Abstract
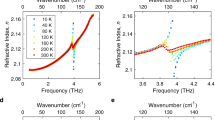
Many optical devices that can be used in terahertz (THz) systems are continuously being researched and developed. Among them, liquid crystal (LC)-based polarizers and phase-shifting devices have been developed. The LC devices used in the THz systems are fabricated in the form of a cell. The substrate of the cell should be transparent and non-birefringent with low absorption in the THz frequency range. In this paper, we report the refractive indices and birefringence measurement results for glass materials, such as slide glass, cover glass, A-cut quartz, and Z-cut quartz in the THz band. Among them, 5CB and E7 nematic LC (NLC) cells are prepared using Z-cut quartz as a substrate. We report the results of the refractive indices, absorption coefficients, and birefringence measurements of each NLC cell in the THz band. It is expected that this result can be used as a LC-based optical device in the THz band in future.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Menikh, R. MacColl, C.A. Mannella, X.C. Zhang, Terahertz biosensing technology: frontiers and progress. ChemPhysChem 3, 655–658 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/1439-7641(20020816)3:8%3c655::AID-CPHC655%3e3.0.CO;2-W
K. Kawase, Y. Ogawa, Y. Watanabe, H. Inoue, Non-destructive terahertz imaging of illicit drugs using spectral fingerprints. Opt. Express 11, 2549–2554 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.11.002549
J.F. Federici, B. Schulkin, F. Huang et al., THz imaging and sensing for security applications—explosives, weapons and drugs. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20, S266–S280 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/20/7/018
K.-H. Kim, D.H. Song, Z.-G. Shen, B.W. Park, K.-H. Park, J.-H. Lee, T.-H. Yoon, Fast switching of long-pitch cholesteric liquid crystal device. Opt. Express 19, 10174–10179 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.19.010174
M.O. Ko, S.-J. Kim, J.-H. Kim, B.W. Lee, M.Y. Jeon, Dynamic measurement for electric field sensor based on wavelength-swept laser. Opt. Express 22, 16139–16147 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.22.016139
M.O. Ko, S.-J. Kim, J.-H. Kim, M.Y. Jeon, In situ observation of dynamic pitch jumps of in-planar cholesteric liquid crystal layers based on wavelength-swept laser. Opt. Express 26, 28751–28762 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.028751
R. Ozaki, K. Kihara, K. Matsuura, K. Kadowaki, T.Q. Duong, H. Moritake, Wavelength and bandwidth control of stop band of ferroelctric liquid crystals by varying incident angle and electric field. Appl. Phys. Express 13, 051003 (2020). https://doi.org/10.35848/1882-0786/ab88c8
S. Ahn, M.O. Ko, J.-H. Kim, Z. Chen, M.Y. Jeon, Characterization of second-order reflection bands from a cholesteric liquid crystal cell based on a wavelength-swept laser. Sensors 20, 4643 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20164643
H.D. Hristov, J.M. Rodriguez, W. Grote, The grooved-dielectric Fresnel zone plate: an effective terahertz lens and antenna. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 54, 1343–1348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.26812
T. Niu, W. Withayachumnankul, A. Upadhyay et al., Terahertz reflectarray as a polarizing beam splitter. Opt. Express 22, 16148–16160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.22.016148
J.B. Masson, G. Gallot, Terahertz achromatic quarter-wave plate. Opt. Lett. 31, 265–267 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.31.000265
P.-Y. Chen, C. Argyropoulos, A. Alu, Terahertz antenna phase shifters using integrally-gated graphene transmission-lines. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61, 1528–1537 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2012.2220327
J.H. Shi, Z.J. Li, D.K. Sang et al., THz photonics in two dimensional materials and metamaterials: properties, devices and prospects. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 1291–1306 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TC05460B
A.I. Hernandez-Serrano, Q. Sun, E.G. Bishop et al., Design and fabrication of 3-D printed conductive polymer structures for THz polarization control. Opt. Express 27, 11635–11641 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.27.011635
R.T. Ako, A. Upadhyay, W. Withayachumnankul et al., Dielectrics for terahertz metasurfaces: material selection and fabrication techniques. Adv. Opt. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201900750
C.-Y. Chen, T.-R. Tsai, C.-L. Pan, R.-P. Pan, Room temperature terahertz phase shifter based on magnetically controlled birefringence in liquid crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4497–4499 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1631064
C.-F. Hsieh, R.-P. Pan, T.-T. Tang et al., Voltage-controlled liquid-crystal terahertz phase shifter and quarter-wave plate. Opt. Lett. 31, 1112–1112 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.31.001112
J. Yang, C.G. Cai, Z.P. Yin et al., Reflective liquid crystal terahertz phase shifter with tuning range of over 360°. IET Microw. Antenna 12, 1466–1469 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2017.0898
M. Naftaly, R.E. Miles, Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy: a new tool for the study of glasses in the far infrared. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351, 3341–3346 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2005.08.003
K. Kanehara, S. Urata, S. Yasuhara et al., Dielectric property and polarization mechanism of sodium silicate glass in GHz-THz range. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.. J. Appl. Phys. (2022). https://doi.org/10.35848/1347-4065/ac7b0f
M.C. Beard, G.M. Turner, C.A. Schmuttenmaer, Terahertz spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 7146–7159 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp020579i
H. Choi, J. Kim, S. Ahn et al., Characterization of the THz absorption spectra of nematic liquid crystals via THz time-domain spectroscopy using mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser. Opt. Fiber Technol.Fiber Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yofte.2021.102685
X. Xin, H. Altan, A. Saint et al., Terahertz absorption spectrum of para and ortho water vapors at different humidities at room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 094905–094905 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2357412
L. Duvillaret, F. Garet, J.L. Coutaz, A reliable method for extraction of material parameters in terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2, 739–746 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/2944.571775
L. Ghivelder, W.A. Phillips, Far infrared-absorption in disordered solids. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 109, 280–288 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(89)90041-0
S.A. Jewell, E. Hendry, T.H. Isaac, J.R. Sambles, Tuneable Fabry-Perot etalon for terahertz radiation. New J. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/10/3/033012
C.-S. Yang, C.-J. Lin, R.-P. Pan et al., The complex refractive indices of the liquid crystal mixture E7 in the terahertz frequency range. J. Opt. Soc. America B 27, 1866–1866 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.27.001866
H. Park, E.P. Parrott, F. Fan et al., Evaluating liquid crystal properties for use in terahertz devices. Opt. Express 20, 11899–11905 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.20.011899
T.-R. Tsai, C.-Y. Chen, C.-L. Pan et al., Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy studies of the optical constants of the nematic liquid crystal 5CB. Appl. Opt. 42, 2372–2372 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.42.002372
R.-P. Pan, C.-F. Hsieh, C.-L. Pan, C.-Y. Chen, Temperature-dependent optical constants and birefringence of nematic liquid crystal 5CB in the terahertz frequency range. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 093523–093523 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2913347
N. Vieweg, M.K. Shakfa, B. Scherger et al., THz properties of nematic liquid crystals. J Infrared Millim Te 31, 1312–1320 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-010-9721-1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research fund of Chungnam National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Kwon, Y.S., Ahn, S. et al. Measurement of refractive indices and absorption coefficients for glass materials and nematic liquid crystals in THz frequency band. J. Korean Phys. Soc. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01055-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-024-01055-1