Abstract
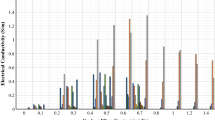
Piezoelectric sensors are useful for structural health monitoring (SHM) applications as they can sense mechanical deformations caused by impact or pressure without external power sources. However, commercial piezoelectric sensors are not suitable for large structures, such as concrete buildings, owing to their low cost-effectiveness and poor bonding compatibility with concrete. Therefore, in this study, piezoelectric cement composites were developed using piezoelectric nano powder with a cement matrix. The impact sensitivity values of the composites with varying piezoelectric nano powder content (1, 5, and 10 wt%) were measured, and the maximum impact sensitivity obtained was 3.9 μV/N at 10 wt%. It was revealed that optimizing the filler concentration for high sensitivity and accuracy is required for impact-monitoring applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
C.R. Farrer, K. Worden, An introduction to structural health monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 365, 303–315 (2007)
G. Stojanović, M. Radovanović, M. Malešev, V. Radonjanin, Monitoring of water content in building materials using a wireless passive sensor. Sensors 10, 4270–4280 (2010)
P. Pekka, M. Ilkka, N. Kaj, S. Heikki, High frequency and ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification passive sensor transponders for humidity and temperature measurement within building structures. IEEE Trans. Instum. Meas. 62, 2559–2566 (2013)
G. Park, T. Rosing, M.D. Todd, C.R. Farrar, W. Hodgkiss, Energy harvesting for structural health monitoring sensor networks. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 14, 64–79 (2008)
J. Curie, P. Curie, Développement par compression de l’électricité polaire dans les cristaux hémièdres à faces inclines. Bull. Mineral. 3, 90–93 (1880)
I. Payo, J.M. Hale, Sensitivity analysis of piezoelectric paint sensors made up of PZT ceramic powder and water-based acrylic polymer. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 168, 77–89 (2011)
Y. Zhang, In situ fatigue crack detection using piezoelectric paint sensor. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 17, 843–852 (2006)
D.-H. Han, L.-H. Kang, Piezoelectric characteristics of PNN-PZT/epoxy paint sensor according to the poling conditions. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 269, 419–426 (2018)
D.-H. Han, L.-H. Kang, Piezoelectric properties of paint sensor according to piezoelectric materials. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2, 025002 (2020)
D.-H. Han, S.-B. Park, L.-H. Kang, Impact signal monitoring of a composite structure using piezoelectric paint sensor. Compos. Res. 27, 141–145 (2014)
K. Choi, W. Choi, C. Yu, Y.T. Park, Enhanced piezoelectric behavior of PVDF nanocomposite by AC dielectrophoresis alignment of ZnO nanowires. J. Nanomater. 2017, 6590121 (2017)
W. Choi, K. Choi, G. Yang, J.C. Kim, C. Yu, Improving piezoelectric performance of lead-free polymer composites with high aspect ratio BaTiO3 nanowires. Polym. Test. 53, 143–148 (2016)
S.-H. Kang, M. Kang, L.-H. Kang, Piezoelectric smart composite blades for collision monitoring: measurement of mechanical properties and impact sensitivity. Compos. Struct. 202, 1295–1307 (2018)
K. Choi, M.-Y. Hwang, D. Kang, M. Kang, D. Ahn, L.-H. Kang, Impact monitoring characteristics of piezoelectric paint sensor by thermal fatigue analysis for railroad vehicle applications. Struct. Health. Monit. 19, 1951–1962 (2020)
M. Matsubara, K. Kikuta, S. Hirano, Piezoelectric properties of (K0.5Na0.5)(Nb1−xTax)O3−K5.4CuTa10O29 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 114105 (2005)
G. D’Ambrogio, O. Zahhaf, M. Bordet, M.Q. Le, N.D. Schiava, R. Liang, P. Cottinet, J. Capsal, Structuring BaTiO3/PDMS nanocomposite via dielectrophoresis for fractional flow reserve measurement. Adv. Eng. Mater. 23, 2100341 (2021)
F. Owusu, F.A. Nuesch, D.M. Opris, Stretchable high response piezoelectric elastomers based on polable polynorbornene fillers in a polydimethylsiloxane matrix. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 2207083 (2022)
