodeposition synthesis of reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube hybrids on indium tin oxide electrode for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. RSC Adv. 5(129), 106307–106314 (2015)
Zou, C.E., Zhong, J., Li, S., Wang, H., Wang, J., Yan, B., Du, Y.: Fabrication of reduced graphene oxide-bimetallic PdAunanocomposites for the electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and rutin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 805, 110–119 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NHK: Conducting experiment and Writing of the article. IMP: Helping in characterization of material, Correction of grammatical mistakes, improving English language. JAB: Interpretation and designing of all graphs. SA: Graphing and helping in experiments. AFM: Helping in experiment and Formatting of article and references. TG: Data collection, sampling. ARS: Conceptualization/ Supervision/editing/correcting draft/ Submission/Correspondence to the Journal.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khand, N.H., Palabiyik, I.M., Buledi, J.A. et al. Functional Co3O4 nanostructure-based electrochemical sensor for direct determination of ascorbic acid in pharmaceutical samples . J Nanostruct Chem 11, 455–468 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-020-00380-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-020-00380-8