Abstract
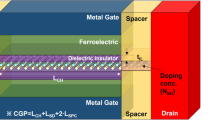
In this study, we propose a ferroelectric FET (FeFET) structure termed dual ferroelectric recessed channel FeFET (DF-RFeFET), employing metal–ferroelectric (FE)–metal–FE–metal–SiO2 interlayer (IL)–silicon (MFMFMIS) structures. The DF-RFeFET is aimed at enhancing the memory window (MW) for high-performance memory applications. TCAD simulations with calibrated FE parameters and device models reveal that the DF-RFeFET can achieve a larger MW thanks to the enhanced geometric advantage to offer a strong and localized electric field at the inner ferroelectrics near the gate metal’s corner. Moreover, design guidelines for the DF-RFeFET are suggested, including adjusting the inner and outer ferroelectric layers' thickness ratio and the recessed channel depth. The effects of introducing a relatively low-k oxide intermediate layer between dual ferroelectric layers and high-k gate stacks of IL on the MW have also been investigated. Through structural optimization, the DF-RFeFET demonstrated a record MW value of 5.5 V among the previously reported Si FeFETs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Mulaosmanovic, E.T. Breyer, S. Dünkel, S. Beyer, T. Mikolajick, S. Slesazeck, Ferroelectric field-effect transistors based on HfO2: a review. Nanotechnol. 32, 502002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac189f
Mikolajick T, Schroeder U, Lomenzo P, Breyer E, Mulaosmanovic H, Hoffmann M, Mittmann T, Mehmood F, Max B, Slesazeck S. "Next generation ferroelectric memories enabled by hafnium oxide," 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM).(2019):15.5. 1-.5. 4. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM19573.2019.8993447
Chan C-Y, Chen K-Y, Peng H-K, Wu Y-H. "FeFET memory featuring large memory window and robust endurance of long-pulse cycling by interface engineering using high-k AlON," 2020 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology.(2020):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1109/VLSITechnology18217.2020.9265103
W. Xiao, C. Liu, Y. Peng, S. Zheng, Q. Feng, C. Zhang, J. Zhang, Y. Hao, M. Liao, Y. Zhou, Memory window and endurance improvement of Hf0. 5Zr0. 5O2-based FeFETs with ZrO2 seed layers characterized by fast voltage pulse measurements. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 14, 1–7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-3063-2
Hu VP-H, Lin H-H, Zheng Z-A, Lin Z-T, Lu Y-C, Ho L-Y, Lee Y-W, Su C-W, Su C-J. "Split-gate FeFET (SG-FeFET) with dynamic memory window modulation for non-volatile memory and neuromorphic applications," 2019 Symposium on VLSI Technology.(2019):T134-T5. https://doi.org/10.23919/VLSIT.2019.8776555
K. Lee, J.-H. Bae, S. Kim, J.-H. Lee, B.-G. Park, D. Kwon, Ferroelectric-gate field-effect transistor memory with recessed channel. IEEE Electr Device L. 41, 1201–1204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2020.3001129
K. Lee, S. Kim, J.-H. Lee, B.-G. Park, D. Kwon, Ferroelectric-Metal Field-Effect Transistor With Recessed Channel for 1T-DRAM Application. IEEE J Electron Devices Soc. 10, 13–18 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2021.3127955
F. Tian, S. Zhao, H. Xu, J. Xiang, T. Li, W. Xiong, J. Duan, J. Chai, K. Han, X. Wang, Impact of interlayer and ferroelectric materials on charge trapping during endurance fatigue of FeFET with TiN/HfxZr1-xO2/interlayer/Si (MFIS) gate structure. IEEE T Electron Dev. 68, 5872–5878 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2021.3114663
B. Kwak, K. Lee, N.-H. Park, S.J. Jeon, H. Kim, D. Kwon, Recessed Channel Ferroelectric-Gate Field-Effect Transistor Memory With Ferroelectric Layer Between Dual Metal Gates. IEEE T Electron Dev. 69, 1054–1057 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2022.3144621
Ali T, Polakowski P, Kühnel K, Czernohorsky M, Kämpfe T, Rudolph M, Pätzold B, Lehninger D, Müller F, Olivo R. "A multilevel FeFET memory device based on laminated HSO and HZO ferroelectric layers for high-density storage," 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM).(2019):28.7. 1-.7. 4. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM19573.2019.8993642
C.-Y. Liao, K.-Y. Hsiang, F.-C. Hsieh, S.-H. Chiang, S.-H. Chang, J.-H. Liu, C.-F. Lou, C.-Y. Lin, T.-C. Chen, C.-S. Chang, Multibit ferroelectric FET based on nonidentical double HfZrO2 for high-density nonvolatile memory. IEEE Electr Device L. 42, 617–620 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2021.3060589
Kim HJ, Park MH, Kim YJ, Lee YH, Jeon W, Gwon T, Moon T, Kim KD, Hwang CS. "Grain size engineering for ferroelectric Hf0. 5Zr0. 5O2 films by an insertion of Al2O3 interlayer," Appl Phys Lett.(2014);105:192903. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4902072
K. Toprasertpong, K. Tahara, Y. Hikosaka, K. Nakamura, H. Saito, M. Takenaka, S. Takagi, Low operating voltage, improved breakdown tolerance, and high endurance in Hf0. 5Zr0. 5O2 ferroelectric capacitors achieved by thickness scaling down to 4 nm for embedded ferroelectric memory. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 14, 51137–51148 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c15369