G. Malucellia, A. Fioravantibc, L. Franciosod, C.D. Pascalid, M.A. Signored, M.C. Carottab, A. Bonannob, D. Duraccioae, Preparation and characterization of UV-cured composite films containing ZnO nanostructures: effect of filler geometric features on piezoelectric response. Prog. Org. Coat. 109, 45–54 (2017)
Z. Li, B. Dong, D. Zhang, Influence of polarization on properties of 0–3 cement-based PZT composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 27, 27–32 (2005)
A. Chaipanich, N. Jaitanong, T. Tunkasiri, Fabrication and properties of PZT—ordinary Portland cement composites. Mater. Lett. 61, 5206–5208 (2007)
N. Jaitanong, A. Chaipanich, T. Tunkasiri, Properties 0–3 PZT—Portland cement composites. Ceram. Int. 34, 793–795 (2008)
A. Chaipanich, Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of PZT—silica fume cement composites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 7, 532–536 (2007)
Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, F. Ding, W. Zhang, Effect of piezoelectric ceramic particles size gradation on piezoelectric properties of 0–3 cement-based piezoelectric composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 27, 085029 (2018)
P. Chomyen, R. Potong, R. Rianyoi, A. Ngamjarurojana, P. Chindaprasirt, A. Chaipanich, Microstructure, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of 0–3 lead free barium zirconate titanate ceramic-Portland fly ash cement composites. Ceram. Int. 44, 76–82 (2018)
T. Wittinanon, R. Rianyoi, A. Ngamjarurojana, A. Chaipanich, Effect of polyvinylidene fluoride on the acoustic impedance matching, poling enhancement and piezoelectric properties of 0–3 smart lead-free piezoelectric Portland cement composites. J. Electroceram. 44, 232–241 (2020)
A.O. Sanches, G.F. Teixeira, M.A. Zaghete, E. Longo, J.A. Malmonge, M.J. Silva, W.K. Sakamoto, Influence of polymer insertion on the dielectric, piezoelectric and acoustic properties of 1–0–3 polyurethane/cement-based piezo composite. Mater. Res. Bull. 119, 110541 (2019)
X. Cheng, D. Xu, L. Lu, S. Huang, M. Jiang, Performance investigation of 1–3 piezoelectric ceramic–cement composite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 121, 63–69 (2010)
L. Qin, S. Huang, X. Cheng, Y. Lu, Z. Li, The application of 1–3 cement-based piezoelectric transducers in active and passive health monitoring for concrete structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 095018 (2009)
D. Xu, X. Cheng, X. Guo, S. Huang, Design, fabrication and property investigation of cement/polymer based 1–3 connectivity piezo-damping composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 84, 219–223 (2015)
X. Guan, Y. Zhang, H. Li, J. Ou, PZT/PVDF composites doped with carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 194, 228–231 (2013)
R. Li, Q. Guo, Z. Shi, J. Pei, Effects of conductive carbon black on PZT/PVDF composites. Ferroelectrics 526, 176–186 (2018)
X.-F. Liu, C.-X. Xiong, H.-J. Sun, L.-J. Dong, R. Li, Y. Liu, Piezoelectric and dielectric properties of PZT/PVC and graphite doped with PZT/PVC composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 127, 261–266 (2006)
M.-Y. Hwang, L.-H. Kang, Characteristics and fabrication of piezoelectric GFRP using smart resin prepreg for detecting impact signals. Compos. Sci. Technol. 194, 224–233 (2018)
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the R&D Program of the Korea Railroad Research Institute, the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE, Korea) under the Sensor Industry Enhancement Program (20003125) and National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00253910).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Choe, J., Bae, H., Rim, Y.S. et al. Impact-monitoring characteristics of piezoelectric smart cement for structural reliability. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 83, 209–215 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00859-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00859-x