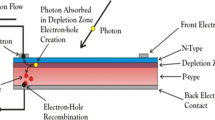
Abstract
In a comparative study, a solar cell structure’s layer thicknesses were optimized using particle swarm optimization (PSO) and simulated annealing (SA). The ideal short-circuit current density was considered as the cost function for both algorithms to minimize the number of function evaluations (NFEs) needed to obtain the optimal thicknesses of the structure layers (ZnO and MoOx layers), separately and simultaneously, being single- and multi-layer optimization. The results were compared to those of genetic algorithm (GA) and brute-force methods that have been reported in the literature. In the single-layer optimization, the results obtained by PSO indicated that the maximum required NFEs for optimizing ZnO was 33.1 ± 23.16 compared to 81 for the brute-force method and 78.16 ± 1.65 for the GA. The PSO method needed 19.6 ± 11.7 NFEs for optimizing the MoOx layer, while, as was reported in Ref. Vincent (E 13:1726 2020), GA optimized this layer by 13.05 ± 3.24 in the best manner by the Roulette wheel method. Both single-based and population-based approaches were implemented for the SA. The results obtained by SA indicated that the required NFEs were estimated higher than that of the GA due to the small search space. The required NFEs for two-layer optimization using PSO amount to 111.27 ± 60.1, which is considerably lower than the 1758.77 ± 39.75 of GA. The NFEs are significantly lower than the similar value obtained using the brute-force approach and GA, even with the highest SD value. In the case of two-layer optimization, SA estimated 65.63 ± 21.1 and 575.76 ± 301.64 NFEs using single-based and population-based methods, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, G., Li, M., Taylor, R., Hao, Y., Besagni, G., Markides, C.N.: Solar energy utilisation: current status and roll-out potential. Appl. Therm. Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118285
Korfiati, A., Gkonos, C., Veronesi, F., Gaki, A., Grassi, S., Schenkel, R., Volkwein, S., Raubal, M., Hurni, L.: Estimation of the global solar energy potential and photovoltaic cost with the use of open data. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Plan. Manag. 9, 17–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5278/ijsepm.2016.9.3
Güney, T.: Solar energy and sustainable development: evidence from 35 countries. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 29, 187–194 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2021.1986749
Kannan, N., Vakeesan, D.: Solar energy for future world: - a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 62, 1092–1105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.05.022
Milichko, V.A., Shalin, A.S., Mukhin, I.S., Kovrov, A.E., Krasilin, A.A., Vinogradov, A.V., Belov, P.A., Simovski, C.R.: Solar photovoltaics: current state and trends. Phys. Usp. 59, 727–772 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3367/UFNE.2016.02.037703/XML
King, R.R., Karam, N.H., Ermer, J.H., Haddad, M., Colter, P., Isshiki, T., Yoon, H., Cotal, H.L., Joslin, D.E., Krut, D.D., Sudharsanan, R., Edmondson, K., Cavicchi, B.T., Lillington, D.R.: Next-generation, high-efficiency III-V multijunction solar cells. Conf. Rec. IEEE Photovolt. Spec. Conf. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/PVSC.2000.916054
Pakhanov, N.A., Andreev, V.M., Shvarts, M.Z., Pchelyakov, O.P.: State-of-the-art architectures and technologies of high-efficiency solar cells based on III–V heterostructures for space and terrestrial applications. Optoelectron. Instrum. Data Process. 54, 187–202 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S8756699018020115
Yamaguchi, M.: Japanese R and D activities of high efficiency III-V compound multi-junction and concentrator solar cells. Energy Procedia. 15, 265–274 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EGYPRO.2012.02.031
Miller, B., Ranum, D.: Problem-solving with algorithms and data structures release 3.0, Franklin, Beedle & Associates (2013)
DIab, A.A.Z., Sultan, H.M., Do, T.D., Kamel, O.M., Mossa, M.A.: Coyote optimization algorithm for parameters estimation of various models of solar cells and PV modules. IEEE Access 8, 111102–111140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3000770
Farah, A., Belazi, A., Benabdallah, F., Almalaq, A., Chtourou, M., Abido, M.A.: Parameter extraction of photovoltaic models using a comprehensive learning Rao-1 algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 252, 115057 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2021.115057