T. Ali, K. Mertens, K. Kühnel, M. Rudolph, S. Oehler, D. Lehninger, F. Müller, R. Revello, R. Hoffmann, K. Zimmermann, A FeFET with a novel MFMFIS gate stack: towards energy-efficient and ultrafast NVMs for neuromorphic computing. Nanotechnology 32, 425201 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac146c
Chen S, Ahn D-H, An SU, Kim Y. "Simulation of a Recessed Channel Ferroelectric-Gate Field-Effect Transistor with a Dual Ferroelectric Gate Stack for Memory Application," 2023 7th IEEE Electron Devices Technology & Manufacturing Conference (EDTM).(2023):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/EDTM55494.2023.10103116
C. Su, Q. Huang, K. Wang, Z. Fu, R. Huang, New Insights Into Memory Window of Ferroelectric FET Impacted by Read Operations With Awareness of Polarization Switching Dynamics. IEEE T Electron Dev. 69, 5310–5315 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2022.3190824
S. Miller, P. McWhorter, Physics of the ferroelectric nonvolatile memory field effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 5999–6010 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351910
P.-H. Bricout, E. Dubois, Short-channel effect immunity and current capability of sub-0.1-micron MOSFET’s using a recessed channel. IEEE T Electron Dev. 43, 1251–1255 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/16.506776
Kato D, Kajiwara Y, Mukai A, Ono H, Shindome A, Tajima J, Hikosaka T, Kuraguchi M, Nunoue S. "Suppression of short-channel effects in normally-off GaN MOSFETs with deep recessed-gate structures," Jpn J Appl Phys.(2020);59:SGGD13. https://doi.org/10.35848/1347-4065/ab6b7f
T. Ali, P. Polakowski, T. Büttner, T. Kämpfe, M. Rudolph, B. Pätzold, R. Hoffmann, M. Czernohorsky, K. Kühnel, P. Steinke, Theory and experiment of antiferroelectric (AFE) Si-doped hafnium oxide (HSO) enhanced floating-gate memory. IEEE T Electron Dev. 66, 3356–3364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2019.2921618
S. Jindal, S.K. Manhas, S.K. Gautam, S. Balatti, A. Kumar, M. Pakala, Investigation of gate-length scaling of ferroelectric FET. IEEE T Electron Dev. 68, 1364–1368 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2021.3054720
D.Y. Chung, J.H. Lee, Effects of Recess Channel (RC) Depth in Super Self-Aligned RC nMOSFET’s for sub-100 nm Device Technology. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 33, S216–S219 (1998)
Kim J, Oh H, Woo D, Lee Y, Kim D, Kim S, Ha G, Kim H, Kang N, Park J. "S-RCAT (sphere-shaped-recess-channel-array transistor) technology for 70nm DRAM feature size and beyond," 2005 Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2005.(2005):34–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/.2005.1469201
Zhai M, Sun B, Huang K, Chang H, Liu, H.: Effect of SiO2 capping layer on the ferroelectricity of Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 films. AIP Adv. (2020);10:115320. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0027476
V. Gaddam, D. Das, S. Jeon, Insertion of HfO2 seed/dielectric layer to the ferroelectric HZO films for heightened remanent polarization in MFM capacitors. IEEE T Electron Dev. 67, 745–750 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2019.2961208
J. Robertson, R.M. Wallace, High-K materials and metal gates for CMOS applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 88, 1–41 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2014.11.001
B.H. Lee, J. Oh, H.H. Tseng, R. Jammy, H. Huff, Gate stack technology for nanoscale devices. Mater. Today 9, 32–40 (2006)
S. Mohsenifar, M. Shahrokhabadi, Gate stack high-κ materials for Si-based MOSFETs past, present, and futures. Microelectron Solid State Electron. 2, 5 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5923/j.msse.20150401.03
D. Matsushita, K. Muraoka, K. Kato, Y. Nakasaki, S. Inumiya, K. Eguchi, M. Takayanagi, Novel fabrication process to realize ultra-thin (EOT= 0.7 nm) and ultra-low-leakage SiON gate dielectrics. Microelectron. Eng. 80, 424–431 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/RTP.2005.1613680
Ando T, Frank M, Choi K, Choi C, Bruley J, Hopstaken M, Copel M, Cartier E, Kerber A, Callegari A. "Understanding mobility mechanisms in extremely scaled HfO2 (EOT 0.42 nm) using remote interfacial layer scavenging technique and Vt-tuning dipoles with gate-first process," 2009 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM).(2009):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM.2009.5424335
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Brain Korea 21 Four Program, Korea Basic Science Institute (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (grant No.2023R1A6C103A035), the Technology Innovation Program (20015909) through the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT), funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea), Korea Basic Science Institute (National research Facilities and Equipment Center) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (grant No.2023R1A6C103A035, No.2021R1A6C101A405) and the IC Design Education Center (IDEC), Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Ahn, DH., An, S.U. et al. TCAD simulation study of dual ferroelectric gate field-effect transistors with a recessed channel geometry for non-volatile memory applications. J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01079-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01079-7