Abstract
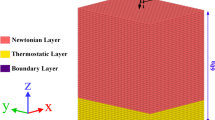
We investigated the atomic structural variations on the free surface of tungsten carbide-cobalt (WC–Co) through both experiments and molecular dynamics simulations under electron beam (e-beam) irradiation. Initially, e-beam experiments were conducted to compare cobalt dissociation and elucidate its physical implications. Subsequently, molecular dynamics simulations qualitatively reproduced the evaporation phenomena that occurred over the free surfaces of the five WC–Co structures. The nano-polycrystalline structure and configurations featuring a small cobalt (Co) surface exhibited a comparatively low number of escaped Co atoms, attributed to their relatively high area/perimeter ratio. This study subsequently investigated the impact of e-beam treatment on the randomness of atomic arrangements and mechanical properties by assessing variations in local entropy and von Mises stress distributions at different positions and in different simulation states. Position-dependent von Mises stress, interatomic potential, and local entropy profiles, reproduced profiles with the same dataset, and two-dimensional colored maps at various simulation states were generated to illustrate individual variations and correlations between local entropy and von Mises stress to demonstrate instability of atomic structures. Our study demonstrated that e-beam treatment influenced the atomic structural instability and mechanical characteristics quantitatively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Yang et al., J. Manuf. Process. 83, 223–234 (2022)
Y.R. Uhm et al., J. Korean Phys. Soc. 82, 286–292 (2023)
S.P. Rao et al., Curr. Appl. Phys.. Appl. Phys. 57, 33–41 (2024)
S.A. Voss, U.C. Matur, H. Cimenoglu, N. Baydogan, Curr. Appl. Phys.. Appl. Phys. 52, 9–23 (2023)
Y. Li et al., Vacuum 216, 112463 (2023)
H. Yuan et al., ACS Omega 9, 18599–18607 (2024)
C. Han et al., Adv. Mater. 32, 1903855 (2020)
Z. Wang et al., Nanoscale Res. Lett.Lett. 14, 1–11 (2019)
J. Kim, W.J. Lee, H.W. Park, Appl. Therm. Eng. 128, 151–158 (2018)
M. Terrones et al., Science 288, 1226–1229 (2000)
H. Gu et al., Sci. Rep. 7, 1–10 (2017)
M. Yasuda et al., Phys. Rev. B 75, 205406 (2007)
A.K. Singla, J. Singh, V.S. Sharma, Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 1603–1640 (2018)
P. Muthuswamy, V.G.V. Murugesan, Eng. Res. Express 3, 045011 (2021)
I. Jeong, Y. -G. Yoon., J. Korean Phys. Soc. 83 675 - 680 (2023)
C.S. Won et al., J. Korean Phys. Soc. 57, 1644–1648 (2010)
K.-S. Kim et al., J. Korean Phys. Soc. 52, 1272–1276 (2008)
A.P. Thompson et al., Comp. Phys. Comm. 271, 108171 (2022)
A. Stukowski, Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 015012 (2010)
H. Xie et al., Sci. Rep. 6, 1–8 (2016)
J. Fang et al., Acta Crystallogr. A Crystallogr. A 75, 134–142 (2019)
M. Petisme, M. Gren, G. Wahnstrom, Int J Refract Hard Met. Materials 49, 75–80 (2015)
P. Erhart, K. Albe, Phys. Rev. B 71, 035211 (2005)
S. Alavi, D.L. Thompson, J. Phys. Chem. A 110, 1518–1523 (2006)
A. Abdullah et al., Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 41, 268–280 (2009)
K.A. Kanaya, S. Okayama, J. Phys. D. 5, 43 (1972)
C.A. Schneider, W.S. Rasband, K.W. Eliceiri, Nat. Methods 9, 671–675 (2012)
D. Şopu et al., Appl. Mater. 21, 100828 (2020)
P.M. Piaggi, O. Valsson, M. Parrinello, Phys. Rev. Lett.Lett. 119, 015701 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.Y., Yi, T. Investigation of the surface characteristics of WC–Co structures under Local E-beam irradiation via experiments and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01091-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01091-x