Kharchouf, Y., Herbazi, R., Chahboun, A.: Parameter’s extraction of solar photovoltaic models using an improved differential evolution algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 251, 114972 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2021.114972
Hemeida, A.M., Omer, A.S., Bahaa-Eldin, A.M., Alkhalaf, S., Ahmed, M., Senjyu, T., El-Saady, G.: Multi-objective multi-verse optimization of renewable energy sources-based micro-grid system: real case. Ain Shams Eng. J. 13, 101543 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASEJ.2021.06.028
Alavi, M., Yoo, Y., Vogel, D.R.: Using information technology to add value to management education. Acad. Manag. J. 40, 1310–1333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5465/257035
Ardito, C., Costabile, M.F., De Marsico, M., Lanzilotti, R., Levialdi, S., Roselli, T., Rossano, V.: An approach to usability evaluation of e-learning applications. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 43, 270–283 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10209-005-0008-6
Boehner, K., DePaula, R., Dourish, P., Sengers, P.: How emotion is made and measured. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 65, 275–291 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHCS.2006.11.016
Meer, K.: Simulated annealing versus metropolis for a TSP instance. Inf. Process. Lett. 104, 216–219 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IPL.2007.06.016
Niknam, T.: An approach based on particle swarm optimization for optimal operation of distribution network considering distributed generators. IECON Proc. Indus. Elect. Conf. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2006.347222
Niknam, T., Firouzi, B.B., Nayeripour, M.: An efficient hybrid evolutionary algorithm for cluster analysis. World Appl. Sci. J. 4(2), 300–307 (2008)
Rajan, C.C.A., Mohan, M.R.: An evolutionary programming based simulated annealing method for solving the unit commitment problem. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 29, 540–550 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJEPES.2006.12.001
Saber, A.Y., Senjyu, T., Yona, A., Urasaki, N., Funabashi, T.: Fuzzy unit commitment solution—A novel twofold simulated annealing approach. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 77, 1699–1712 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EPSR.2006.12.002
Vincent, P., Sergio, G.C., Jang, J., Kang, I.M., Park, J., Kim, H., Lee, M., Bae, J.H.: Application of genetic algorithm for more efficient multi-layer thickness optimization in solar cells. Energies 13, 1726 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/EN13071726
Anabestani, H.: Investigation on performance enhancement of micro-sized IR photodetectors, UWSpace. http://hdl.handle.net/10012/17406 (2021)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. Proc. ICNN’95 Int. Conf. Neural Netw. 4, 1942–1948 (1942). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Kennedy, J.F., Eberhart, R.C., Shi, Y.: Swarm intelligence, vol. 512. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco (2001)
Niknam, T., Amiri, B., Olamaei, J., Arefi, A.: An efficient hybrid evolutionary optimization algorithm based on PSO and SA for clustering. J. Zhejiang Univ. A 10, 512–519 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/JZUS.A0820196
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, C.D., Vecchi, M.P.: Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 80(220), 671–680 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.220.4598.671
Rutenbar, R.A.: Simulated annealing algorithms: an overview. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 5, 19–26 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/101.17235
Siddique, N., Adeli, H.: Simulated annealing its variants and engineering applications. Inte. J. Artif. Intell. Tools (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218213016300015
Acknowledgements
The support from Shahid Beheshti University is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is NO Competing Interest. The authors declare no competing financial and non-financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kargaran, H., Bayat, E., Hassanzadeh, A. et al. High efficient solar cells through multi-layer thickness optimization using particle swarm optimization and simulated annealing. Int J Energy Environ Eng 14, 661–670 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-022-00541-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-022-00541-1